Beta Spectroscopy
Beta Spectroscopy
Beta Spectroscopy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
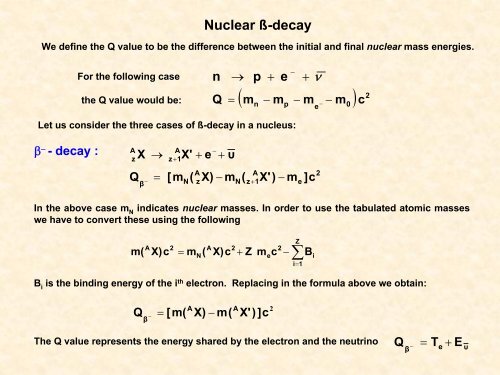
Nuclear ß-decay<br />
We define the Q value to be the difference between the initial and final nuclear mass energies.<br />
For the following case<br />
the Q value would be:<br />
n<br />
Q<br />
→<br />
p<br />
+<br />
e<br />
−<br />
+ ν<br />
2<br />
( m − m − m − m ) c<br />
=<br />
n p<br />
−<br />
e<br />
0<br />
Let us consider the three cases of ß-decay in a nucleus:<br />
β − - decay :<br />
A<br />
z<br />
X<br />
→<br />
A<br />
z+<br />
1<br />
X'<br />
+ e<br />
−<br />
+<br />
υ<br />
Q<br />
−<br />
β<br />
=<br />
[m<br />
N<br />
(<br />
A<br />
z<br />
X) − m<br />
N<br />
(<br />
A<br />
z+<br />
1<br />
X') − m<br />
e<br />
]c<br />
2<br />
In the above case m N<br />
indicates nuclear masses. In order to use the tabulated atomic masses<br />
we have to convert these using the following<br />
m(<br />
A<br />
X)c<br />
2<br />
= m<br />
N<br />
(<br />
A<br />
X)c<br />
2<br />
+ Z<br />
m c<br />
e<br />
2<br />
−<br />
Z<br />
∑<br />
i=<br />
1<br />
B<br />
i<br />
B i<br />
is the binding energy of the i th electron. Replacing in the formula above we obtain:<br />
Q<br />
−<br />
β<br />
= [m(<br />
A<br />
X) − m(<br />
A<br />
X') ]c<br />
2<br />
The Q value represents the energy shared by the electron and the neutrino<br />
Q = T + E<br />
−<br />
β<br />
e<br />
υ