Product Reference - Oriental Motor
Product Reference - Oriental Motor
Product Reference - Oriental Motor
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
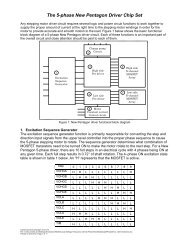
◇Slip<br />
The following formula is one method of expressing speed:<br />
Ns − N<br />
S = or N = Ns (1 − S)<br />
Ns<br />
NS : Synchronous speed [r/min]<br />
N : Speed under a given load [r/min]<br />
In the case of a four-pole, 60 Hz induction motor operated with a slip<br />
of S = 0.1, the speed under a given load will be:<br />
120 × 60<br />
N =<br />
(1 − 0.1) = 1800 (1 − 0.1) = 1620 [r/min]<br />
4<br />
●Overrun<br />
◇Overrun<br />
This is the number of excess rotations the motor makes from the<br />
instant the power is cut off to the time that it actually stops. It is<br />
normally indicated either by angle or by rotations.<br />
●Gearhead<br />
◇Gear Ratio<br />
The gear ratio is the ratio by which the gearhead reduces the motor<br />
1<br />
speed. The speed at the gearhead's output shaft is Gear Ratio times the<br />
motor speed.<br />
◇Maximum Permissible Torque<br />
This is the maximum load torque that can be applied to the<br />
gearhead.<br />
It is dependent upon such mechanical strength factors as the<br />
materials of gearheads and bearings, and size. Therefore, it varies<br />
according to the gearhead type and gear ratio.<br />
◇Service Factor<br />
This is a coefficient used to estimate the gearhead life.<br />
These values are determined in accordance with the results of life<br />
tests under various loads and conditions of use.<br />
◇Transmission Efficiency<br />
This is the efficiency when the torque is transmitted with the<br />
gearhead combined.<br />
It is expressed as a percentage (%) and is determined by the friction<br />
in the gears and bearings used in the gearhead and the resistance of<br />
the lubrication grease.<br />
Transmission efficiency is, when using a GN gearhead, usually<br />
90% for one stage of reduction gears, and is 81% for two stage<br />
gearheads. As the gear ratio increases, the number of reduction gear<br />
stages increases, with a consequent reduction in the gear efficiency<br />
to 73% and 66% for each gear stage added.<br />
◇Overhung Load<br />
This is a load on the gearhead output shaft in the vertical direction.<br />
The maximum overhung load on a gearhead shaft is called the<br />
permissible overhung load, and it varies with the gearhead type and<br />
distance from the shaft end.<br />
This is equivalent to tension under belt drive.<br />
◇Thrust Load<br />
This is the load that is placed in the direction of the gearhead output<br />
shaft.<br />
The maximum thrust load on the gearhead is called the permissible<br />
thrust load, which varies with the gearhead type.<br />
Gearhead<br />
Overhung Load<br />
Thrust Load<br />
●Others<br />
◇CW, CCW<br />
These show the direction of motor rotation.<br />
CW is clockwise as seen from the output shaft, while CCW is<br />
counterclockwise.<br />
Technical <strong>Reference</strong><br />
Selection<br />
Calculations Service Life<br />
Standard<br />
AC <strong>Motor</strong>s<br />
Speed<br />
Control<br />
Systems<br />
Stepping<br />
<strong>Motor</strong>s Gearheads<br />
Linear<br />
Heads<br />
Linear and<br />
Rotary<br />
Actuators Cooling Fans<br />
F-39