JetNet Series Industrial L2 / L3 Rackmount / Rail Ethernet Switch
JetNet Series Industrial L2 / L3 Rackmount / Rail Ethernet Switch
JetNet Series Industrial L2 / L3 Rackmount / Rail Ethernet Switch
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Static Route<br />
When 2 or more Layer 3 routers or switches are<br />
connected together, the IP traffic must be forwarded to<br />
next hop by static configuration or dynamic target IP<br />
address learning.<br />
Static Route: If the IP address of the next hop is<br />
specified, or if it is assigned by Internet Service<br />
Provider, the IP address of the next hop can be statically<br />
configured. In this case the 2 or more Layer 3 routers/<br />
switches direct the traffic according to the settings.<br />
Default Route: The IP address of the default route is<br />
usually assigned by ISP. Configure the unidirectional<br />
static routes to and from a sub network to allow<br />
communication to occur.<br />
Dynamic Route: Through learning the ARP packets,<br />
the layer 3 router/switch can learn the destination IP<br />
addresses and write the related connection among the<br />
routers to the routing tables.<br />
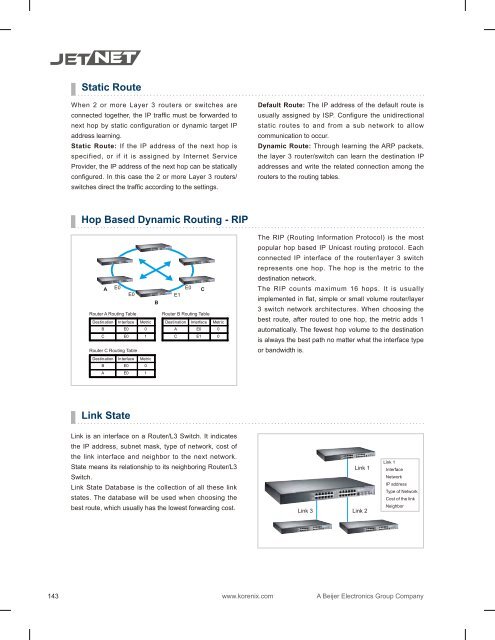
Hop Based Dynamic Routing - RIP<br />
The RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is the most<br />
popular hop based IP Unicast routing protocol. Each<br />
connected IP interface of the router/layer 3 switch<br />
represents one hop. The hop is the metric to the<br />
destination network.<br />
A E0<br />
E0<br />
Router A Routing Table<br />
Destination Interface Metric<br />
B E0 0<br />
C E0 1<br />
Router C Routing Table<br />
B<br />
E0 C<br />
E1<br />
Router B Routing Table<br />
Destination Interface Metric<br />
A E0 0<br />
C E1 0<br />
The RIP counts maximum 16 hops. It is usually<br />
implemented in flat, simple or small volume router/layer<br />
3 switch network architectures. When choosing the<br />
best route, after routed to one hop, the metric adds 1<br />
automatically. The fewest hop volume to the destination<br />
is always the best path no matter what the interface type<br />
or bandwidth is.<br />
Destination<br />
Interface<br />
Metric<br />
B E0 0<br />
A<br />
E0 1<br />
Link State<br />
Link is an interface on a Router/<strong>L3</strong> <strong>Switch</strong>. It indicates<br />
the IP address, subnet mask, type of network, cost of<br />
the link interface and neighbor to the next network.<br />
State means its relationship to its neighboring Router/<strong>L3</strong><br />
<strong>Switch</strong>.<br />
Link State Database is the collection of all these link<br />
states. The database will be used when choosing the<br />
best route, which usually has the lowest forwarding cost.<br />
Link 1<br />
Link 3 Link 2<br />
Link 1<br />
Interface<br />
Network<br />
IP address<br />
Type of Network<br />
Cost of the link<br />
Neighbor<br />
143 www.korenix.com<br />
A Beijer Electronics Group Company