You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
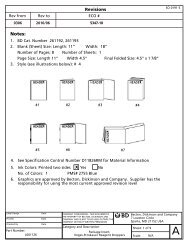
EXAMPLE:<br />
Calculating Laurie’s Correction Dose<br />
• Laurie’s ISF is 1 unit of rapid or short<br />
acting insulin for every 50 mg/dl of<br />
blood glucose.<br />
• Her target pre-meal blood glucose is<br />
100 mg/dl, but her pre-dinner blood<br />
glucose reading is 250 mg/dl.<br />
• She is 150 mg/dl over her target level.<br />
Current blood glucose – target blood<br />
glucose = amount of glucose over target<br />
[250 mg/dl – 100 mg/dl = 150 mg/dl]<br />
• Using Laurie’s ISF, she would divide<br />
150 mg/dl by 50 to find that she<br />
would need to add an extra 3 units<br />
of rapid or short acting insulin to her<br />
meal-time dose to correct the blood<br />
glucose to 100 mg/dl.<br />
Amount of glucose<br />
over target<br />
ISF<br />
[ 150 = 3<br />
50 ]<br />
= correction dose<br />
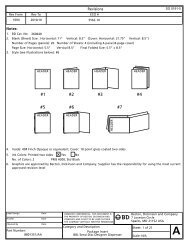
If Laurie’s pre-dinner blood glucose was<br />
75, she would reduce her insulin dose in<br />
the same manner as outlined above.<br />
• Her target pre-meal blood glucose is<br />
100 mg/dl, but her pre-dinner blood<br />
glucose reading is 75 mg/dl.<br />
• She is 25 mg/dl below her target level.<br />
Current blood glucose – target blood<br />
glucose = amount of glucose over target<br />
[75 mg/dl – 100 mg/dl = -25 mg/dl]<br />
• Using Laurie’s ISF, she would divide<br />
25 mg/dl by 50 to find that she would<br />
need to subtract 0.5 units of rapid or<br />
short acting insulin to her meal-time<br />
dose to correct the blood glucose to<br />
100 mg/dl.<br />
Amount of glucose<br />
= correction dose<br />
over target<br />
ISF<br />
[ -25 = -0.5 units<br />
50 ]<br />
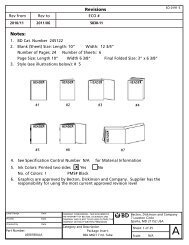
Peak Action – The time when insulin<br />
is working the hardest to bring blood<br />
glucose down. It is essential to know<br />
when your insulin peaks so that you can<br />
prepare for possible low glucose levels at<br />
these peak times. Types of insulin with<br />
peak action times are:<br />
Name of Type of Peak Action<br />
<strong>Insulin</strong> <strong>Insulin</strong><br />
Humalog ® , Rapid 30 min. to<br />
Novolog ® , 1 1/2 hours<br />
Apidra ®<br />
Lantus ® Long No peak action<br />
*Regular Short 2 to 4 hours<br />
*UltraLente ® Long 8 to 30 hours<br />
*NPH Intermediate 4 to 12 hours<br />
*Lente ® Intermediate 7 to 15 hours<br />
*Not commonly used in Flexible <strong>Insulin</strong> Therapy<br />
8