Alloy Performance Guide - Rolled Alloys
Alloy Performance Guide - Rolled Alloys
Alloy Performance Guide - Rolled Alloys
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
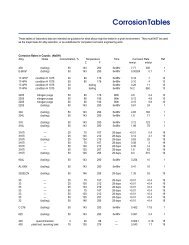
People. Service. Expertise. Inventory.Pitting and CreviceCorrosionPitting and crevice corrosion are most often caused by chlorides. Molybdenum is the alloying element that primarilyprovides resistance. Nitrogen enhances the effect of molybdenum. A measure of resistance to pitting corrosionis the Critical Pitting Temperature, or CPT, which is the highest temperature at which an alloy resists pitting ina given environment. Likewise crevice corrosion resistance may be quantified as the Critical Crevice CorrosionTemperature, CCCT. It is crevice corrosion, which is the limiting factor in service. AL-6XN, ZERON 100 and 625have sufficient resistance to be a practical choice for hot seawater. The lower molybdenum grades, even 2205, areusually unsuitable for use in seawater. For the highest level of localized corrosion resistance alloys C-276, C22 orINCONEL ® 686 should be considered.Crevice Corrosion andPitting Resistance<strong>Alloy</strong> % Mo CCCT, °F CPT, °F PRE N316L 2.1 < 28 68 24LDX 2101 0.3 < 28 68 26317L 3.2 35 94 29317LMN 4.4 68 – 332205 3.1 68 120 35904L 4.4 75 130 36ZERON 100 3.5 108 180 41AL-6XN <strong>Alloy</strong> 6.2 110 172 44<strong>Alloy</strong>s 625 9.0 113 – 51C22 13 – – 64C-276 15.5 130 > 217 67CCCT - 10% FeCl 3 • 6H 2 O, per ASTM G 48 Practice B, CPT - 1 M NaCl, per ASTM G 150, PRE N = Cr + 3.3 Mo + 16NStress CorrosionCrackingStress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the mode of failure for a significant percentage of 304L and 316L stainlesschemical process equipment. For SCC to occur in stainless steels three general conditions must be met: there is asource of tensile stress, temperatures must be above 120°F, and aqueous chlorides must be present. The sourceof tensile stress is usually a combination of residual forming and welding stresses. Chlorides concentrate from traceamounts present in the cooling water and/or from the product itself. If chlorides cannot be eliminated, or preventedfrom concentrating, an alloy change may be considered.A cost - effective choice is a duplex stainless such as LDX 2101, 2205 or ZERON 100. These grades may handlemany of the environments, which crack 316L over a few years time. More severe, or low pH, environments requirehigher nickel grades such as AL-6XN, Allloy 20, ZERON 100 or 625. <strong>Alloy</strong>s with 45% or more nickel are consideredpractically immune to chloride SCC.13<strong>Rolled</strong> <strong>Alloy</strong>s



![RA333 Data Sheet [Heat Resistant Alloys] - Rolled Alloys](https://img.yumpu.com/50335849/1/190x245/ra333-data-sheet-heat-resistant-alloys-rolled-alloys.jpg?quality=85)