Test on Unit 4 - University City Schools
Test on Unit 4 - University City Schools
Test on Unit 4 - University City Schools
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
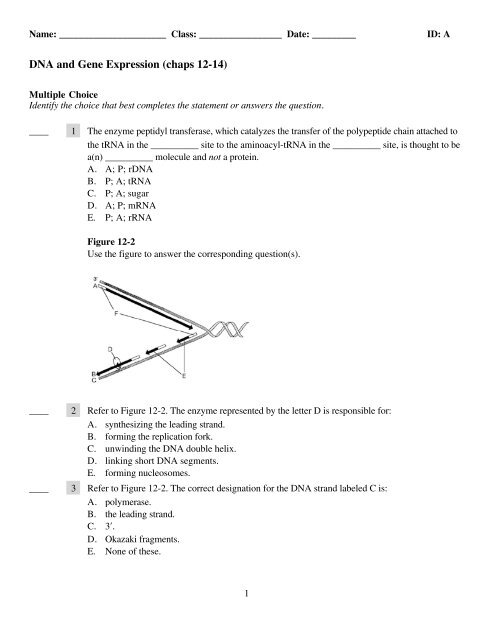
Name: ______________________ Class: _________________ Date: _________ID: ADNA and Gene Expressi<strong>on</strong> (chaps 12-14)Multiple ChoiceIdentify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the questi<strong>on</strong>.____1 The enzyme peptidyl transferase, which catalyzes the transfer of the polypeptide chain attached tothe tRNA in the __________ site to the aminoacyl-tRNA in the __________ site, is thought to bea(n) __________ molecule and not a protein.A. A; P; rDNAB. P; A; tRNAC. P; A; sugarD. A; P; mRNAE. P; A; rRNAFigure 12-2Use the figure to answer the corresp<strong>on</strong>ding questi<strong>on</strong>(s).________2 Refer to Figure 12-2. The enzyme represented by the letter D is resp<strong>on</strong>sible for:A. synthesizing the leading strand.B. forming the replicati<strong>on</strong> fork.C. unwinding the DNA double helix.D. linking short DNA segments.E. forming nucleosomes.3 Refer to Figure 12-2. The correct designati<strong>on</strong> for the DNA strand labeled C is:A. polymerase.B. the leading strand.C. 3′.D. Okazaki fragments.E. N<strong>on</strong>e of these.1
Name: ______________________ID: A________________4 Refer to Figure 12-2. The segments labeled F are resp<strong>on</strong>sible for:A. unwinding the DNA double helix.B. linking short DNA segments.C. forming the replicati<strong>on</strong> fork.D. synthesizing the leading strand.E. initiating DNA synthesis.5 Refer to Figure 12-2. The structures represented by the letter E are called:A. DNA polymerases.B. Okazaki fragments.C. nucleosomes.D. replicati<strong>on</strong> forks.E. leading fragments6 Uracil forms a complementary pair with __________ in RNA and __________ in DNA.A. uracil; adenineB. adenine; adenineC. thymine; thymineD. adenine; thymineE. adenine; uracil7 The tRNA:A. must have an anticod<strong>on</strong>.B. must be recognized by ribosomes.C. must be recognized by a specific aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that adds the correctamino acid.D. must have an attachment site for the amino acid.E. All of these.2
Name: ______________________ID: AFigure 13-2Use the figure to answer the corresp<strong>on</strong>ding questi<strong>on</strong>(s).________8 Refer to Figure 13-2. The porti<strong>on</strong> of the molecule labeled 5 is:A. the attached amino acid.B. the cod<strong>on</strong>.C. a double-stranded regi<strong>on</strong>.D. a single-stranded regi<strong>on</strong>.E. the anticod<strong>on</strong>.9 The main reas<strong>on</strong> scientists thought that proteins, rather than DNA, were the carriers of geneticmaterial in the cell was:A. their ability to self replicate within the cytoplasm.B. the large number of possible amino acid combinati<strong>on</strong>s.C. their abundance within the cell.D. their ability to be exported from the cell.E. their presence within the nucleus.3
Name: ______________________ID: A________________________10 Genes that encode proteins that are always needed are called:A. repressible genes.B. promoter genes.C. oper<strong>on</strong>s.D. c<strong>on</strong>stitutive genes.E. inducible genes.11 The cod<strong>on</strong> is found in the:A. n<strong>on</strong>template strand of DNA.B. rRNA.C. template strand of DNA.D. mRNA.E. tRNA.12 The 3′ end of eukaryotic pre-mRNAs are changed by:A. cutting and adding 100−250 adenine nucleotides.B. removing the last phosphate group.C. phosphorylati<strong>on</strong> of the mRNA molecule.D. copying the last few bases so that it can form a duplex structure.E. adding a "cap."13 In eukaryotes, some DNA sequences act as intr<strong>on</strong>s in some cells and as ex<strong>on</strong>s in other cells. Thisis an example of __________.A. gene repressi<strong>on</strong>B. gene processingC. mRNA splicingD. differential mRNA processingE. gene amplificati<strong>on</strong>14 The first experimenters to use Griffith's transformati<strong>on</strong> assay to identify the genetic material were:A. Mesels<strong>on</strong> and Stahl.B. Franklin and Wilkins.C. Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty.D. Wats<strong>on</strong> and Crick.E. Hershey and Chase.15 The DNA strand that is replicated smoothly and c<strong>on</strong>tinuously is called the:A. leading strand.B. alpha strand.C. primary strand.D. lagging strand.E. first strand.4
Name: ______________________ID: A________________________16 Translati<strong>on</strong>al c<strong>on</strong>trols regulate:A. the uptake of nucleic acids into the cell.B. the attachment of phosphate groups to polypeptides.C. the rate at which an mRNA molecule is synthesized.D. the rate at which an mRNA molecule is translated.E. the activity of a protein end-product that is produced.17 RNA differs from DNA in all the following except:A. RNA is a larger molecule than DNA.B. RNA c<strong>on</strong>tains uracil and DNA c<strong>on</strong>tains thymine.C. RNA c<strong>on</strong>tains ribose and DNA c<strong>on</strong>tains deoxyribose.D. RNA is single stranded and DNA is double stranded.E. N<strong>on</strong>e of the above.18 In replicati<strong>on</strong>, <strong>on</strong>ce the DNA strands have been separated, reformati<strong>on</strong> of the double helix isprevented by:A. DNA polymerases.B. ATP.C. DNA helicase enzyme.D. single-strand binding proteins.E. GTP.19 Retroviruses or RNA tumor viruses use __________ to make DNA.A. DNA-dependent RNA polymeraseB. reverse transcriptaseC. DNA polymeraseD. RNA polymeraseE. primase20 During protein synthesis, ribosomes:A. transcribe mRNA to tRNA.B. translate mRNA into DNA.C. attach to the mRNA molecule and travel al<strong>on</strong>g its length.D. translate mRNA into tRNA.E. attach to the DNA molecule and travel al<strong>on</strong>g its length to produce an mRNAmolecule.21 __________ determined the structure of the molecule DNA.A. FranklinB. Franklin and CrickC. Wats<strong>on</strong> and CrickD. Wats<strong>on</strong>, Crick, and WilkinsE. Crick and Wilkins5
Name: ______________________ID: A________________22 Initiati<strong>on</strong> of transcripti<strong>on</strong> requires:A. an RNA primer.B. a DNA primer.C. DNA polymerase.D. a promoter sequence.E. Okazaki fragments.23 __________ used x-ray diffracti<strong>on</strong> to provide images of DNA.A. Erwin ChargaffB. Frederick GriffithC. Rosalind FranklinD. Francis CrickE. James Wats<strong>on</strong>24 Chargaff determined that DNA from any source c<strong>on</strong>tains about the same amount of guanine as__________.A. adenineB. guanineC. thymineD. uracilE. cytosine25 The focus of gene regulati<strong>on</strong> in multicellular organisms is <strong>on</strong>:A. the specificity of products in different tissues.B. rapid turnover of RNA molecules.C. oper<strong>on</strong>s.D. ec<strong>on</strong>omizing resources at all levels.E. All of these.6
Name: ______________________ID: AFigure 12-1Use the figure to answer the corresp<strong>on</strong>ding questi<strong>on</strong>(s).________26 The porti<strong>on</strong> of the molecule in box 3 of Figure 12-1 is:A. a sugar.B. a nucleotide.C. a protein.D. a purine.E. a pyrimidine.27 The porti<strong>on</strong> of the molecule in box 5 of Figure 12-1 is:A. a nucleotide.B. a protein.C. a hydrogen b<strong>on</strong>d.D. a pyrimidine.E. a phosphate.7
Name: ______________________ID: AFigure 13-3Use the figure to answer the corresp<strong>on</strong>ding questi<strong>on</strong>(s).________________28 The process illustrated in Figure 13-3 is:A. transcripti<strong>on</strong>.B. DNA synthesis.C. a frame shift mutati<strong>on</strong>.D. protein synthesis.E. translati<strong>on</strong>.29 The bacteriophages used in Alfred Hershey's and Martha Chase's experiments showed that:A. proteins were resp<strong>on</strong>sible for the producti<strong>on</strong> of new viruses within the bacteria.B. proteins were injected into bacteria.C. DNA was injected into bacteria.D. DNA and protein were injected into bacteria.E. DNA remained <strong>on</strong> the outer coat of bacteria.30 Substituti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>on</strong>e base pair for another can result in a __________ mutati<strong>on</strong> that results in thec<strong>on</strong>versi<strong>on</strong> of an amino acid specifying cod<strong>on</strong> to a terminati<strong>on</strong> cod<strong>on</strong>.A. n<strong>on</strong>senseB. chromosomalC. frameshiftD. missenseE. N<strong>on</strong>e of these.31 Feedback inhibiti<strong>on</strong> of the first enzyme of a pathway by the end product of the pathway is anexample of:A. posttranslati<strong>on</strong>al c<strong>on</strong>trol.B. inhibiting c<strong>on</strong>trol.C. translati<strong>on</strong>al c<strong>on</strong>trol.D. transcripti<strong>on</strong>al c<strong>on</strong>trol.E. repressi<strong>on</strong>.8
Name: ______________________ID: A________________________32 An inducible oper<strong>on</strong> is usually c<strong>on</strong>trolled by:A. an inducer molecule that keeps it in the "off" state.B. being active at all times.C. allolactose.D. being turned "off," usually by the end product of the pathway.E. an active repressor that keeps it in the "off" state.33 The ends of eukaryotic chromosomes can be lengthened by:A. DNA polymerase.B. primase.C. reverse transcriptase.D. apoptosis.E. telomerase.34 Interrupted coding sequences include l<strong>on</strong>g sequences of bases that do not code for amino acids.These n<strong>on</strong>coding sequences, called __________, are found in __________ cells.A. ex<strong>on</strong>s; eukaryoticB. intr<strong>on</strong>s; eukaryoticC. intr<strong>on</strong>s; prokaryoticD. ex<strong>on</strong>s; prokaryoticE. N<strong>on</strong>e of these.35 The gene that codes for the repressor protein of the E. coli lactose oper<strong>on</strong> is:A. turned off most of the time.B. downstream from the promoter regi<strong>on</strong>.C. downstream from the operator.D. located between the operator and the promoter.E. c<strong>on</strong>stitutive.36 Increasing the stability of a particular mRNA __________ the expressi<strong>on</strong> of that gene.A. does not affectB. increasesC. decreasesD. eliminatesE. N<strong>on</strong>e of these.37 Regulati<strong>on</strong> of gene expressi<strong>on</strong> can be accomplished by c<strong>on</strong>trolling:A. the rate of translati<strong>on</strong> of mRNA.B. the rate of mRNA degradati<strong>on</strong>.C. the activity of a protein product.D. the amount of mRNA that is available.E. All of these.9
Name: ______________________ID: A________________________38 Hydrogen b<strong>on</strong>ds can form between guanine and __________, and between adenine and__________.A. cytosine; thymineB. adenine; guanineC. thymine; cytosineD. phosphate; sugarE. sugar; phosphate39 Who first c<strong>on</strong>firmed that the replicati<strong>on</strong> of DNA was semic<strong>on</strong>servative?A. Avery and GriffithB. Wats<strong>on</strong>, Crick, and WilkinsC. Wats<strong>on</strong> and CrickD. Mesels<strong>on</strong> and StahlE. Chargaff and Hershey40 What prevents knot formati<strong>on</strong> in replicating DNA?A. chromatinB. scaffolding proteinsC. hist<strong>on</strong>esD. topoisomerasesE. protosomes41 An mRNA "5′ cap":A. prevents translati<strong>on</strong>.B. marks the mRNA for degradati<strong>on</strong>.C. facilitates binding of ribosomes.D. protects newly synthesized mRNA from degradati<strong>on</strong>.E. decreases the half-life of the mRNA.42 Two chains of DNA must run in __________ directi<strong>on</strong>(s) and must be __________ if they are tob<strong>on</strong>d with each other.A. parallel; complementaryB. antiparallel; complementaryC. parallel; uncomplementaryD. opposite; uncomplementaryE. the same; uncomplementary43 Transformati<strong>on</strong> is a process whereby:A. plasmids are transferred into viral cells.B. plasmids are transferred into bacterial cells.C. bacteria are transferred into viral cells.D. bacteria are transferred into plasmid cells.E. viruses are transferred into bacterial cells.10
Name: ______________________ID: A________________________44 DNA sequences that are methylated by a cell are usually genes that:A. are inactive.B. are repressed.C. are actively expressed.D. have been replicatedE. are c<strong>on</strong>stitutive.45 __________, the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, shorten with every cell replicati<strong>on</strong> event.A. NucleosomesB. CentromeresC. TelomeresD. PrimosomesE. Kinetochores46 Frameshift mutati<strong>on</strong>s result from:A. the substituti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>on</strong>e base pair for another.B. the substituti<strong>on</strong> of a start cod<strong>on</strong> for an amino acid cod<strong>on</strong>.C. the substituti<strong>on</strong> of a stop cod<strong>on</strong> for an amino acid-specifying cod<strong>on</strong>.D. the inserti<strong>on</strong> or deleti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>on</strong>e or two base pairs.E. the substituti<strong>on</strong> of more than <strong>on</strong>e base pair.47 A mutati<strong>on</strong> that replaces <strong>on</strong>e amino acid in a protein with another is called a __________ mutati<strong>on</strong>.A. missenseB. neutralC. frameshiftD. recombinantE. n<strong>on</strong>sense48 Which of the following cause the unwinding of the DNA double helix?A. RNA primerB. DNA polymeraseC. DNA helicaseD. RNA polymeraseE. primosome49 In the experiments of Griffith, the c<strong>on</strong>versi<strong>on</strong> of n<strong>on</strong>lethal R-strain bacteria to lethal S-strainbacteria:A. could not be reproduced by other researchers.B. was the result of genetic mutati<strong>on</strong>.C. was an example of c<strong>on</strong>jugati<strong>on</strong>.D. supported the case for proteins as the genetic material.E. was an example of the genetic exchange known as transformati<strong>on</strong>.11
Name: ______________________ID: A________________________50 In all organisms, the AUG cod<strong>on</strong> codes for:A. the initiati<strong>on</strong> of translati<strong>on</strong>.B. the terminati<strong>on</strong> of transcripti<strong>on</strong>.C. a terminati<strong>on</strong> tRNA molecule.D. the terminati<strong>on</strong> of chain el<strong>on</strong>gati<strong>on</strong>.E. the amino acid valine.51 One of the mRNA cod<strong>on</strong>s specifying the amino acid leucine is 5′-CUA-3′. Its corresp<strong>on</strong>dinganticod<strong>on</strong> is:A. 5′-GAU-3′.B. 3′-AUC-5′.C. 5′-GAT-3′.D. 3′-GAU-5′.E. 3′-GAT-5′.52 How does the lactose repressor block transcripti<strong>on</strong> of the lactose oper<strong>on</strong>?A. by slowing the uptake of lactose into the cellB. by "turning off" the appropriate genes in the intr<strong>on</strong>C. by binding allosterically to the appropriate genesD. by regulating the activity of the enzymes that the oper<strong>on</strong> codes forE. by binding to the operator53 Cancer cells differ from n<strong>on</strong>cancerous cells in that:A. they have the ability to resist apoptosis.B. they have elevated levels of telomerase.C. they are virtually immortal.D. they can maintain telomere length as they divide.E. All of these.54 Which of the following statements about DNA is false?A. DNA is <strong>on</strong>ly found in eukaryotic cells.B. DNA is capable of forming many different sequences.C. DNA c<strong>on</strong>tains the sugar deoxyribose.D. DNA is double-stranded rather than single-stranded.E. DNA c<strong>on</strong>tains thymine instead of uracil.55 Which of the following types of processing does eukaryotic mRNA undergo before it becomesfuncti<strong>on</strong>al?A. removal of intr<strong>on</strong>sB. polyadenylati<strong>on</strong>C. cappingD. splicingE. All of these.12
Name: ______________________ID: A________________________56 Which of the following adds new nucleotides to a growing DNA chain?A. DNA polymeraseB. RNA primerC. primaseD. RNA polymeraseE. DNA helicase57 The informati<strong>on</strong> carried by DNA is incorporated in a code specified by the:A. number of bases in a DNA strand.B. number of separate strands of DNA.C. size of a particular chromosome.D. phosphodiester b<strong>on</strong>ds of the DNA strand.E. specific nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule.58 A gene can now be defined as:A. a DNA nucleotide sequence that carries informati<strong>on</strong> to produce an enzyme.B. a DNA or RNA sequence that carries informati<strong>on</strong> to produce a specific polypeptide.C. a DNA or RNA sequence that carries informati<strong>on</strong> to produce a single polypeptide.D. a DNA sequence that carries informati<strong>on</strong> to produce a specific RNA or proteinproduct.E. a DNA nucleotide sequence that carries informati<strong>on</strong> to produce a specificpolypeptide.59 Bacterial gene regulati<strong>on</strong> occurs mainly at the __________ level.A. transcripti<strong>on</strong>alB. feedback inhibiti<strong>on</strong>C. posttranscripti<strong>on</strong>alD. translati<strong>on</strong>alE. posttranslati<strong>on</strong>al60 A cell may meet the need for large quantities of a specific protein by:A. having multiple copies of the gene that codes for that protein.B. c<strong>on</strong>tinuously synthesizing the mRNA molecule that specifies that protein.C. increasing the half-life of the mRNA that specifies the protein.D. All of these.E. N<strong>on</strong>e of these.61 Which of the following nucleotide sequences represents the complement to the DNA strand5′ − AGATCCG- 3′?A. 5′ − AGATCCG- 3′B. 3′ − CTCGAAT- 5′C. 5′ − CTCGAAT- 3′D. 3′ − AGATCCG- 5′E. 3′ − TCTAGGC- 5′13
Name: ______________________ID: A____________62 Primase is the enzyme resp<strong>on</strong>sible for:A. introducing nicks into the DNA double strand in order to prevent the formati<strong>on</strong> ofknots.B. hydrolyzing ATP to facilitate DNA unwinding.C. forming a replicati<strong>on</strong> fork in the DNA double helix.D. unwinding the DNA double strand to allow DNA polymerase access to thetemplate DNA.E. making short strands of RNA at the site of replicati<strong>on</strong> initiati<strong>on</strong>.63 Repressible genes are usually actively transcribed when:A. quantities of precursor materials are high.B. the supply of the end product formed by the enzymes encoded by these genes islow.C. tryptophan accumulates in the cell.D. repressor molecules bind to the promoter.E. there is no other substrate that can be used by the cell.64 Which of the following serves as an "adapter" in protein synthesis and bridges the gap betweenmRNA and proteins?A. promoter sequencesB. DNAC. tRNAD. rRNAE. cDNA14
ID: ADNA and Gene Expressi<strong>on</strong> (chaps 12-14)Answer Secti<strong>on</strong>MULTIPLE CHOICE1 ANS: E2 ANS: D3 ANS: E4 ANS: E5 ANS: B6 ANS: B7 ANS: E8 ANS: A9 ANS: B10 ANS: D11 ANS: D12 ANS: A13 ANS: D14 ANS: C15 ANS: A16 ANS: D17 ANS: A18 ANS: D19 ANS: B20 ANS: C21 ANS: C22 ANS: D23 ANS: C24 ANS: E25 ANS: A26 ANS: D27 ANS: E28 ANS: A1
ID: A29 ANS: C30 ANS: A31 ANS: A32 ANS: E33 ANS: E34 ANS: B35 ANS: E36 ANS: B37 ANS: E38 ANS: A39 ANS: D40 ANS: D41 ANS: D42 ANS: B43 ANS: B44 ANS: A45 ANS: C46 ANS: D47 ANS: A48 ANS: C49 ANS: E50 ANS: A51 ANS: D52 ANS: E53 ANS: E54 ANS: A55 ANS: E56 ANS: A57 ANS: E58 ANS: D59 ANS: A60 ANS: D2
ID: A61 ANS: E62 ANS: E63 ANS: B64 ANS: CESSAY65 ANS:answers will vary3