Task Force Report - Govind Ballabh Pant Institute of Himalayan ...
Task Force Report - Govind Ballabh Pant Institute of Himalayan ...
Task Force Report - Govind Ballabh Pant Institute of Himalayan ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
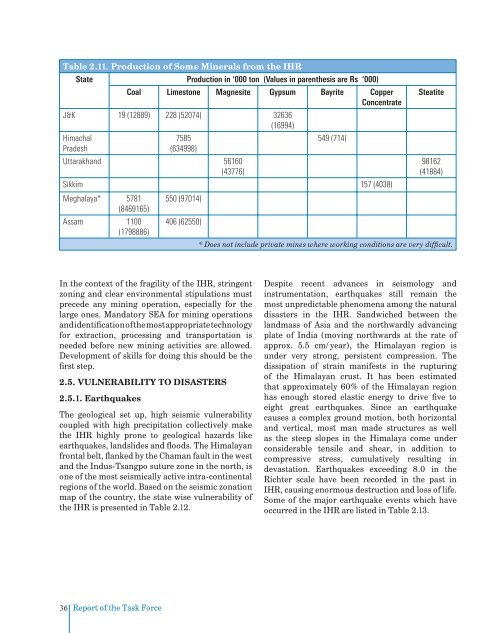
Table 2.11. Production <strong>of</strong> Some Minerals from the IHR<br />
State Production in ‘000 ton (Values in parenthesis are Rs ‘000)<br />
Coal Limestone Magnesite Gypsum Bayrite Copper<br />
Concentrate<br />
J&K 19 (12889) 228 (52074) 32636<br />
(16994)<br />
Himachal<br />
7585<br />
549 (714)<br />
Pradesh<br />
(634998)<br />
Uttarakhand 56160<br />
(43776)<br />
Sikkim 157 (4038)<br />
Meghalaya* 5781 550 (97014)<br />
(8469165)<br />
Assam 1100 406 (62550)<br />
(1798886)<br />
Steatite<br />
98162<br />
(41884)<br />
* Does not include private mines where working conditions are very difficult.<br />
In the context <strong>of</strong> the fragility <strong>of</strong> the IHR, stringent<br />
zoning and clear environmental stipulations must<br />
precede any mining operation, especially for the<br />
large ones. Mandatory SEA for mining operations<br />
and identification <strong>of</strong> the most appropriate technology<br />
for extraction, processing and transportation is<br />
needed before new mining activities are allowed.<br />
Development <strong>of</strong> skills for doing this should be the<br />
first step.<br />
2.5. VULNERABILITY TO DISASTERS<br />
2.5.1. Earthquakes<br />
The geological set up, high seismic vulnerability<br />
coupled with high precipitation collectively make<br />
the IHR highly prone to geological hazards like<br />
earthquakes, landslides and floods. The <strong>Himalayan</strong><br />
frontal belt, flanked by the Chaman fault in the west<br />
and the Indus-Tsangpo suture zone in the north, is<br />
one <strong>of</strong> the most seismically active intra-continental<br />
regions <strong>of</strong> the world. Based on the seismic zonation<br />
map <strong>of</strong> the country, the state wise vulnerability <strong>of</strong><br />
the IHR is presented in Table 2.12.<br />
Despite recent advances in seismology and<br />
instrumentation, earthquakes still remain the<br />
most unpredictable phenomena among the natural<br />
disasters in the IHR. Sandwiched between the<br />
landmass <strong>of</strong> Asia and the northwardly advancing<br />
plate <strong>of</strong> India (moving northwards at the rate <strong>of</strong><br />
approx. 5.5 cm/year), the <strong>Himalayan</strong> region is<br />
under very strong, persistent compression. The<br />
dissipation <strong>of</strong> strain manifests in the rupturing<br />
<strong>of</strong> the <strong>Himalayan</strong> crust. It has been estimated<br />
that approximately 60% <strong>of</strong> the <strong>Himalayan</strong> region<br />
has enough stored elastic energy to drive five to<br />
eight great earthquakes. Since an earthquake<br />
causes a complex ground motion, both horizontal<br />
and vertical, most man made structures as well<br />
as the steep slopes in the Himalaya come under<br />
considerable tensile and shear, in addition to<br />
compressive stress, cumulatively resulting in<br />
devastation. Earthquakes exceeding 8.0 in the<br />
Richter scale have been recorded in the past in<br />
IHR, causing enormous destruction and loss <strong>of</strong> life.<br />
Some <strong>of</strong> the major earthquake events which have<br />
occurred in the IHR are listed in Table 2.13.<br />
36<br />
<strong>Report</strong> <strong>of</strong> the <strong>Task</strong> <strong>Force</strong>