- Page 1 and 2: 802.11® Wireless Networks: The Def
- Page 3 and 4: 8. Contention-Free Service with the
- Page 5 and 6: ERRATA: Confirmed errors: {47} Figu
- Page 7 and 8: network can often be reduced to a m
- Page 9 and 10: suffer from a number of propagation
- Page 11 and 12: Chapter 2. Overview of 802.11 Netwo
- Page 13 and 14: Figure 2-3. Components of 802.11 LA
- Page 15 and 16: the number of mobile stations that
- Page 17 and 18: system. After all, they are connect
- Page 19 and 20: The services are described in the f
- Page 21 and 22: 2.3.1.1 Station services Station se
- Page 23 and 24: Chapter 3. The 802.11 MAC This chap
- Page 25 and 26: 3.1.2 The Hidden Node Problem In Et
- Page 27 and 28: sensing hardware for RF-based media
- Page 29 and 30: grab the medium before another type
- Page 31 and 32: 3.3.2 Backoff with the DCF After fr
- Page 33: 802.11 MAC frames do not include so
- Page 37 and 38: destined to a node on an Ethernet c
- Page 39 and 40: Both RFC 1042 and 802.1h are deriva
- Page 41 and 42: to boost speed over a single hop wi
- Page 43 and 44: stations receiving a PS-Poll to upd
- Page 45 and 46: Chapter 4. 802.11 Framing in Detail
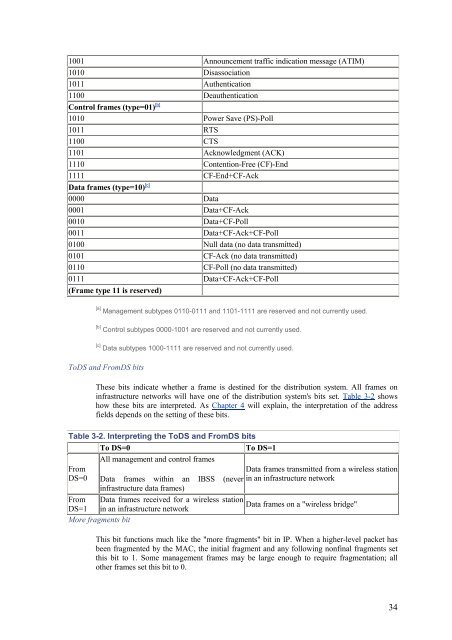
- Page 47 and 48: 4.1.3 Addressing and DS Bits The nu
- Page 49 and 50: Figure 4-6. Wireless distribution s
- Page 51 and 52: Figure 4-9. Data frames from the AP
- Page 53 and 54: Control frames arbitrate access to
- Page 55 and 56: Duration The sender of a CTS frame
- Page 57 and 58: the association. Including this ID
- Page 59 and 60: This section presents the fixed fie
- Page 61 and 62: Table 4-4. Interpretation of pollin
- Page 63 and 64: 6 Incorrect frame type or subtype r
- Page 65 and 66: Figure 4-33. Supported Rates inform
- Page 67 and 68: DTIM Period This one-byte field ind
- Page 69 and 70: sending Probe Response frames for t
- Page 71 and 72: Figure 4-47. Authentication frames
- Page 73 and 74: Chapter 5. Wired Equivalent Privacy
- Page 75 and 76: WEP on the card, and patents preven
- Page 77 and 78: stations in a service set. Once a s
- Page 79 and 80: 2. In spite of vendor claims to the
- Page 81 and 82: Furthermore, 802.11 networks announ
- Page 83 and 84: Figure 6-1. EAP architecture 6.1.1
- Page 85 and 86:
6.1.2.4 Type code 4: MD-5 Challenge
- Page 87 and 88:
8. Once again, the user types a res
- Page 89 and 90:
0011 0000 0100 EAPOL- Encapsulated-
- Page 91 and 92:
6.3 802.1x on Wireless LANs 802.1x
- Page 93 and 94:
Chapter 7. Management Operations Wh
- Page 95 and 96:
Figure 7-2. Passive scanning 7.2.2
- Page 97 and 98:
These three facets of the network h
- Page 99 and 100:
to connect. While address filtering
- Page 101 and 102:
Figure 7-6b shows what happens when
- Page 103 and 104:
2. The access point processes the R
- Page 105 and 106:
Figure 7-10. PS-Poll frame retrieva
- Page 107 and 108:
interval, a frame has also been buf
- Page 109 and 110:
Figure 7-15. ATIM effects on power-
- Page 111 and 112:
7.6.1 Infrastructure Timing Synchro
- Page 113 and 114:
Chapter 8. Contention-Free Service
- Page 115 and 116:
the result is a bit strange. A sing
- Page 117 and 118:
Figure 8-3. Data+CF-Ack usage This
- Page 119 and 120:
8.2.1 Contention-Free End (CF-End)
- Page 121 and 122:
CFP DurRemaining This value is the
- Page 123 and 124:
The IR PHY 802.11 also includes a s
- Page 125 and 126:
• Bluetooth, a short-range wirele
- Page 127 and 128:
9.2.2.1 Types of spread spectrum Th
- Page 129 and 130:
usually buy some cable to separate
- Page 131 and 132:
This figure shows three paths from
- Page 133 and 134:
Figure 10-1. Frequency hopping Freq
- Page 135 and 136:
Table 10-2. Size of hop sets in eac
- Page 137 and 138:
Figure 10-5. 2-level GFSK The rate
- Page 139 and 140:
with ISO reference model terminolog
- Page 141 and 142:
transmitted using a different encod
- Page 143 and 144:
used in the encoding process. There
- Page 145 and 146:
power at the channel center. Figure
- Page 147 and 148:
Figure 10-19. DBPSK encoding Table
- Page 149 and 150:
10.2.3 DS Physical-Layer Convergenc
- Page 151 and 152:
10.2.4.3 CS/CCA for the DS PHY 802.
- Page 153 and 154:
Barker spreading, as used in the lo
- Page 155 and 156:
Figure 10-27. Service field in the
- Page 157 and 158:
Figure 10-30. 802.11b transmission
- Page 159 and 160:
area. The total aggregate throughpu
- Page 161 and 162:
OFDM devices use one wide frequency
- Page 163 and 164:
11.1.3 Guard Time With the physical
- Page 165 and 166:
11.1.5 Convolution Coding Strictly
- Page 167 and 168:
11.2.3 Operating Channels In the U.
- Page 169 and 170:
Figure 11-12. Preamble and frame st
- Page 171 and 172:
keying (QPSK) to encode 2 bits per
- Page 173 and 174:
Chapter 12. Using 802.11 on Windows
- Page 175 and 176:
Figure 12-3. Driver installation pr
- Page 177 and 178:
Figure 12-7. Addressing and login o
- Page 179 and 180:
When troubleshooting connectivity p
- Page 181 and 182:
12.1.4 Configuring WEP Despite its
- Page 183 and 184:
Long retry limit 4 attempts Passive
- Page 185 and 186:
Figure 12-21. Smart-card management
- Page 187 and 188:
12.2.2 The Client Manager and Netwo
- Page 189 and 190:
Figure 12-30. Power management conf
- Page 191 and 192:
Chapter 13. Using 802.11 on Linux O
- Page 193 and 194:
Figure 13-1. Linux PCMCIA configura
- Page 195 and 196:
Module install directory [/lib/modu
- Page 197 and 198:
Table 13-3. Common I/O ports Device
- Page 199 and 200:
• Building with debugging informa
- Page 201 and 202:
mibattribute=dot11WEPDefaultKey3=01
- Page 203 and 204:
lan_connector Closed connector stan
- Page 205 and 206:
13.3.6 Common Problems Most common
- Page 207 and 208:
13.4.1 Kernel 2.0/2.2: wvlan_cs In
- Page 209 and 210:
13.4.1.6 Setting the network mode a
- Page 211 and 212:
1-3 system (2), or ad hoc network (
- Page 213 and 214:
Chapter 14. Using 802.11 Access Poi
- Page 215 and 216:
• They are often deployed by user
- Page 217 and 218:
802.11 includes a number of power-s
- Page 219 and 220:
14.2 ORiNOCO (Lucent) AP-1000 Acces
- Page 221 and 222:
One nice thing about the AP Manager
- Page 223 and 224:
Figure 14-6. Ethernet interface con
- Page 225 and 226:
Figure 14-10. Access control tab 14
- Page 227 and 228:
Figure 14-14. Web-based management
- Page 229 and 230:
CMD:set long_retry 7 Configuration
- Page 231 and 232:
14.3.3 Configuring DHCP DHCP is use
- Page 233 and 234:
Figure 14-17. Advanced WEP configur
- Page 235 and 236:
Up to 200 name/MAC pairs can be sto
- Page 237 and 238:
LAN Statistics: Last 10s Cumulative
- Page 239 and 240:
Chapter 15. 802.11 Network Deployme
- Page 241 and 242:
is in motion. This is critical for
- Page 243 and 244:
Tagged links can vary widely in cos
- Page 245 and 246:
Within the context of Figure 15-1,
- Page 247 and 248:
makes a useful speed bump for attac
- Page 249 and 250:
15.1.2.3 Availability through redun
- Page 251 and 252:
Can address translation be used to
- Page 253 and 254:
For 2-Mbps networks, this translate
- Page 255 and 256:
15.2.3.1 Network addressing 802.11
- Page 257 and 258:
Antenna type Gain The antenna type
- Page 259 and 260:
antennas are good at radiating out
- Page 261 and 262:
15.3.2.3 Bring on the heat Amplifie
- Page 263 and 264:
After locating the access points, m
- Page 265 and 266:
Figure 15-7. Wireless LAN naming co
- Page 267 and 268:
Chapter 16. 802.11 Network Analysis
- Page 269 and 270:
16.3 Commercial Network Analyzers W
- Page 271 and 272:
ar rc libpcap.a pcap-linux.o pcap.o
- Page 273 and 274:
16.4.2 Running Ethereal To start Et
- Page 275 and 276:
16.4.2.2 Saving data to a file To s
- Page 277 and 278:
Figure 16-4. Header component varia
- Page 279 and 280:
fields and are decoded in the tree
- Page 281 and 282:
Figure 16-7. PRISM monitoring heade
- Page 283 and 284:
16.5 802.11 Network Analysis Exampl
- Page 285 and 286:
Figure 16-12. The second random 802
- Page 287 and 288:
Figure 16-14. Expanded view of Prob
- Page 289 and 290:
Figure 16-16. Second authentication
- Page 291 and 292:
Figure 16-18. Association response
- Page 293 and 294:
processed by the access point. Note
- Page 295 and 296:
Figure 16-24. DNS reply 16.5.3.5 Th
- Page 297 and 298:
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/
- Page 299 and 300:
0.00user 0.01system 0:00.01elapsed
- Page 301 and 302:
Chapter 17. 802.11 Performance Tuni
- Page 303 and 304:
Decreasing the retry limit reduces
- Page 305 and 306:
17.4 Physical Operations Most wirel
- Page 307 and 308:
Chapter 18. The Future, at Least fo
- Page 309 and 310:
However, 802.11 offers only link-la
- Page 311 and 312:
network provider that leases space
- Page 313 and 314:
A.2 Station Management Station mana
- Page 315 and 316:
dot11DesiredBSSType (enumerated) Li
- Page 317 and 318:
dot11WEPDefaultKeyValue (WEPKeytype
- Page 319 and 320:
dot11TransmittedFragmentCount (Coun
- Page 321 and 322:
A.4 Physical-Layer Management Physi
- Page 323 and 324:
A.4.3 DSSS Table The direct-sequenc
- Page 325 and 326:
choosing how to configure TCP/IP. F
- Page 327 and 328:
Figure B-4. AirPort status icon In
- Page 329 and 330:
Figure B-8. AirPort preferences tab
- Page 331 and 332:
Figure B-10. Network name and passw
- Page 333 and 334:
B.2.2.2 Configuration of the WAN in
- Page 335:
http://www.msrl.com/airport-gold/ O