- Page 1 and 2:
STANDARD Y S F- MEB X D 21 WILLIAM
- Page 5:
STANDARD HANDBOOK OF Engineering
- Page 8 and 9:
STANDARD HANDBOOK OF ROLEUM L GAS E
- Page 10 and 11:
3-Auxiliary Equipment .............
- Page 12 and 13:
Murty Kuntamukkla, Ph.D. Westinghou
- Page 14 and 15:
Petroleum Institute and the Society
- Page 17:
Patricia Duettra Consultant Applied
- Page 20 and 21:
4 Mathematics triangle has no congr
- Page 22 and 23:
6 Mathematics rectangular parallelp
- Page 24 and 25:
+ (XZYS + (XSYI 8 Mathematics Any t
- Page 26 and 27:
10 Mathematics Annulus (Figure 1-9)
- Page 28 and 29:
12 Mathematics In any hyperbola, sh
- Page 30 and 31:
14 Mathematics . Any prism or cylin
- Page 32 and 33:
16 Mathematics 9 Hollow sphere, or
- Page 34 and 35:
18 Mathematics Spheroid (or ellipso
- Page 36 and 37:
20 Mathematics Rules of Multiplicat
- Page 38 and 39:
22 Mathematics log(a/b) = log a - l
- Page 40 and 41:
24 Mathematics If the kth differenc
- Page 42 and 43:
26 Mathematics First-degree equatio
- Page 44 and 45:
28 Mathematics -4 A directe angle m
- Page 46 and 47:
30 Mathematics Table 1-1 Angle Redu
- Page 48 and 49:
32 Mathematics (text continued from
- Page 50 and 51:
34 Mathematics Polar Coordinate Sys
- Page 52 and 53:
36 Mathematics Table 1-6 Table of D
- Page 54 and 55:
38 Mathematics and xl, xp, x3, and
- Page 56 and 57:
40 Mathematics In polar coordinates
- Page 58 and 59:
42 Mathematics 1. 1 df(x) = f(x) +
- Page 60 and 61:
44 Mathematics (text continued from
- Page 62 and 63:
46 Mathematics equation involves an
- Page 64 and 65:
48 Mathematics the general solution
- Page 66 and 67:
+ F(s) 50 Mathematics The transform
- Page 68 and 69:
52 Mathematics then the equation of
- Page 70 and 71:
54 Mathematics Origin at vertex y2
- Page 72 and 73:
56 Mathematics Equation of the tang
- Page 74 and 75:
58 Mathematics Equations (standard
- Page 76 and 77:
60 Mathematics NUMERICAL METHODS Se
- Page 78 and 79:
62 Mathematics I I fi-4 I f t a I f
- Page 80 and 81:
64 Mathematics Interpolation A forw
- Page 82 and 83:
66 Mathematics Table 1-13 Central D
- Page 84 and 85:
68 Mathematics as long as there are
- Page 86 and 87:
70 Mathematics Because of round off
- Page 88 and 89:
72 Mathematics and The transpose of
- Page 90 and 91:
74 Mathematics then, by replacement
- Page 92 and 93:
76 Mathematics Relaxation methods m
- Page 94 and 95:
78 Mathematics Table 1-14 Chebyshev
- Page 96 and 97:
80 Mathematics and the next higher
- Page 98 and 99:
82 Mathematics a semi-open formula
- Page 100 and 101:
AY., 84 Mathematics 2. Boundary val
- Page 102 and 103:
~ ~ 86 Mathematics Ei+l - Yi+l - Yi
- Page 104 and 105:
88 Mathematics 3. Corrector 1 3 y p
- Page 106 and 107:
90 Mathematics with boundary condit
- Page 108 and 109:
92 Mathematics The three primary ad
- Page 110 and 111:
94 Mathematics Moment Ratios The mo
- Page 112 and 113:
96 Mathematics Table 1-19 Critical
- Page 114 and 115:
Table 1-20 Critical Values for the
- Page 116 and 117:
Table 1-21 Critical Values for the
- Page 118 and 119:
102 Mathematics (text continued fro
- Page 120 and 121:
104 Mathematics where K,,, = estima
- Page 122 and 123:
106 Mathematics A second definition
- Page 124 and 125:
108 Mathematics The confidence inte
- Page 126 and 127:
110 Mathematics addition of control
- Page 128 and 129:
112 Mathematics their subscripts, t
- Page 130 and 131:
114 Mathematics With little extra e
- Page 132 and 133:
116 Mathematics Dimension statement
- Page 134 and 135:
118 Mathematics A D E F G H I L P S
- Page 136 and 137:
120 Mathematics Conditional stateme
- Page 138 and 139:
122 Mathematics Table 1-27 FORTRAN
- Page 140 and 141:
124 Mathematics Pascal Language Pas
- Page 142 and 143:
126 Mathematics Constant declaratio
- Page 144 and 145:
128 Mathematics READ(variab1e list)
- Page 146 and 147:
130 Mathematics Iterative statement
- Page 148 and 149:
132 Mathematics System Hardware Sys
- Page 150 and 151:
134 Mathematics 21. Strang, G., and
- Page 153 and 154:
2 General Engineering and Science B
- Page 155 and 156:
Basic Mechanics (Statics and Dynami
- Page 157 and 158:
Basic Mechanics (Statics and Dynami
- Page 159 and 160:
Basic Mechanics (Statics and Dynami
- Page 161 and 162:
Basic Mechanics (Statics and Dynami
- Page 163 and 164:
Basic Mechanics (Statics and Dynami
- Page 165 and 166:
Dynamics 149 One of the simplest st
- Page 167 and 168:
Dynamics 151 P// ' I 1 Figure 2-8.
- Page 169 and 170:
Dynamics 153 x Component: The initi
- Page 171 and 172:
Dynamics 155 z A '\ 4t x = R, COS e
- Page 173 and 174:
Dynamics 157 d aH = --(vH) = -LO; c
- Page 175 and 176:
Dynamics 159 point on a line throug
- Page 177 and 178:
Table 2-6 Moments of Inertia of Com
- Page 179 and 180:
Dynamics 163 If 0 is a fixed axis o
- Page 181 and 182:
Dynamics 165 Note that e is defined
- Page 183 and 184:
Dynamics 167 The constant k, called
- Page 185 and 186:
Fluid Mechanics 169 The governing e
- Page 187 and 188:
Fluid Mechanics 171 Rrrnoulli 'F eq
- Page 189 and 190:
Fluid Mechanics 173 (2-57) (2-58) =
- Page 191 and 192:
Fluid Mechanics 175 0.051 0.041 0.0
- Page 193 and 194:
Fluid Mechanics 177 At 104°F Becau
- Page 195 and 196:
Fluid Mechanics 179 4 Figure 2-22.
- Page 197 and 198:
Fluid Mechanics 181 Example 2-1 6 A
- Page 199 and 200:
Fluid Mechanics 183 If the pressure
- Page 201 and 202:
Strength of Materials 185 A = n( =
- Page 203 and 204:
Strength of Materials 187 stress is
- Page 205 and 206:
Strength of Materials 189 Figure 2-
- Page 207 and 208:
Strength of Materials 191 (2-92) wh
- Page 209 and 210:
Strength of Materials 193 Example 2
- Page 211 and 212:
Table 2-15 Mechanical Properties of
- Page 213 and 214:
I9 0 2 1 22 23 24 2.5 Material CAST
- Page 215 and 216:
- Typical mechanical properties No.
- Page 217 and 218:
Typical mechanical properties Mater
- Page 219 and 220:
P- I 6 % " G el. = -
- Page 221 and 222:
cc - c
- Page 223 and 224:
Strength of Materials 207 Table 2-1
- Page 225 and 226:
Thermodynamics 209 Figure 2-30. Dia
- Page 227 and 228:
z;, Thermodynamics 2 1 1 Q = A(U +
- Page 229 and 230:
Thermodynamics 2 13 Example 2-23. H
- Page 231 and 232:
( Thermodynamics 2 15 For the gener
- Page 233 and 234: Thermodynamics 217 The second law y
- Page 235 and 236: Thermodynamics 219 (2-137) Combinin
- Page 237 and 238: Thermodynamics 221 Figure 2-34. The
- Page 239 and 240: Summary of Thermodynamic Equations
- Page 241 and 242: a 9 + % I- ll I U % a I k v) I a U
- Page 243 and 244: Thermodynamics 227 Entropy BtuAb f
- Page 245 and 246: ~ Thermodynamics 229 Table 2-20 Pro
- Page 247 and 248: Thermodynamics 231 Table 2-20 (cont
- Page 249 and 250: Thermodynamics 233 Table 2-20 (cont
- Page 251 and 252: Thermodynamics 235 1.2154 1272.0 1.
- Page 253 and 254: Thermodynamics 237 Table 2-23 Prope
- Page 255 and 256: Thermodynamics 239 - k. M 8 B ; -40
- Page 257 and 258: Geological Engineering 241 pressure
- Page 259 and 260: Geological Engineering 243 Table 2-
- Page 261 and 262: Geological Engineering 245 Table 2-
- Page 263 and 264: Geological Engineering 247 likely c
- Page 265 and 266: Geological Engineering 249 Hinge po
- Page 267 and 268: Geological Engineering 25 1 Disharm
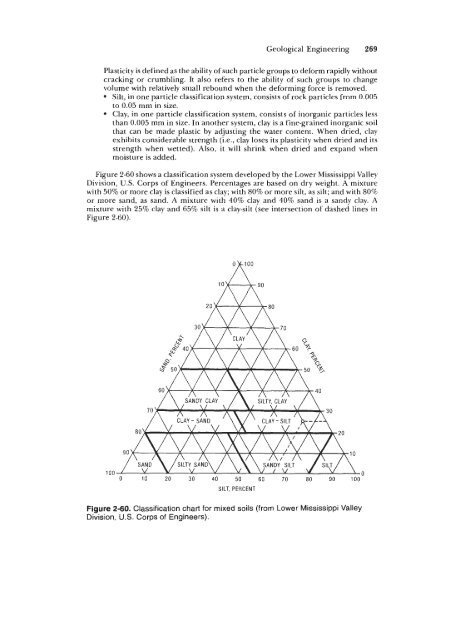
- Page 269 and 270: Geological Engineering 253 Figure 2
- Page 271 and 272: Geological Engineering 255 ssw LOW
- Page 273 and 274: Geological Engineering 257 SH ss LM
- Page 275 and 276: Geological Engineering 259 Consider
- Page 277 and 278: Geological Engineering 261 of drill
- Page 279 and 280: Geological Engineering 263 Equation
- Page 281 and 282: Geological Engineering 265 Subsurfa
- Page 283: Geological Engineering 267 0.7 0.75
- Page 287 and 288: Geological Engineering 271 Degree o
- Page 289 and 290: Geological Engineering 273 Silt, or
- Page 291 and 292: Geological Engineering 275 Specific
- Page 293 and 294: Geological Engineering 277 Table 2-
- Page 295 and 296: Electricity 279 Table 2-32 Electric
- Page 297 and 298: Electricity 281 where A is cross-se
- Page 299 and 300: ~~ ~~ Electricity 283 (a) SHORT CIR
- Page 301 and 302: Electricity 285 the potential by 90
- Page 303 and 304: Electricity 287 Quantity Magnetomot
- Page 305 and 306: Electricity 289 Figure 2-68. Basic
- Page 307 and 308: Electricity 291 where k' is constan
- Page 309 and 310: Electricity 293 coil of the element
- Page 311 and 312: Electricity 295 quite involved, and
- Page 313 and 314: Chemistry 297 Interior wiring desig
- Page 315 and 316: Chemistry 299 Hydrogen fluoride Wat
- Page 317 and 318: Chemistry 301 Table 239 Typical Cru
- Page 319 and 320: HY DROCARBONS ALIP~ATIC (ACYCLIC 1
- Page 321 and 322: Chemistry 305 [ nC,H,, (n-pentane)]
- Page 323 and 324: Chemistry 307 Alkenes also form a h
- Page 325 and 326: Chemistry 309 b"" ( 1,2-dirnethylcy
- Page 327 and 328: Chemistry 311 If several groups are
- Page 329 and 330: Chemistry 313 Table 2-42 Selected F
- Page 331 and 332: Chemistry 315 organic compounds con
- Page 333 and 334: Chemistry 317 COOH COOH COOH I HO-C
- Page 335 and 336:
Chemistry 319 Table 2-43 (continued
- Page 337 and 338:
Chemistry 321 Table 2-44 (continued
- Page 339 and 340:
Chemistry 323 -675°C (-1250°F) un
- Page 341 and 342:
Chemistry 325 The aniline cloud poi
- Page 343 and 344:
Chemistry 327 mass (m) of a mixture
- Page 345 and 346:
Chemistry 329 Compositions of Liqui
- Page 347 and 348:
Chemistry 331 g-moles of solute (v)
- Page 349 and 350:
[ inflow the:Ilem entering or symbo
- Page 351 and 352:
Chemistry 335 circumstances, the re
- Page 353 and 354:
Chemistry 337 The values in parenth
- Page 355 and 356:
Chemistry 339 Mass density of the v
- Page 357 and 358:
Chemistry 341 Component i MI (IWlb-
- Page 359 and 360:
I J SOLID - LIQUID I I I TEMPEWITUR
- Page 361 and 362:
Chemistry 345 - e n v Lu U 3 u3 w a
- Page 363 and 364:
Chemistry 347 Solution Two estimate
- Page 365 and 366:
Chemistry 349 Solution MW of solute
- Page 367 and 368:
Chemistry 351 (w~,Jw~,~) = Ki = 0.3
- Page 369 and 370:
Chemistry 353 AH:(25"C,1 atm) = Euj
- Page 371 and 372:
Chemistry 355 Check: Using heats of
- Page 373 and 374:
Chemistry 357 In a more compact not
- Page 375 and 376:
Chemistry 359 where d/aP denotes pa
- Page 377 and 378:
Chemistry 361 - An alternative repr
- Page 379 and 380:
Chemistry 363 Gas a b x lo2 c x lo5
- Page 381 and 382:
Engineering Design 365 Because the
- Page 383 and 384:
Engineering Design 367 Table 2-48 C
- Page 385 and 386:
~~ Engineering Design 369 Table 2-5
- Page 387 and 388:
Engineering Design 371 is always th
- Page 389 and 390:
Engineering Design 373 Table 2-52 (
- Page 391 and 392:
Engineering Design 375 and 114 is n
- Page 393 and 394:
Engineering Design 377 1 10 Figure
- Page 395 and 396:
Engineering Design 379 3. Engineers
- Page 397 and 398:
Engineering Design 381 NSPE Code of
- Page 399 and 400:
Engineering Design 383 The term tra
- Page 401 and 402:
Engineering Design 385 mark used in
- Page 403 and 404:
References 387 20. Fellinger, R. C.
- Page 405:
References 389 70. Langhaar, H. L.,
- Page 409 and 410:
Chapter 3 Auxiliary Equipment This
- Page 411 and 412:
Prime Movers 395 The four-stroke en
- Page 413 and 414:
Prime Movers 397 RECOMMENDED SPEEDS
- Page 415 and 416:
~~~ ~~~~ ~ Prime Movers 399 Table 3
- Page 417 and 418:
Prime Movers 401 Generator Starting
- Page 419 and 420:
Prime Movers 403 Alternating-Curren
- Page 421 and 422:
Prime Movers 405 Repulsion Motor. A
- Page 423 and 424:
Prime Movers 407 breakdown torque,
- Page 425 and 426:
Prime Movers 409 X, = Stator leakag
- Page 427 and 428:
Prime Movers 41 1 ZIP Synchronous s
- Page 429 and 430:
Prime Movers 413 100 90 80 al 0. cn
- Page 431 and 432:
Prime Movers 415 The relative stren
- Page 433 and 434:
Prime Movers 417 Natural Gas Pipeli
- Page 435 and 436:
Prime Movers 419 for the losses in
- Page 437 and 438:
Power Transmission 421 3. Ribbed, o
- Page 439:
Power Transmission 423 Sel Keyed 10
- Page 442 and 443:
426 Auxiliary Equipment Figure 3-23
- Page 444 and 445:
5000 4000 3450 3000 2500 2000 1750
- Page 446 and 447:
Table 3-9 Horsepower Ratings for A
- Page 448 and 449:
Table 3-1 0 Horsepower Ratings for
- Page 450 and 451:
RRI Table 3-12 Horsepower Ratings f
- Page 452 and 453:
Table 3-1 4 Horsepower Ratings for
- Page 454 and 455:
Table 3-16 Horsepower Ratings for 8
- Page 456 and 457:
440 Auxiliary Equipment Varies with
- Page 458 and 459:
442 Auxiliary Equipment under load
- Page 460 and 461:
444 Auxiliary Equipment Llnk. ‘Sp
- Page 462 and 463:
446 Auxiliary Equipment This chain
- Page 464 and 465:
448 Auxiliary Equipment 14 13 12 11
- Page 466 and 467:
450 Auxiliary Equipment The method
- Page 468 and 469:
452 Auxiliary Equipment Calculation
- Page 470 and 471:
454 Auxiliary Equipment Roller Chai
- Page 472 and 473:
456 Auxiliary EqGpment Teeth 12 15
- Page 474 and 475:
458 Auxiliary Equipment No. of teet
- Page 476 and 477:
460 Auxiliary Equipment I Ir STEAM
- Page 478 and 479:
462 Auxiliary Equipment I Q I 1 P F
- Page 480 and 481:
464 Auxiliary Equipment The single-
- Page 482 and 483:
466 Auxiliary Equipment Figure 3-53
- Page 484 and 485:
468 Auxiliary Equipment r C+D Figur
- Page 486 and 487:
470 Auxiliary Equipment Figure 3-58
- Page 488 and 489:
472 Auxiliary Equipment Calculation
- Page 490 and 491:
474 Auxiliary Equipment POINT OF EN
- Page 492 and 493:
476 Auxiliary Equipment & L d Y 1 5
- Page 494 and 495:
478 Auxiliary Equipment E Canter of
- Page 496 and 497:
480 Auxiliary Equipment FLOW RATE (
- Page 498 and 499:
482 Auxiliary Equipment S =rVn I (3
- Page 500:
484 Auxiliary Equipment P = n, (3-7