Polyatomic molecules - Cobalt
Polyatomic molecules - Cobalt
Polyatomic molecules - Cobalt
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The set of linear equations reads<br />
C ( α− E)<br />
+ C β = 0<br />
11<br />
12<br />
C β + C ( α− E)<br />
+ C β =0<br />
11 12<br />
13<br />
C<br />
12<br />
β<br />
+C<br />
12<br />
( α− E)<br />
= 0<br />
We get<br />
1 1 1<br />
1 1<br />
1 1 1<br />
ψ = ϕ + ϕ + ϕ ; ψ = ϕ − ϕ ; ψ = ϕ − ϕ + ϕ<br />
2 2 2<br />
2 2 2 2 2<br />
1 1 2 3 2 1 3 3 1 2 3<br />
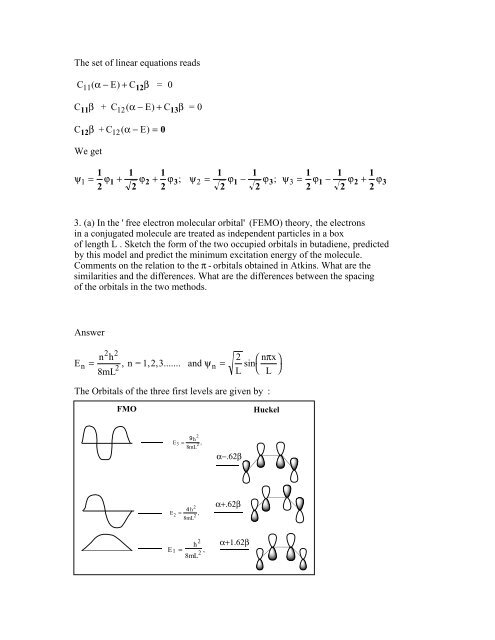
3. (a) In the ' free electron molecular orbital' (FEMO) theory, the electrons<br />
in a conjugated molecule are treated as independent particles in a box<br />
of length L . Sketch the form of the two occupied orbitals in butadiene, predicted<br />
by this model and predict the minimum excitation energy of the molecule.<br />
Comments on the relation to the π - orbitals obtained in Atkins. What are the<br />
similarities and the differences. What are the differences between the spacing<br />
of the orbitals in the two methods.<br />
Answer<br />
2 2<br />
n h<br />
2 n x<br />
En = =<br />
⎛ π<br />
, n = 1,2,3....... and ψ sin<br />
⎞<br />
2<br />
n<br />
8mL<br />
L ⎝ L ⎠<br />
The Orbitals of the three first levels are given by :<br />
FMO<br />
Huckel<br />
E 3 =<br />
9h 2<br />
8mL 2 ,<br />
α−.62β<br />
4 h 2<br />
E 2 =<br />
8mL 2 ,<br />
α+.62β<br />
E 1 =<br />
h 2<br />
8mL 2 ,<br />
α+1.62β