District of Sechelt Urban Forest Plan
District of Sechelt Urban Forest Plan
District of Sechelt Urban Forest Plan
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>District</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Sechelt</strong> <strong>Urban</strong> <strong>Forest</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> 2010<br />
nurture resilience, to retain corridors for species migration and to preserve diversity (genetic, structural<br />
and species). 16<br />
Loss <strong>of</strong> Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services<br />
Treed environments <strong>of</strong> native species are important for the maintenance <strong>of</strong> biodiversity and ecosystem<br />
services.<br />
“When considering the loss <strong>of</strong> biodiversity, species loss has become the most widely used<br />
measure. The subject <strong>of</strong> biodiversity loss is, however, broader and more complex than this,<br />
because there is diversity at other levels <strong>of</strong> organization as well. For example, genetic diversity<br />
exists among members <strong>of</strong> an individual species, and a species can lose some <strong>of</strong> this diversity when<br />
local populations are lost even though the species itself has not gone extinct.” 17<br />
Species and genetic diversity in the tree canopy, shrubs, ground cover, fungi, and soils are integral to the<br />
resilience <strong>of</strong> our forests (“a system's capacity to recover from external pressures such as droughts or<br />
management mistakes” 18 ) and their ability to deliver ecosystem services, such as improving water and air<br />
quality.<br />
“Ecosystem services are generated by a complex <strong>of</strong> natural cycles, ranging from the short life<br />
cycles <strong>of</strong> microbes that break down toxic chemicals to the long-term and planet wide cycles <strong>of</strong><br />
water and <strong>of</strong> elements such as carbon and nitrogen that have sustained life for hundreds <strong>of</strong><br />
millions <strong>of</strong> years. Disruption <strong>of</strong> these natural cycles can result in the disastrous problems for<br />
human beings.” 19<br />
Scientific research suggests that biodiversity and ecosystem service provision can be nurtured by<br />
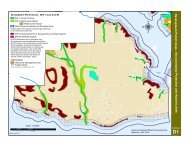
ensuring that structurally characteristic patches <strong>of</strong> native vegetation are present throughout the <strong>District</strong>.<br />
It is also important to maintain and expand natural wildlife corridors and provide stepping stone patches<br />
<strong>of</strong> native vegetation between larger areas <strong>of</strong> forest to allow for species migration. To protect sensitive<br />
ecosystems buffers <strong>of</strong> native vegetation should surround them. 20<br />
16 Please see cited resources for more detail on the impacts <strong>of</strong> climate change.<br />
17 Pimm, Stuart L., Maria Alice S. Alves, Eric Chivian and Aaron Bernstein. 2008. “What is Biodiversity” In Sustaining Life: how Human Health<br />
Depends on Biodiversity, eds. Eric Chivian and Aaron Bernstein. New York: Oxford University Press.<br />
18 Joern Fischer, David B. Lindenmayer, and Adrian D. Manning. 2006. “Biodiversity, Ecosystem Function, and Resilience: Ten Guiding<br />
Principles for Commodity Production Landscapes. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 4 (2): 80-86.<br />
19 Melillo, Jerry and Osvaldo Sala. 2008. “Ecosystem Services.” In Sustaining Life: How Human Health Depends on Biodiversity, eds. Eric Chivian<br />
and Aaron Bernstein. New York: Oxford University Press.<br />
20 Melillo and Sala. 2008.<br />
November 2010 Page 21