NITRIFICATION AND ACTIVATED SLUDGE FOAMING ...
NITRIFICATION AND ACTIVATED SLUDGE FOAMING ...
NITRIFICATION AND ACTIVATED SLUDGE FOAMING ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
nitrification performance. The WRF performance has become more consistent and with experience, the<br />
plant staff has become keenly aware of how quickly the system can react to changes in WAS to promote<br />
foam and scum increases.<br />
Given this sensitivity which has been seen to be more pronounced in winter operations, additional means<br />
to help reduce ammonia nitrogen pass-through during periods of higher foaming conditions were<br />
investigated. Data from the on-line ammonia analyzer monitoring secondary influent provided information<br />
that ammonia nitrogen concentrations in the influent after flow equalization varied significantly during a 24<br />
hour period. Historically, the WRF has operated on the basis of equalized diurnal flow. This system is<br />
automated through SCADA programming for control of flow equalization basins and pumping systems.<br />
With the ammonia nitrogen concentration variability, a constant flow approach created a wide range of<br />
actual ammonia nitrogen loading to the activated sludge system. Using the SCADA system, online<br />
ammonia analyzer, and existing equalization system capabilities, an ammonia nitrogen load control<br />
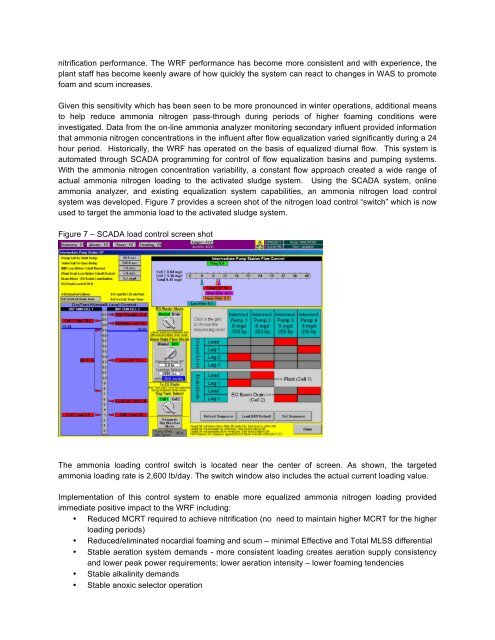
system was developed. Figure 7 provides a screen shot of the nitrogen load control “switch” which is now<br />
used to target the ammonia load to the activated sludge system.<br />
Figure 7 – SCADA load control screen shot<br />
The ammonia loading control switch is located near the center of screen. As shown, the targeted<br />
ammonia loading rate is 2,600 lb/day. The switch window also includes the actual current loading value.<br />
Implementation of this control system to enable more equalized ammonia nitrogen loading provided<br />
immediate positive impact to the WRF including:<br />
• Reduced MCRT required to achieve nitrification (no need to maintain higher MCRT for the higher<br />
loading periods)<br />
• Reduced/eliminated nocardial foaming and scum – minimal Effective and Total MLSS differential<br />
• Stable aeration system demands - more consistent loading creates aeration supply consistency<br />
and lower peak power requirements; lower aeration intensity – lower foaming tendencies<br />
• Stable alkalinity demands<br />
• Stable anoxic selector operation