LARGE-SCALE PARALLEL GRAPH-BASED SIMULATIONS - MATSim
LARGE-SCALE PARALLEL GRAPH-BASED SIMULATIONS - MATSim
LARGE-SCALE PARALLEL GRAPH-BASED SIMULATIONS - MATSim
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Abstract<br />
When systems are modeled, different techniques are used. Computer simulation is one of these<br />
techniques. It draws attention since it makes it possible to model a system that might be real<br />
or theoretical, to execute the model on a computer, and to analyze the output of the execution<br />
of the model. Execution of a model on a computer develops through time, i.e. the states of<br />
the different parts of a system, such as variables and environment, are updated through time<br />
according to the rules defined in the model.<br />
Computer simulations come into prominence since they allow models to have complex<br />
objects/variables, allow objects to have complex relationships, allow users to model artificial<br />
worlds, etc. This thesis focuses on different parts of a transportation planning system, MATSIM<br />
(Multi-Agent Transportation SIMulation), which is a computer simulation.<br />
In MATSIM, similar to other multi-agent simulations, all entities are treated at the individual<br />
level. Their behavior and interactions, both with each other and with the environment, are<br />
defined by their internal rules.<br />
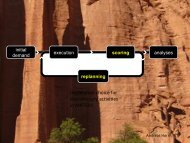
There are two layers in a transportation planning system: the physical layer that includes<br />
a traffic flow simulator, and the strategic layer. In the traffic flow simulator, the agents are<br />
interacts with each other and with the environment based on the rules defined in the model. In<br />
the strategic layer, the agents make their strategies. The relationship between these two layers<br />
is best understood in an implementation called a framework.<br />
A framework couples the modules such as traffic flow simulator, router, agent database,<br />
activity generator, etc. A traffic flow simulator defines the rules of interactions of the entities in<br />
the system. The traffic flow simulator used in MATSIM is based on a queue model developed<br />
by Gawron. It reads the street network of the area to be simulated and the plans of the agents,<br />
then it executes these plans according to the rules of the queue model. The output of the traffic<br />
flow simulation, the events, are used to evaluate the performance of the plans. The evaluation<br />
is achieved by the modules of the strategic layer. The evaluated plans are fed to traffic flow<br />
simulator simulator by starting a new iteration.<br />
Parallel computing issues are applied to the traffic simulator to handle the large-scale scenarios<br />
detailed at microscopic level. Different communication media and different communication<br />
libraries are used during this process.<br />
The coupling of modules by framework is via files. From the viewpoint of a traffic flow<br />
simulator, this means two files: plans as input and events as output. To avoid the inefficiencies<br />
of file I/O, a message passing approach is developed for plans and events. Different methods<br />
for creating and transferring different types of messages are investigated.<br />
The traffic flow simulator based on the queue model can be used for simulating other types<br />
of entities such as Internet data packet traffic. As Internet grows more, analyzing the data<br />
flowing through Internet becomes more interesting between researchers.<br />
i