- Page 2 and 3: ISBN:0-8247-0491-6 This book is pri
- Page 4 and 5: iv Preface biodegrade rapidly and h
- Page 7 and 8: Contents Preface iii Contributors i
- Page 9 and 10: Contributors Shoaib Arif Home Care,
- Page 11 and 12: 1 Alkyl Polyglycosides KARL SCHMID
- Page 13 and 14: FIG. 2 Summary of methods for the s
- Page 15 and 16: Alkyl Polyglycosides 5 kernel oil f
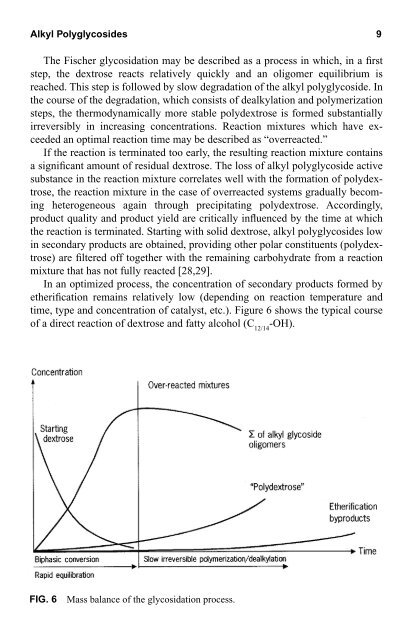
- Page 17: Alkyl Polyglycosides 7 synthesis an
- Page 21 and 22: Alkyl Polyglycosides 11 In case of
- Page 23 and 24: Alkyl Polyglycosides 13 TABLE 1 Com
- Page 25 and 26: Alkyl Polyglycosides 15 dencies, nu
- Page 27 and 28: Alkyl Polyglycosides 17 FIG. 13 Pha
- Page 29 and 30: Alkyl Polyglycosides 19 is at its l
- Page 31 and 32: Alkyl Polyglycosides 21 The lamella
- Page 33 and 34: FIG. 17 Dishwashing performance of
- Page 35 and 36: FIG. 19 Dishwashing performance of
- Page 37 and 38: Alkyl Polyglycosides 27 FIG. 22 Muc
- Page 39 and 40: Alkyl Polyglycosides 29 FIG. 23 Dis
- Page 41 and 42: Alkyl Polyglycosides 31 polyglycosi
- Page 43 and 44: Alkyl Polyglycosides 33 ing deterge
- Page 45 and 46: Alkyl Polyglycosides 35 TABLE 6 C 1
- Page 47 and 48: Alkyl Polyglycosides 37 FIG. 28 Per
- Page 49 and 50: Alkyl Polyglycosides 39 1. All-Purp
- Page 51 and 52: Alkyl Polyglycosides 41 FIG. 29 Cle
- Page 53 and 54: Alkyl Polyglycosides 43 TABLE 13 Ge
- Page 55 and 56: Alkyl Polyglycosides 45 alkyl chain
- Page 57 and 58: Alkyl Polyglycosides 47 FIG. 35 Inc
- Page 59 and 60: Alkyl Polyglycosides 49 sides in a
- Page 61 and 62: Alkyl Polyglycosides 51 alkyl polyg
- Page 63 and 64: Alkyl Polyglycosides 53 Of greater
- Page 65 and 66: Alkyl Polyglycosides 55 FIG. 43 Inc
- Page 67 and 68: Alkyl Polyglycosides 57 parting imp
- Page 69 and 70:
Alkyl Polyglycosides 59 move scales
- Page 71 and 72:
Alkyl Polyglycosides 61 the skin is
- Page 73 and 74:
Alkyl Polyglycosides 63 TABLE 20 Al
- Page 75 and 76:
Alkyl Polyglycosides 65 FIG. 45 Bio
- Page 77 and 78:
Alkyl Polyglycosides 67 34. N Busch
- Page 79:
Alkyl Polyglycosides 69 100. Henkel
- Page 82 and 83:
72 Arif and Friedli esters as worka
- Page 84 and 85:
74 Arif and Friedli FIG. 3 CMC of C
- Page 86 and 87:
76 Arif and Friedli TABLE 1 Deterge
- Page 88 and 89:
78 Arif and Friedli TABLE 3 Effect
- Page 90 and 91:
80 Arif and Friedli TABLE 6 Correla
- Page 92 and 93:
82 Arif and Friedli TABLE 9 Dye Tra
- Page 94 and 95:
84 Arif and Friedli TABLE 15 Fine-F
- Page 96 and 97:
86 Arif and Friedli The monoethanol
- Page 98 and 99:
88 Arif and Friedli TABLE 20 Averag
- Page 100 and 101:
90 Arif and Friedli TABLE 26 Heavy-
- Page 102 and 103:
92 Arif and Friedli FIG. 8 Synthesi
- Page 104 and 105:
94 Arif and Friedli Amphoterics/bet
- Page 106 and 107:
96 Arif and Friedli TABLE 32 Laundr
- Page 108 and 109:
98 Arif and Friedli TABLE 38 Base B
- Page 110 and 111:
100 Arif and Friedli alkaline produ
- Page 112 and 113:
102 Arif and Friedli TABLE 50 Tub a
- Page 114 and 115:
104 Arif and Friedli TABLE 55 Glass
- Page 116 and 117:
106 Arif and Friedli well for thick
- Page 118 and 119:
108 Arif and Friedli FIG. 12 Amine
- Page 120 and 121:
110 Arif and Friedli TABLE 65 Dye T
- Page 122 and 123:
112 Arif and Friedli FIG. 13 Specia
- Page 124 and 125:
114 Arif and Friedli complete biode
- Page 127 and 128:
3 Sulfonated Methyl Esters TERRI GE
- Page 129 and 130:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 119 SMEs m
- Page 131 and 132:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 121 Kamesh
- Page 133 and 134:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 123 FIG. 5
- Page 135 and 136:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 125 FIG. 8
- Page 137 and 138:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 127 FIG. 1
- Page 139 and 140:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 129 TABLE
- Page 141 and 142:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 131 soft w
- Page 143 and 144:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 133 cotton
- Page 145 and 146:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 135 factan
- Page 147 and 148:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 137 FIG. 1
- Page 149 and 150:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 139 ethoxy
- Page 151 and 152:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 141 FIG. 1
- Page 153:
Sulfonated Methyl Esters 143 35. Pr
- Page 156 and 157:
146 Quencer and Loughney Traditiona
- Page 158 and 159:
148 Quencer and Loughney FIG. 2 Pro
- Page 160 and 161:
150 Quencer and Loughney FIG. 3 Com
- Page 162 and 163:
152 Quencer and Loughney A phase in
- Page 164 and 165:
154 Quencer and Loughney from hydro
- Page 166 and 167:
156 Quencer and Loughney FIG. 8 Mod
- Page 168 and 169:
158 Quencer and Loughney Subsequent
- Page 170 and 171:
160 Quencer and Loughney IV. ENVIRO
- Page 172 and 173:
162 Quencer and Loughney FIG. 12 Pr
- Page 174 and 175:
164 Quencer and Loughney ACKNOWLEDG
- Page 177 and 178:
5 Methyl Ester Ethoxylates MICHAEL
- Page 179 and 180:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 169 duces
- Page 181 and 182:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 171 B C
- Page 183 and 184:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 173 FIG. 4
- Page 185 and 186:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 175 FIG. 5
- Page 187 and 188:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 177 cohol
- Page 189 and 190:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 179 FIG. 8
- Page 191 and 192:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 181 FIG. 1
- Page 193 and 194:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 183 ably d
- Page 195 and 196:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 185 TABLE
- Page 197 and 198:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 187 B. C 1
- Page 199 and 200:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 189 FIG. 1
- Page 201 and 202:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 191 FIG. 2
- Page 203:
Methyl Ester Ethoxylates 193 19. Y
- Page 206 and 207:
196 Crudden and complexing agent. T
- Page 208 and 209:
198 Crudden FIG. 2 Titration of LED
- Page 210 and 211:
200 Crudden FIG. 3 Surface tension
- Page 212 and 213:
202 Crudden FIG. 5 Lather drainage
- Page 214 and 215:
204 Crudden FIG. 7 Calcium chelatio
- Page 216 and 217:
206 Crudden FIG. 10 Influence of co
- Page 218 and 219:
208 Crudden FIG. 12 Draves Wetting
- Page 220 and 221:
210 Crudden Percent Hydrotrope (to
- Page 222 and 223:
212 Crudden TABLE 4 Brightness Gain
- Page 224 and 225:
214 Crudden weight loss % 90 80 70
- Page 226 and 227:
216 Crudden 1. Dermal Irritation Na
- Page 228 and 229:
218 Crudden The results indicate th
- Page 231 and 232:
7 Surfactants for the Prewash Marke
- Page 233 and 234:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 235 and 236:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 237 and 238:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 239 and 240:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 241 and 242:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 243 and 244:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 245 and 246:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 247 and 248:
Surfactants for the Prewash Market
- Page 249 and 250:
8 Dry Cleaning Surfactants AL DABES
- Page 251 and 252:
Dry Cleaning Surfactants 241 blend
- Page 253 and 254:
Dry Cleaning Surfactants 243 Progre
- Page 255 and 256:
Dry Cleaning Surfactants 245 3. Pet
- Page 257 and 258:
Dry Cleaning Surfactants 247 with l
- Page 259 and 260:
Dry Cleaning Surfactants 249 Format
- Page 261 and 262:
Dry Cleaning Surfactants 251 equili
- Page 263 and 264:
Dry Cleaning Surfactants 253 black
- Page 265 and 266:
9 Concentrated and Efficient Fabric
- Page 267 and 268:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 269 and 270:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 271 and 272:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 273 and 274:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 275 and 276:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 277 and 278:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 279 and 280:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 281 and 282:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 283 and 284:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 285 and 286:
(a) (b) Concentrated and Efficient
- Page 287 and 288:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 289 and 290:
Concentrated and Efficient Fabric S
- Page 291 and 292:
Index Acid cleaners, 104-107, 136 A
- Page 293 and 294:
Index 283 Hair conditioner, 255 Har