Biogas production in climates with long cold winters - SuSanA
Biogas production in climates with long cold winters - SuSanA
Biogas production in climates with long cold winters - SuSanA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2. Background on biogas <strong>production</strong><br />
2.1 Anaerobic digestion<br />
Anaerobic Digestion (AD) is a biological process that happens naturally when bacteria breaks<br />
down organic matter <strong>in</strong> environments <strong>with</strong> little or no oxygen. AD produces a biogas made up<br />
of around 60 per cent methane and 40 per cent carbon dioxide (CO2). This can be burnt to<br />
generate heat or electricity or can be used as a vehicle fuel. As well as biogas, AD produces a<br />
residue called digestate which can be used as a soil conditioner to fertilize land.<br />
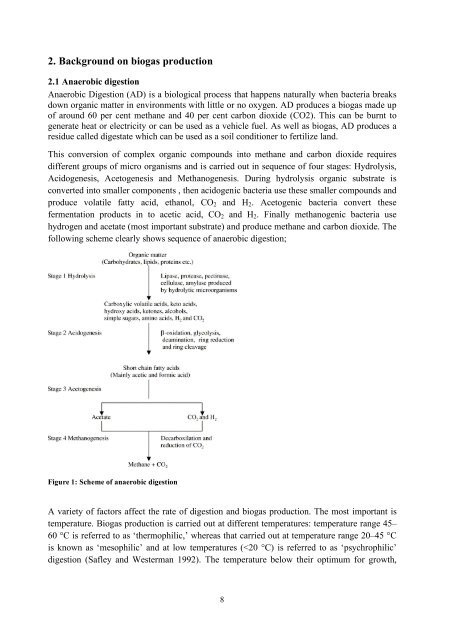
This conversion of complex organic compounds <strong>in</strong>to methane and carbon dioxide requires<br />
different groups of micro organisms and is carried out <strong>in</strong> sequence of four stages: Hydrolysis,<br />
Acidogenesis, Acetogenesis and Methanogenesis. Dur<strong>in</strong>g hydrolysis organic substrate is<br />
converted <strong>in</strong>to smaller components , then acidogenic bacteria use these smaller compounds and<br />
produce volatile fatty acid, ethanol, CO 2 and H 2 . Acetogenic bacteria convert these<br />
fermentation products <strong>in</strong> to acetic acid, CO 2 and H 2 . F<strong>in</strong>ally methanogenic bacteria use<br />
hydrogen and acetate (most important substrate) and produce methane and carbon dioxide. The<br />
follow<strong>in</strong>g scheme clearly shows sequence of anaerobic digestion;<br />
Figure 1: Scheme of anaerobic digestion<br />
A variety of factors affect the rate of digestion and biogas <strong>production</strong>. The most important is<br />
temperature. <strong>Biogas</strong> <strong>production</strong> is carried out at different temperatures: temperature range 45–<br />
60 °C is referred to as ‘thermophilic,’ whereas that carried out at temperature range 20–45 °C<br />
is known as ‘mesophilic’ and at low temperatures (