Using Caché Objects - InterSystems Documentation
Using Caché Objects - InterSystems Documentation
Using Caché Objects - InterSystems Documentation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Data Types<br />
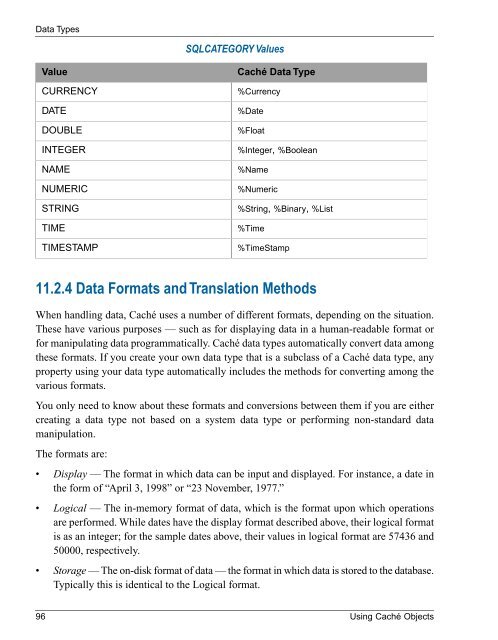
SQLCATEGORY Values<br />
Value<br />
CURRENCY<br />
DATE<br />
DOUBLE<br />
INTEGER<br />
NAME<br />
NUMERIC<br />
STRING<br />
TIME<br />
TIMESTAMP<br />
<strong>Caché</strong> Data Type<br />
%Currency<br />
%Date<br />
%Float<br />
%Integer, %Boolean<br />
%Name<br />
%Numeric<br />
%String, %Binary, %List<br />
%Time<br />
%TimeStamp<br />
11.2.4 Data Formats and Translation Methods<br />
When handling data, <strong>Caché</strong> uses a number of different formats, depending on the situation.<br />
These have various purposes — such as for displaying data in a human-readable format or<br />
for manipulating data programmatically. <strong>Caché</strong> data types automatically convert data among<br />
these formats. If you create your own data type that is a subclass of a <strong>Caché</strong> data type, any<br />
property using your data type automatically includes the methods for converting among the<br />
various formats.<br />
You only need to know about these formats and conversions between them if you are either<br />
creating a data type not based on a system data type or performing non-standard data<br />
manipulation.<br />
The formats are:<br />
• Display — The format in which data can be input and displayed. For instance, a date in<br />
the form of “April 3, 1998” or “23 November, 1977.”<br />
• Logical — The in-memory format of data, which is the format upon which operations<br />
are performed. While dates have the display format described above, their logical format<br />
is as an integer; for the sample dates above, their values in logical format are 57436 and<br />
50000, respectively.<br />
• Storage — The on-disk format of data — the format in which data is stored to the database.<br />
Typically this is identical to the Logical format.<br />
96 <strong>Using</strong> <strong>Caché</strong> <strong>Objects</strong>