Nicotine replacement therapy … - Carlos A ... - Entretiens du Carla
Nicotine replacement therapy … - Carlos A ... - Entretiens du Carla
Nicotine replacement therapy … - Carlos A ... - Entretiens du Carla
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
References<br />
(1) Bergstrom HC,<br />
McDonald CG, French<br />
HT, Smith RF.<br />
Continuous nicotine<br />
administration pro<strong>du</strong>ces<br />
selective, agedependent<br />
structural<br />
alteration of pyramidal<br />
neurons from prelimbic<br />
cortex. Synapse 2008;<br />
62(1): 31-39.<br />
(2) Debry SC, Tiffany ST.<br />
Tobacco-in<strong>du</strong>ced neurotoxicity<br />
of adolescent<br />
cognitive development<br />
(TINACD): A proposed<br />
model for the development<br />
of impulsivity in<br />
nicotine dependence.<br />
<strong>Nicotine</strong> Tob Res 2008;<br />
10(1): 11-25.<br />
(3) Wessels C, Winterer<br />
G. [Effects of nicotine<br />
on neurodevelopment.].<br />
Nervenarzt<br />
2008; 79(1): 7-16.<br />
(4) Johnson JG, Cohen<br />
P, Pine DS, Klein DF,<br />
Kasen S, Brook JS.<br />
Association between<br />
cigarette smoking and<br />
anxiety disorders<br />
<strong>du</strong>ring adolescence and<br />
early a<strong>du</strong>lthood. JAMA<br />
2000; 284(18): 2348-<br />
2351.<br />
(5) DiFranza JR, Rigotti<br />
NA, McNeill AD et al.<br />
Initial symptoms of<br />
nicotine dependence in<br />
adolescents. TobControl<br />
2000; 9(3): 313-319.<br />
(6) Kandel DB, Hu MC,<br />
Griesler PC, Schaffran<br />
C. On the development<br />
of nicotine dependence<br />
in adolescence. Drug<br />
Alcohol Depend 2007;<br />
91(1): 26-39.<br />
(7) Breslau N, Peterson<br />
EL. Smoking cessation<br />
in young a<strong>du</strong>lts: age at<br />
initiation of cigarette<br />
smoking and other suspected<br />
influences. Am J<br />
Public Health 1996;<br />
86(2): 214-220.<br />
Most smokers start smoking <strong>du</strong>ring<br />
adolescence, at an age when the maturation of<br />
the central nervous system is incomplete and<br />
when cholinergic mechanisms play a major role<br />
in the regulation of its development.<br />
<strong>Nicotine</strong> and developing<br />
brain<br />
Use of NRTs among<br />
adolescents<br />
Jean-Pierre Zellweger<br />
Pneumologist<br />
Fribourg, Switzerland<br />
Disturbance of the maturation processes can<br />
lead to permanent impairment of the neuronal<br />
architecture (1) or suboptimal function of some<br />
parts of the system. Given its neurotropic effect<br />
and the high density of nicotinic receptors in<br />
the central nervous system, nicotine has a<br />
major impact on cerebral development in<br />
adolescents (2). It has thus been demonstrated<br />
that nicotine interacts with the normal<br />
maturation processes of the cholinergic system<br />
and that smoking in adolescents can in<strong>du</strong>ce<br />
impairment of the mechanisms of impulsivity<br />
control, similar to the impairments that<br />
characterize attention deficit hyperactivity<br />
disorder (ADHD) (3). Some adolescent smokers<br />
also develop an anxiety disorder (4).<br />
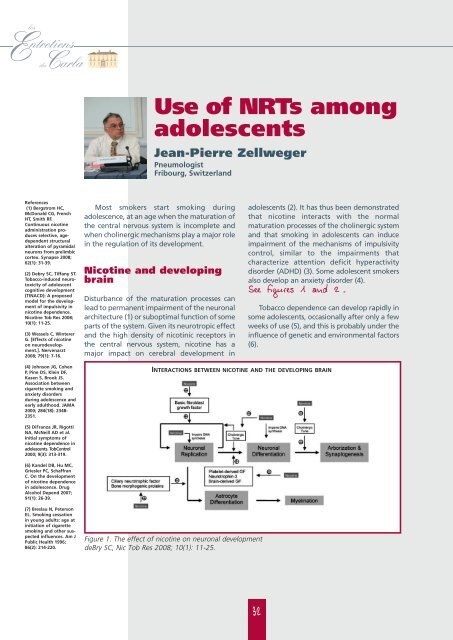
See figures 1 and 2.<br />
Tobacco dependence can develop rapidly in<br />
some adolescents, occasionally after only a few<br />
weeks of use (5), and this is probably under the<br />
influence of genetic and environmental factors<br />
(6).<br />
INTERACTIONS BETWEEN NICOTINE AND THE DEVELOPING BRAIN<br />
Figure 1. The effect of nicotine on neuronal development<br />
deBry SC, Nic Tob Res 2008; 10(1): 11-25.<br />
32