Isolated ileal interposition in enteroendocrine L cells differentiation
Isolated ileal interposition in enteroendocrine L cells differentiation
Isolated ileal interposition in enteroendocrine L cells differentiation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
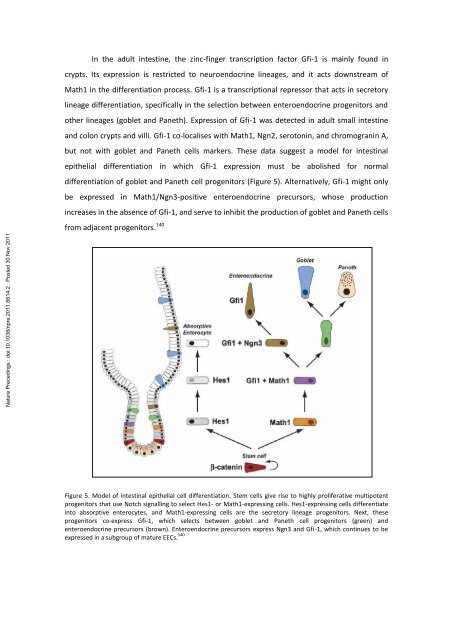
In the adult <strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>e, the z<strong>in</strong>c-f<strong>in</strong>ger transcription factor Gfi-1 is ma<strong>in</strong>ly found <strong>in</strong><br />
crypts. Its expression is restricted to neuroendocr<strong>in</strong>e l<strong>in</strong>eages, and it acts downstream of<br />
Nature Preced<strong>in</strong>gs : doi:10.1038/npre.2011.6614.2 : Posted 30 Nov 2011<br />
Math1 <strong>in</strong> the <strong>differentiation</strong> process. Gfi-1 is a transcriptional repressor that acts <strong>in</strong> secretory<br />
l<strong>in</strong>eage <strong>differentiation</strong>, specifically <strong>in</strong> the selection between enteroendocr<strong>in</strong>e progenitors and<br />
other l<strong>in</strong>eages (goblet and Paneth). Expression of Gfi-1 was detected <strong>in</strong> adult small <strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>e<br />
and colon crypts and villi. Gfi-1 co-localises with Math1, Ngn2, seroton<strong>in</strong>, and chromogran<strong>in</strong> A,<br />
but not with goblet and Paneth <strong>cells</strong> markers. These data suggest a model for <strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>al<br />
epithelial <strong>differentiation</strong> <strong>in</strong> which Gfi-1 expression must be abolished for normal<br />
<strong>differentiation</strong> of goblet and Paneth cell progenitors (Figure 5). Alternatively, Gfi-1 might only<br />
be expressed <strong>in</strong> Math1/Ngn3-positive enteroendocr<strong>in</strong>e precursors, whose production<br />
<strong>in</strong>creases <strong>in</strong> the absence of Gfi-1, and serve to <strong>in</strong>hibit the production of goblet and Paneth <strong>cells</strong><br />
from adjacent progenitors. 140<br />
Figure 5. Model of <strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>al epithelial cell <strong>differentiation</strong>. Stem <strong>cells</strong> give rise to highly proliferative multipotent<br />
progenitors that use Notch signall<strong>in</strong>g to select Hes1- or Math1-express<strong>in</strong>g <strong>cells</strong>. Hes1-express<strong>in</strong>g <strong>cells</strong> differentiate<br />
<strong>in</strong>to absorptive enterocytes, and Math1-express<strong>in</strong>g <strong>cells</strong> are the secretory l<strong>in</strong>eage progenitors. Next, these<br />
progenitors co-express Gfi-1, which selects between goblet and Paneth cell progenitors (green) and<br />
enteroendocr<strong>in</strong>e precursors (brown). Enteroendocr<strong>in</strong>e precursors express Ngn3 and Gfi-1, which cont<strong>in</strong>ues to be<br />
expressed <strong>in</strong> a subgroup of mature EECs. 140