Hypothesis Testing Using z- and t-tests In hypothesis testing, one ...
Hypothesis Testing Using z- and t-tests In hypothesis testing, one ...
Hypothesis Testing Using z- and t-tests In hypothesis testing, one ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
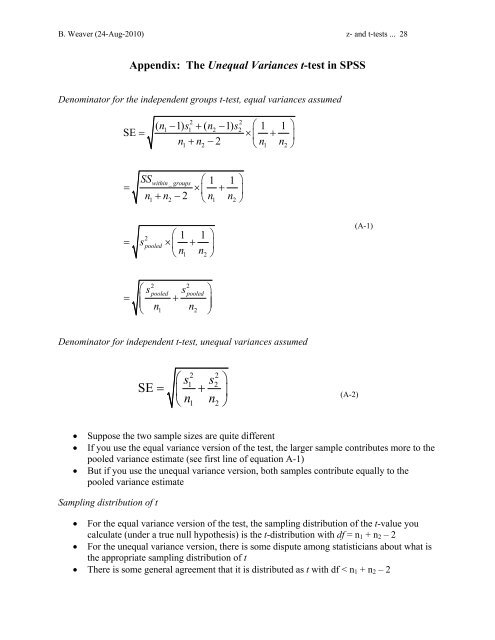
B. Weaver (24-Aug-2010) z- <strong>and</strong> t-<strong>tests</strong> ... 28Appendix: The Unequal Variances t-test in SPSSDenominator for the independent groups t-test, equal variances assumed2 2( n1− 1) s1 + ( n2 −1) s ⎛21 1 ⎞SE = × ⎜ + ⎟n1+ n2 −2⎝n1 n2⎠SS ⎛ 1 1 ⎞⎜ ⎟n1+ n2 −2⎝n1 n2⎠within _ groups= × +2⎛ 1 1 ⎞= spooled× ⎜ + ⎟⎝n1 n2⎠(A-1)⎛ss= +⎜⎝ n n2 2pooled pooled1 2⎞⎟⎠Denominator for independent t-test, unequal variances assumedSE⎛ss= ⎜ +⎝ n n2 21 21 2⎞⎟⎠(A-2)• Suppose the two sample sizes are quite different• If you use the equal variance version of the test, the larger sample contributes more to thepooled variance estimate (see first line of equation A-1)• But if you use the unequal variance version, both samples contribute equally to thepooled variance estimateSampling distribution of t• For the equal variance version of the test, the sampling distribution of the t-value youcalculate (under a true null <strong>hypothesis</strong>) is the t-distribution with df = n 1 + n 2 – 2• For the unequal variance version, there is some dispute among statisticians about what isthe appropriate sampling distribution of t• There is some general agreement that it is distributed as t with df < n 1 + n 2 – 2