Inhibition of Contractile Vacuole Function by ... - Universität zu Köln
Inhibition of Contractile Vacuole Function by ... - Universität zu Köln
Inhibition of Contractile Vacuole Function by ... - Universität zu Köln
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
202<br />
(Nakayama et al. 1998, Chapman and Waters 2002). The flagella<br />
are covered <strong>by</strong> three different types <strong>of</strong> non-mineralized<br />
scales referred to as pentagonal, man (double, rod-shaped) and<br />
hair scales based on their shapes as revealed <strong>by</strong> scanning electron<br />
microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy<br />
(TEM) (Melkonian and Preisig 1986, Becker et al. 1990). The<br />
cell body is covered <strong>by</strong> a cell wall derived ontogenetically from<br />
scales which coalesce extracellularly to form a cell wall called<br />
a theca (McFadden et al. 1986, Melkonian and Preisig 1986).<br />
Scales consist mainly <strong>of</strong> carbohydrates (Becker et al. 1991) and<br />
are synthesized in the Golgi complex (Melkonian et al. 1991,<br />
Becker et al. 1994). In vivo, the biogenesis <strong>of</strong> scales is<br />
restricted to cell division. However, biogenesis <strong>of</strong> flagellar<br />
scales can be induced <strong>by</strong> experimental amputation <strong>of</strong> the flagella.<br />
Upon deflagellation, cells regenerate new flagella including<br />
their scaly covering. Using this experimental system, the<br />
anterograde transport <strong>of</strong> scales through the Golgi complex in S.<br />
The contractile vacuole <strong>of</strong> S. dubia<br />
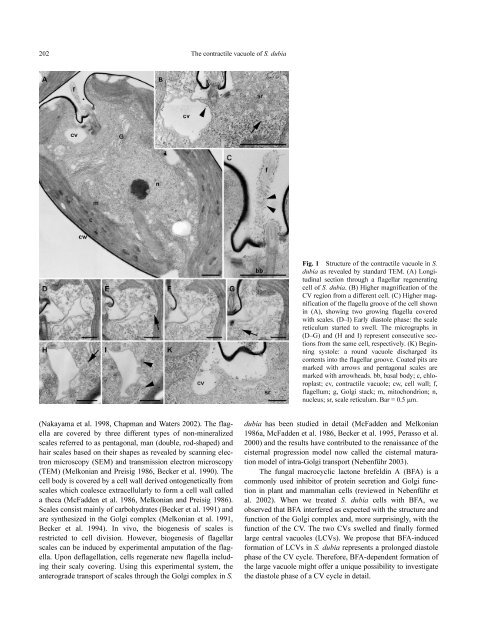
Fig. 1 Structure <strong>of</strong> the contractile vacuole in S.<br />
dubia as revealed <strong>by</strong> standard TEM. (A) Longitudinal<br />
section through a flagellar regenerating<br />
cell <strong>of</strong> S. dubia. (B) Higher magnification <strong>of</strong> the<br />
CV region from a different cell. (C) Higher magnification<br />
<strong>of</strong> the flagella groove <strong>of</strong> the cell shown<br />
in (A), showing two growing flagella covered<br />
with scales. (D–I) Early diastole phase: the scale<br />
reticulum started to swell. The micrographs in<br />
(D–G) and (H and I) represent consecutive sections<br />
from the same cell, respectively. (K) Beginning<br />
systole: a round vacuole discharged its<br />
contents into the flagellar groove. Coated pits are<br />
marked with arrows and pentagonal scales are<br />
marked with arrowheads. bb, basal body; c, chloroplast;<br />
cv, contractile vacuole; cw, cell wall; f,<br />
flagellum; g, Golgi stack; m, mitochondrion; n,<br />
nucleus; sr, scale reticulum. Bar = 0.5 µm.<br />
dubia has been studied in detail (McFadden and Melkonian<br />
1986a, McFadden et al. 1986, Becker et al. 1995, Perasso et al.<br />
2000) and the results have contributed to the renaissance <strong>of</strong> the<br />
cisternal progression model now called the cisternal maturation<br />
model <strong>of</strong> intra-Golgi transport (Nebenführ 2003).<br />
The fungal macrocyclic lactone brefeldin A (BFA) is a<br />
commonly used inhibitor <strong>of</strong> protein secretion and Golgi function<br />
in plant and mammalian cells (reviewed in Nebenführ et<br />
al. 2002). When we treated S. dubia cells with BFA, we<br />
observed that BFA interfered as expected with the structure and<br />
function <strong>of</strong> the Golgi complex and, more surprisingly, with the<br />
function <strong>of</strong> the CV. The two CVs swelled and finally formed<br />
large central vacuoles (LCVs). We propose that BFA-induced<br />
formation <strong>of</strong> LCVs in S. dubia represents a prolonged diastole<br />
phase <strong>of</strong> the CV cycle. Therefore, BFA-dependent formation <strong>of</strong><br />
the large vacuole might <strong>of</strong>fer a unique possibility to investigate<br />
the diastole phase <strong>of</strong> a CV cycle in detail.