Ensembl Compara - CNB - Protein Design Group
Ensembl Compara - CNB - Protein Design Group
Ensembl Compara - CNB - Protein Design Group
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Timeline 2 : Genomes9/01 Release with Mouse genome (gp)2/03 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 10 (Fugu, worm, fly, Anopheles, briggsae; 1stmajor schema/API rewrite)11/03 First <strong>Ensembl</strong> SAB1/04 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 20 (2nd major schema/API rewrite)12/04 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 27 (Variation schema/API rewrite)2/05 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 28 (archive sites, bioMart replaces Mart)7/05 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 32 (website redesign)10/05 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 34 (multiple genome alignment data/AlignSliceAPI)10/05 WT Funding approved (WTSI + <strong>Ensembl</strong>) until 201112/05 Switch from monthly to bimonthly cycle2/06 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 37 (mouse SNPs, transcriptSNPview)4/06 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 38 (Combined Havana<strong>Ensembl</strong> Humangeneset)12/06 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 42 (Platypus!)4/07 <strong>Ensembl</strong> 44 (37 species, more than 500 Gb behind thewebsite)Jul 2007 T. Hubbard
<strong>Ensembl</strong>: What do you get?Jul 2007Genome Annotation– <strong>Protein</strong> coding gene structureConsistent with genome, predicted across all vertebratesManual annotations (human, mouse, zebrafish, MHC)– RNA genes (including miRNA)• Consistent with genome, predicted in across mammalsAdditional identifiers per genesAffymetrix, EntrezGene, Uniprot…• <strong>Compara</strong>tive & Functional GenomicsGenome alignmentsBlastz, Blat, coordinated with UCSC– Homologues between genomes– <strong>Protein</strong> treesVariants (SNPs), strains, genotypesTiling array data• Infrastructure– Website, Data mining tool, database and data dump– Portable, extendable, open source system with database, API, website,pipeline
<strong>Ensembl</strong> groupsJul 2007GeneBuilders: sequence masking, gene buildingCore: database schema, stable id mapping<strong>Compara</strong>: protein homology, genomic sequencealignmentsFunctional Genomics: SNPs, probe mapping,functional dataMart: martification of the previous data for dataminingWeb: web site, new views for new dataUser support: help, workshops, tutorialsMore people: Research, DAS, VectorBase, Zebrafish,Systems...
*<strong>Ensembl</strong> release cyclegenebuilder (10+3+4)~ 3 monthscore (4)compara (6)functional genomics (5)mart (4)web (7)release!!1 release coordinator+ 1 assistantJul 2007
BilateriaNCBI Taxonomy for the 31species in <strong>Ensembl</strong> 43ChordatesAmniotesTetrapodsMammalsEutherianPrimatesGliresCarnivoraHomo sapiensPan troglodytesMacaca mulattaRattus norvegicusMus musculusCavia porcellusOryctolagus cuniculusTupaia belangeriBos taurusErinaceus europaeusFelis catusCanis familiarisLoxodonta africanaEchinops telfairiDasypus novemcinctusMonodelphis domesticaOrnithorhynchus anatinusGallus gallusXenopus tropicalisDanio rerioTakifugu rubripesTetraodon nigroviridisGasterosteus aculeatusOryzias latipesCiona intestinalisCiona savignyiAedes aegyptiAnopheles gambiaeDrosophila melanogasterCaenorhabditis elegansSaccharomyces cerevisiaeJul 2007
Genomes: the futureAnother 28 mammals being sequencedMain driver is evolution, but perhapsopening up biology• New technology sequencing454 currently about 5 fold cheaperSolexa currently about 100 foldcheaperJul 2007
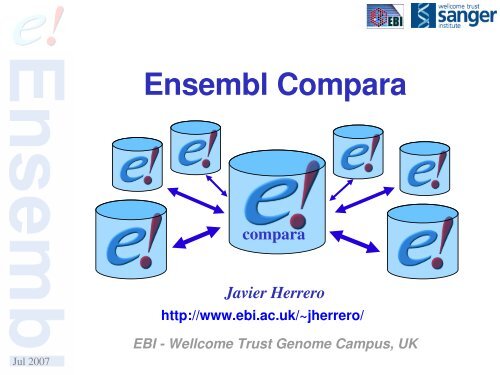
<strong>Ensembl</strong> <strong>Compara</strong>A single database which contains precalculatedcomparative genomics data and which is linked toall the <strong>Ensembl</strong> Species databases.Access via web interface, perl API and mysqlA production system for generating that databaseJul 2007
<strong>Compara</strong> dataRaw genomic sequenceWhole genome alignments(tBLAT, BlastZnet, PECAN)Syntenic regions (based on BlastZnet)<strong>Protein</strong> sequence Raw protein alignments (wublastp) <strong>Protein</strong> Family clusters <strong>Protein</strong> trees (since Jun 2006 v39) Gene orthology / paralogy predictionsJul 2007
Genomic AlignmentsBlastZNetused to compare closely related pair of speciesBlastZraw > BlastZchain > BlastZnetJul 2007Translated BLAT used to compare more distant pair of speciesPecanmultiple global alignments all vs all coding exons wublastp > Mercator >Pecan on each syntenic block
Global vs. Local AlignmentsGlobalLocalinversionduplication1 21 2()LocalAdvantagesFor large genomic regionsCan identify inversionsDisadvantagesFails to identify insertions ordeletionsGlobalCan detect insertions ordeletionsFails to detect inversionsJul 2007
Pecana consistency based multiplealignment programATGGGCTTTTGCATTTG}ATGGGCAGCATTTGACGGGCATTTGCTTCTGATGGGCTTTTGCATTTGATGGGCAGCATTTGvsATGGGCTTTTGCATTTGATGGGCAGCATTTGATGGGCTTTTGCATTTGACGGGCATTTGCTTCTGJul 2007ATGGGCAGCATTTGACGGGCATTTGCTTCTGTakes into account all pairwisealignments, across the entire treeATGGGCTTTTGCATTTGATGGGCAGCATTTGACGGGCATTTGCTTCTG
Pecan optimizationscut-lineLook for anchors (exonerate)perform a banded alignmentBreakup alignments intofragmentsMuch redundancy betweenpairwise alignments: usetransitive anchorsBhiddencut-pointACABJul 2007C
Encode ComparisonSPECIFICITYCOVERAGEJul 2007
Jul 2007Example of AlignSliceView betweenHuman/Mouse/Rat/Dog with PECAN
How to align suchlarge segments?New challengesHow to deal withduplications?Jul 2007How to predictancestralgenomes?
EnredoAnchors500.000 anchorsfor mammalsmorethan 1 anchorper 10KbJul 2007
EnredoSolving the graphJul 2007Common paths definecolinear regionsThis process allows for mismatches in the paths
Jul 2007ORTHEUSan ancestral sequence inference programAddresses the inference of insertiondeletion historiesand substitution eventsStarts from a (multiple) alignment and assumes afixed treeReconstructs the ancestral sequences in the tree andrefines the input alignmentInsertion/deletion events are handled using a branchtransducer modelSubstitution are handled using TamuraNeinucleotide substitution modelAncestral sequence are inferred using weightedsequence graph
ORTHEUSBranch Transducer ModelFour transition parameters model:Insertion(cont.)Applied to a tree:Deletion(cont.)InsertionDeletionJul 2007Matches and insertion/deletion eventsare propagated down the tree
<strong>Protein</strong> Homology (e! 38):Orthologue predictions based on ‘best reciprocalblast hits’ and ‘synteny extensions’Young paralogues for a selected set of species e! 39+:orthologues and paralogues are inferred fromprotein treesJul 2007
HomologyBRH/RHS pairs of species (n*(n1)/2)Cases of fast evolving genesGlobal view of the evolution history of the gene considered✔Phylogeny: Orthology/Paralogy in one goJul 2007
Load Genes and LongestTranslation from all species in<strong>Ensembl</strong>. 25 species in v40hoursWU Blastp + SmithWaterman longesttranslation of every Gene against everyother in a genomewise mannerhours/daysBuild a graph of gene relationsbased on BRH 1 and BSR 2Extract the connected components(= single linkage clusters)23 days 1CPUFor each cluster, build a multiplealignment (MUSCLE) based on theprotein sequenceshoursFrom each alignment, build a genetree (PHYML)hours/daysReconcile each gene tree with thespecies tree to call duplicationevent on internal nodes (RAP)hoursInference of orthologs and paralogs(OrthoTree)hoursJul 2007BSR: Blast Score Ratio. When 2 proteins P1 and P2 are compared,BSR=scoreP1P2/max(selfscoreP1 or selfscoreP2). The default threshold usedin the initial clustering step is 0.33.
Load Genes and LongestTranslation from all species in<strong>Ensembl</strong>. 26 species in v41hoursWU Blastp + SmithWaterman longesttranslation of every Gene against everyother in a genomewise mannerhours/daysBuild a graph of gene relationsbased on BRH 1 and BSR 2Extract the connected components(= single linkage clusters)23 days 1CPUFor each cluster, build a multiplealignment (MUSCLE) based on theprotein sequenceshoursmultifurcated species treeReconcile each gene tree with thespecies tree to call duplicationevent on internal nodes (RAP)hoursv41From each alignment, build a genetree (PHYML)hours/daysInference of orthologs and paralogs(OrthoTree)hoursJul 2007BSR: Blast Score Ratio. When 2 proteins P1 and P2 are compared,BSR=scoreP1P2/max(selfscoreP1 or selfscoreP2). The default threshold usedin the initial clustering step is 0.33.
Load Genes and LongestTranslation from all species in<strong>Ensembl</strong>. 31? species in v42WU Blastp + SmithWaterman longesttranslation of every Gene against everyother in a genomewise mannerBuild a graph of gene relationsbased on BRH 1 and BSR 2Extract the connected components(= single linkage clusters)For each cluster, build a multiplealignment (MUSCLE) based on theprotein sequencesInference of orthologs and paralogs(OrthoTree)From each alignment, build a geneand reconcile with the species treeto call duplication events oninternal nodes (NJTREE_PHYML)v42Jul 2007BSR: Blast Score Ratio. When 2 proteins P1 and P2 are compared,BSR=scoreP1P2/max(selfscoreP1 or selfscoreP2). The default threshold usedin the initial clustering step is 0.33.
<strong>Protein</strong> trees and homologyDuplication nodeSpeciation nodeH1M1H2ortholog_one2oneH1:M1between_species_paralogM1:H2EuarchontogliresH2’M2M2’within_species_paralogH2:H2’ Homo sapiensortholog_many2manyH2:M2, H2:M2’,H2’:M2, H2’:M2’within_species_paralogM2:M2’ Mus musculusH3M3ortholog_one2manyH3:M3, H3:M3’within_species_paralogM2’:M3’ EuarchontogliresM3’Jul 2007Orthologues : any gene pairwise relation where the ancestor node is a SPECIATION event.Paralogues : any gene pairwise relation where the ancestor node is a DUPLICATION event.
A special case of homologyDuplication nodeSpeciation nodeMortholog_one2oneH:Mgene lossR’HH’gene lossgene lossM’apparent_ortholog_one2oneM:R, H:RRJul 2007Orthologues : any gene pairwise relation where the ancestor node is a SPECIATION event.Paralogues : any gene pairwise relation where the ancestor node is a DUPLICATION event.
Gene tree : 1st data assessmentGood concordance with the classical BRH/RHS pairedspecies approach (RHS are based on gene order conservation)Find more complex onetomany and manytomany relationsHuman/MouseHuman/DrosophilaRHSBRHNEWBRHNEWmany2many1771131,439many2many1701,599one2manyone2one7252051,30910,7362,81510919,381one2manyone2one1,8708804,5638011,443apparent one2one781,571104apparent one2one2,040241lost2,0272,060lost620Future plans: convergence with TreeFamJul 2007
FamilyGene family clustering predictionsRuns on all <strong>Ensembl</strong> transcripts plus allUniprot/SWISSPROT and Uniprot/SPTREMBLmetazoan proteinsAlgorithm is based on all vs all blastp, MCLclustering, Muscle multiple alignerJul 2007
Jul 2007