Annual Report 2012 - Latvijas Universitātes Cietvielu fizikas institūts
Annual Report 2012 - Latvijas Universitātes Cietvielu fizikas institūts
Annual Report 2012 - Latvijas Universitātes Cietvielu fizikas institūts
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
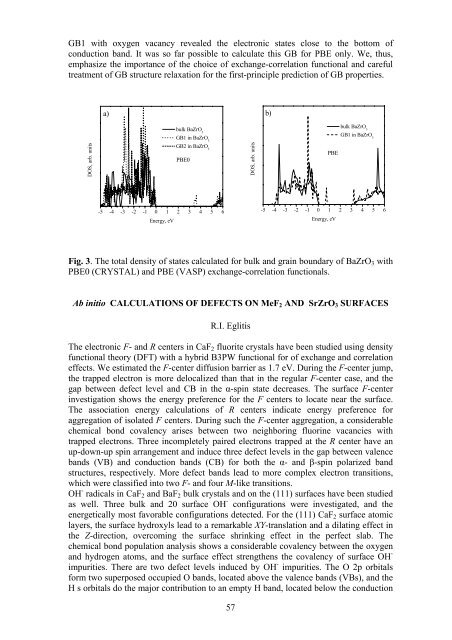
GB1 with oxygen vacancy revealed the electronic states close to the bottom of<br />
conduction band. It was so far possible to calculate this GB for PBE only. We, thus,<br />
emphasize the importance of the choice of exchange-correlation functional and careful<br />
treatment of GB structure relaxation for the first-principle prediction of GB properties.<br />
a)<br />
b)<br />
bulk BaZrO 3<br />
GB1 in BaZrO 3<br />
bulk BaZrO 3<br />
GB1 in BaZrO 3<br />
DOS, arb. units<br />
GB2 in BaZrO 3<br />
PBE0<br />
DOS, arb. units<br />
PBE<br />
-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6<br />
Energy, eV<br />
-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6<br />
Energy, eV<br />
Fig. 3. The total density of states calculated for bulk and grain boundary of BaZrO 3 with<br />
PBE0 (CRYSTAL) and PBE (VASP) exchange-correlation functionals.<br />
Ab initio CALCULATIONS OF DEFECTS ON MeF 2 AND SrZrO 3 SURFACES<br />
R.I. Eglitis<br />
The electronic F- and R centers in CaF 2 fluorite crystals have been studied using density<br />
functional theory (DFT) with a hybrid B3PW functional for of exchange and correlation<br />
effects. We estimated the F-center diffusion barrier as 1.7 eV. During the F-center jump,<br />
the trapped electron is more delocalized than that in the regular F-center case, and the<br />
gap between defect level and CB in the α-spin state decreases. The surface F-center<br />
investigation shows the energy preference for the F centers to locate near the surface.<br />
The association energy calculations of R centers indicate energy preference for<br />
aggregation of isolated F centers. During such the F-center aggregation, a considerable<br />
chemical bond covalency arises between two neighboring fluorine vacancies with<br />
trapped electrons. Three incompletely paired electrons trapped at the R center have an<br />
up-down-up spin arrangement and induce three defect levels in the gap between valence<br />
bands (VB) and conduction bands (CB) for both the α- and β-spin polarized band<br />
structures, respectively. More defect bands lead to more complex electron transitions,<br />
which were classified into two F- and four M-like transitions.<br />
OH - radicals in CaF 2 and BaF 2 bulk crystals and on the (111) surfaces have been studied<br />
as well. Three bulk and 20 surface OH - configurations were investigated, and the<br />
energetically most favorable configurations detected. For the (111) CaF 2 surface atomic<br />
layers, the surface hydroxyls lead to a remarkable XY-translation and a dilating effect in<br />
the Z-direction, overcoming the surface shrinking effect in the perfect slab. The<br />
chemical bond population analysis shows a considerable covalency between the oxygen<br />
and hydrogen atoms, and the surface effect strengthens the covalency of surface OH -<br />
impurities. There are two defect levels induced by OH - impurities. The O 2p orbitals<br />
form two superposed occupied O bands, located above the valence bands (VBs), and the<br />
H s orbitals do the major contribution to an empty H band, located below the conduction<br />
57