INTRODUCTION TO ENGLISH TEXT LINGUISTICS
INTRODUCTION TO ENGLISH TEXT LINGUISTICS
INTRODUCTION TO ENGLISH TEXT LINGUISTICS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1.0 Introduction<br />
Professor Christopher Gledhill<br />
(Notes de cours, Linguistique du texte anglais, 48LGAN23, EILA, Université Paris Diderot)<br />
<strong>TO</strong>PIC 1. LINGUISTIC TERMINOLOGY<br />
In order to analyse and compare texts, you need to know the technical words and systems that<br />
linguists have developed use to describe language. In this course, I use the same terminology as<br />
the British linguist Michael Halliday (see Bibliography). In order to do Exercise 1, you’ll need to<br />
know the main levels or ‘ranks’ of language (see tables 1 and 2) as well as the basic ‘lexical classes’<br />
(also known as ‘parts of speech’, see table 3).<br />
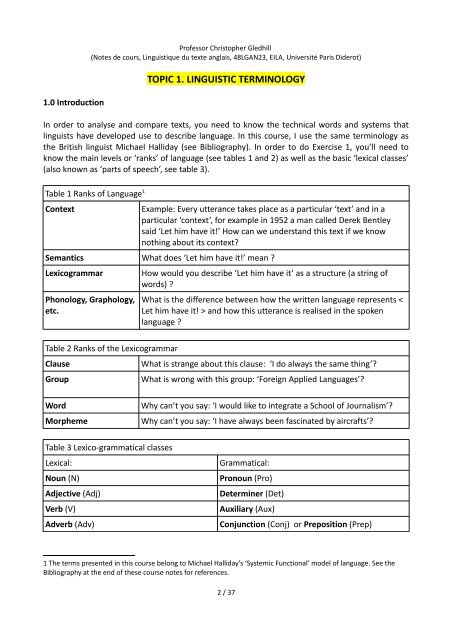
Table 1 Ranks of Language 1<br />
Context<br />
Example: Every utterance takes place as a particular ‘text’ and in a<br />
particular ‘context’, for example in 1952 a man called Derek Bentley<br />
said ‘Let him have it!’ How can we understand this text if we know<br />
nothing about its context?<br />
Semantics What does ‘Let him have it!’ mean ?<br />
Lexicogrammar<br />
Phonology, Graphology,<br />
etc.<br />
How would you describe ‘Let him have it’ as a structure (a string of<br />
words) ?<br />
What is the difference between how the written language represents <<br />
Let him have it! > and how this utterance is realised in the spoken<br />
language ?<br />
Table 2 Ranks of the Lexicogrammar<br />
Clause<br />
What is strange about this clause: ‘I do always the same thing’?<br />
Group<br />
What is wrong with this group: ‘Foreign Applied Languages’?<br />
Word<br />
Morpheme<br />
Why can’t you say: ‘I would like to integrate a School of Journalism’?<br />
Why can’t you say: ‘I have always been fascinated by aircrafts’?<br />
Table 3 Lexico-grammatical classes<br />
Lexical:<br />
Noun (N)<br />
Adjective (Adj)<br />
Verb (V)<br />
Adverb (Adv)<br />
Grammatical:<br />
Pronoun (Pro)<br />
Determiner (Det)<br />
Auxiliary (Aux)<br />
Conjunction (Conj) or Preposition (Prep)<br />
1 The terms presented in this course belong to Michael Halliday’s ‘Systemic Functional’ model of language. See the<br />
Bibliography at the end of these course notes for references.<br />
2 / 37