hvvrq $ulwkphwlf 6htxhqfhv dqg 6hulhv - NCPN
hvvrq $ulwkphwlf 6htxhqfhv dqg 6hulhv - NCPN
hvvrq $ulwkphwlf 6htxhqfhv dqg 6hulhv - NCPN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
∞<br />
3 4 <br />
∑ (<br />
=0<br />
3)<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
∞<br />
3 1<br />
4<br />
+ 4<br />
∑ ( )<br />
<br />
4 3 =<br />
0<br />
9<br />
<br />
4 3<br />
<br />
<br />
ACTIVE LEARNING<br />
Length of Perimeter<br />
Iteration<br />
Side of Shape<br />
1 1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
5 <br />
<br />
<br />
4 9<br />
<br />
<br />
2 3<br />
5<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
2 3<br />
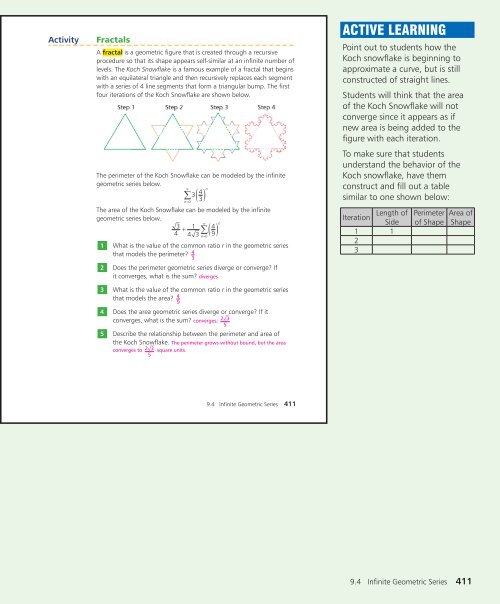
Point out to students how the<br />
Koch snowflake is beginning to<br />
approximate a curve, but is still<br />
constructed of straight lines.<br />
Students will think that the area<br />
of the Koch Snowflake will not<br />
converge since it appears as if<br />
new area is being added to the<br />
figure with each iteration.<br />
To make sure that students<br />
understand the behavior of the<br />
Koch snowflake, have them<br />
construct and fill out a table<br />
similar to one shown below:<br />
Area of<br />
Shape<br />
<br />
9.4 Infinite Geometric Series 411