- Page 1 and 2: Realtime Ray Tracing and Interactiv
- Page 3 and 4: iii Abstract One of the most sought
- Page 5: v Acknowledgements This thesis woul
- Page 8 and 9: viii CONTENTS 6.4 Implications on t
- Page 10 and 11: x CONTENTS
- Page 12 and 13: xii LIST OF FIGURES 9.5 Instantiati
- Page 14 and 15: xiv LIST OF TABLES
- Page 17 and 18: Chapter 1 Introduction Over the las
- Page 19 and 20: 1.1 Outline of This Thesis 5 how to
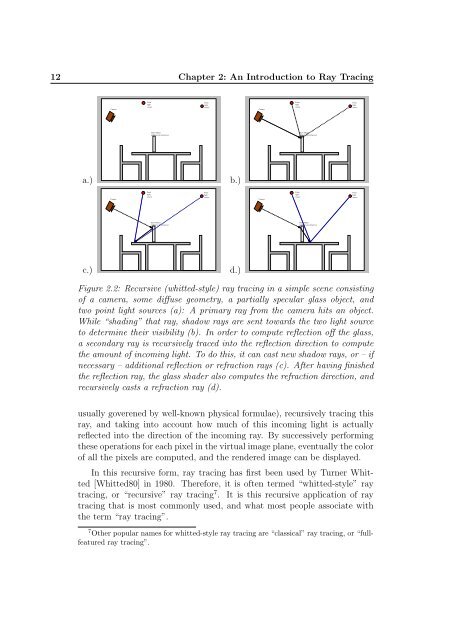
- Page 21 and 22: Chapter 2 An Introduction to Ray Tr
- Page 23 and 24: 2.1 The Core Concept - Ray Shooting
- Page 25: 2.2 The Ray Tracing Rendering Algor
- Page 29 and 30: 2.2 The Ray Tracing Rendering Algor
- Page 31 and 32: 2.3 General Ray Tracing based Algor
- Page 33 and 34: Chapter 3 A Brief Survey of Ray Tra
- Page 35 and 36: 3.1 Computing less Samples in the I
- Page 37 and 38: 3.2 Reducing the Number of Secondar
- Page 39 and 40: 3.2 Reducing the Number of Secondar
- Page 41 and 42: 3.2 Reducing the Number of Secondar
- Page 43 and 44: 3.3 Accelerating Ray-Scene Intersec
- Page 45 and 46: 3.3 Accelerating Ray-Scene Intersec
- Page 47 and 48: 3.3 Accelerating Ray-Scene Intersec
- Page 49 and 50: 3.4 Summary 35 any ray tracer: fast
- Page 51 and 52: Chapter 4 Interactive Ray Tracing I
- Page 53 and 54: 4.1 Why Interactive Ray Tracing ? 3
- Page 55 and 56: 4.2 Why not earlier, and why today
- Page 57 and 58: 4.2 Why not earlier, and why today
- Page 59 and 60: Chapter 5 Towards Realtime Ray Trac
- Page 61 and 62: 5.1 Realtime Ray Tracing in Softwar
- Page 63 and 64: 5.1 Realtime Ray Tracing in Softwar
- Page 65 and 66: 5.2 Ray Tracing on Programmable GPU
- Page 67 and 68: 5.2 Ray Tracing on Programmable GPU
- Page 69 and 70: 5.3 The SaarCOR Realtime Ray Tracin
- Page 71 and 72: 5.3 The SaarCOR Realtime Ray Tracin
- Page 73 and 74: 5.3 The SaarCOR Realtime Ray Tracin
- Page 75 and 76: 5.3 The SaarCOR Realtime Ray Tracin
- Page 77 and 78:
5.4 Towards Realtime Ray Tracing -
- Page 79:
Part II The RTRT/OpenRT Realtime Ra
- Page 82 and 83:
68 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 84 and 85:
70 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 86 and 87:
72 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 88 and 89:
74 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 90 and 91:
76 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 92 and 93:
78 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 94 and 95:
80 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 96 and 97:
82 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 98 and 99:
84 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 100 and 101:
86 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 102 and 103:
88 Chapter 6: General Design Issues
- Page 104 and 105:
90 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inter
- Page 106 and 107:
92 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inter
- Page 108 and 109:
94 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inter
- Page 110 and 111:
96 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inter
- Page 112 and 113:
98 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inter
- Page 114 and 115:
100 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 116 and 117:
102 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 118 and 119:
104 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 120 and 121:
106 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 122 and 123:
108 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 124 and 125:
110 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 126 and 127:
112 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 128 and 129:
114 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 130 and 131:
116 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 132 and 133:
118 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 134 and 135:
120 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 136:
122 Chapter 7: The RTRT Core - Inte
- Page 139 and 140:
7.5 Future Work 125 SSE code could
- Page 141 and 142:
Chapter 8 The RTRT Parallelization
- Page 143 and 144:
8.1 General System Design 129 acros
- Page 145 and 146:
8.2 Optimizations 131 (for an overv
- Page 147 and 148:
8.3 Results 133 8.2.5 Multithreadin
- Page 149 and 150:
8.4 Potential Improvements 135 this
- Page 151 and 152:
8.4 Potential Improvements 137 8.4.
- Page 153 and 154:
8.5 Conclusions 139 The distributio
- Page 155 and 156:
Chapter 9 Handling Dynamic Scenes
- Page 157 and 158:
9.1 Previous Work 143 arising in dy
- Page 159 and 160:
9.2 A Hierarchical Approach 145 wel
- Page 161 and 162:
9.3 Static and Hierarchical Motion
- Page 163 and 164:
9.4 Fast Handling of Unstructured M
- Page 165 and 166:
9.5 Fast Top-Level BSP Construction
- Page 167 and 168:
9.7 Experiments and Results 153 9.6
- Page 169 and 170:
9.7 Experiments and Results 155 ing
- Page 171 and 172:
9.7 Experiments and Results 157 Fig
- Page 173 and 174:
9.7 Experiments and Results 159 wit
- Page 175 and 176:
9.8 Discussion 161 shading normal o
- Page 177 and 178:
9.8 Discussion 163 9.8.6 Scalabilit
- Page 179 and 180:
9.10 Future Work 165 For unstructur
- Page 181 and 182:
Chapter 10 The OpenRT Application P
- Page 183 and 184:
10.1 General Design of OpenRT 169 i
- Page 185 and 186:
10.2 Application Programming Interf
- Page 187 and 188:
10.2 Application Programming Interf
- Page 189 and 190:
10.2 Application Programming Interf
- Page 191 and 192:
10.2 Application Programming Interf
- Page 193 and 194:
10.2 Application Programming Interf
- Page 195 and 196:
10.3 OpenRTS Shader Programming Int
- Page 197 and 198:
10.3 OpenRTS Shader Programming Int
- Page 199 and 200:
10.3 OpenRTS Shader Programming Int
- Page 201 and 202:
10.4 Taking it all together 187 5.
- Page 203 and 204:
10.5 Conclusions and Future Work 18
- Page 205 and 206:
Chapter 11 Applications and Case St
- Page 207 and 208:
11.2 Physically Correct Reflections
- Page 209 and 210:
11.3 Visualizing Massively Complex
- Page 211 and 212:
11.4 Interactive Ray Tracing in Vir
- Page 213 and 214:
11.5 Interactive Global Lighting Si
- Page 215:
Part III Instant Global Illuminatio
- Page 218 and 219:
204 Chapter 12: Interactive Global
- Page 220 and 221:
206 Chapter 12: Interactive Global
- Page 222 and 223:
208 Chapter 12: Interactive Global
- Page 224 and 225:
210 Chapter 12: Interactive Global
- Page 226 and 227:
212 Chapter 12: Interactive Global
- Page 228 and 229:
214 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 230 and 231:
216 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 232 and 233:
218 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 234 and 235:
220 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 236 and 237:
222 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 238 and 239:
224 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 240 and 241:
226 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 242 and 243:
228 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 244 and 245:
230 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 246 and 247:
232 Chapter 13: Instant Global Illu
- Page 248 and 249:
234 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 250 and 251:
236 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 252 and 253:
238 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 254 and 255:
240 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 256 and 257:
242 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 258 and 259:
244 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 260 and 261:
246 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 262 and 263:
248 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 264 and 265:
250 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 266 and 267:
252 Chapter 14: IGI in Complex and
- Page 268 and 269:
254 Chapter 15: Instant Global Illu
- Page 270 and 271:
256 Chapter 15: Instant Global Illu
- Page 272 and 273:
258 Chapter 16: Final Summary, Conc
- Page 274 and 275:
260 Chapter 16: Final Summary, Conc
- Page 276 and 277:
262 Chapter 16: Final Summary, Conc
- Page 278 and 279:
264 Chapter 16: Final Summary, Conc
- Page 280 and 281:
266 Chapter 16: Final Summary, Conc
- Page 282 and 283:
268 Chapter A: List of Related Pape
- Page 284 and 285:
270 Chapter A: List of Related Pape
- Page 286 and 287:
272 BIBLIOGRAPHY [AMD03a] Advanced
- Page 288 and 289:
274 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Bekaert01] Philip
- Page 290 and 291:
276 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Cook84b] Robert L
- Page 292 and 293:
278 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Durgin97] Greg D.
- Page 294 and 295:
280 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Goldsmith87] [Goo
- Page 296 and 297:
282 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Havran99] [Havran
- Page 298 and 299:
284 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Jensen96] [Jensen
- Page 300 and 301:
286 BIBLIOGRAPHY 21(3):557-563, 200
- Page 302 and 303:
288 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Meissner98] M. Me
- Page 304 and 305:
290 BIBLIOGRAPHY [PCI Express] PCI
- Page 306 and 307:
292 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Sbert97] Mateu Sb
- Page 308 and 309:
294 BIBLIOGRAPHY [Sung92] Kelvin Su
- Page 310 and 311:
296 BIBLIOGRAPHY ity PC Clusters -