Genetic susceptibility to adverse drug effects - Epidemiology ...
Genetic susceptibility to adverse drug effects - Epidemiology ...
Genetic susceptibility to adverse drug effects - Epidemiology ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 4.3<br />
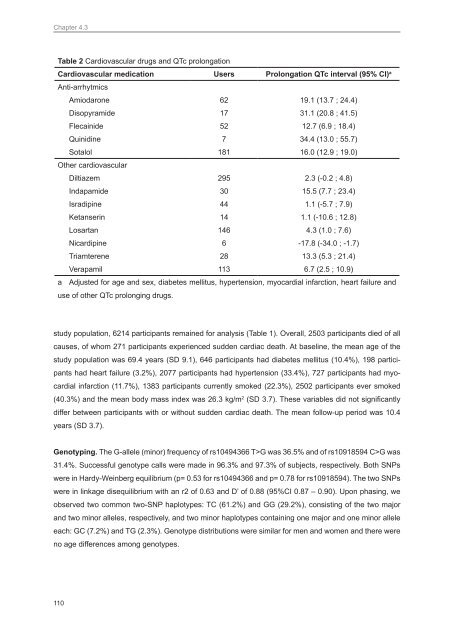
Table 2 Cardiovascular <strong>drug</strong>s and QTc prolongation<br />
Cardiovascular medication Users Prolongation QTc interval (95% CI) a<br />
Anti-arrhytmics<br />
Amiodarone 62 19.1 (13.7 ; 24.4)<br />
Disopyramide 17 31.1 (20.8 ; 41.5)<br />
Flecainide 52 12.7 (6.9 ; 18.4)<br />
Quinidine 7 34.4 (13.0 ; 55.7)<br />
Sotalol 181 16.0 (12.9 ; 19.0)<br />
Other cardiovascular<br />
Diltiazem 295 2.3 (-0.2 ; 4.8)<br />
Indapamide 30 15.5 (7.7 ; 23.4)<br />
Isradipine 44 1.1 (-5.7 ; 7.9)<br />
Ketanserin 14 1.1 (-10.6 ; 12.8)<br />
Losartan 146 4.3 (1.0 ; 7.6)<br />
Nicardipine 6 -17.8 (-34.0 ; -1.7)<br />
Triamterene 28 13.3 (5.3 ; 21.4)<br />
Verapamil 113 6.7 (2.5 ; 10.9)<br />
a Adjusted for age and sex, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, myocardial infarction, heart failure and<br />
use of other QTc prolonging <strong>drug</strong>s.<br />
study population, 6214 participants remained for analysis (Table 1). Overall, 2503 participants died of all<br />
causes, of whom 271 participants experienced sudden cardiac death. At baseline, the mean age of the<br />
study population was 69.4 years (SD 9.1), 646 participants had diabetes mellitus (10.4%), 198 participants<br />
had heart failure (3.2%), 2077 participants had hypertension (33.4%), 727 participants had myocardial<br />
infarction (11.7%), 1383 participants currently smoked (22.3%), 2502 participants ever smoked<br />
(40.3%) and the mean body mass index was 26.3 kg/m 2 (SD 3.7). These variables did not significantly<br />
differ between participants with or without sudden cardiac death. The mean follow-up period was 10.4<br />
years (SD 3.7).<br />
Genotyping. The G-allele (minor) frequency of rs10494366 T>G was 36.5% and of rs10918594 C>G was<br />
31.4%. Successful genotype calls were made in 96.3% and 97.3% of subjects, respectively. Both SNPs<br />
were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (p= 0.53 for rs10494366 and p= 0.78 for rs10918594). The two SNPs<br />
were in linkage disequilibrium with an r2 of 0.63 and D’ of 0.88 (95%CI 0.87 – 0.90). Upon phasing, we<br />
observed two common two-SNP haplotypes: TC (61.2%) and GG (29.2%), consisting of the two major<br />
and two minor alleles, respectively, and two minor haplotypes containing one major and one minor allele<br />
each: GC (7.2%) and TG (2.3%). Genotype distributions were similar for men and women and there were<br />
no age differences among genotypes.<br />
110