Tectonostratigraphic architecture and uplift history of the Eastern ...
Tectonostratigraphic architecture and uplift history of the Eastern ...
Tectonostratigraphic architecture and uplift history of the Eastern ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
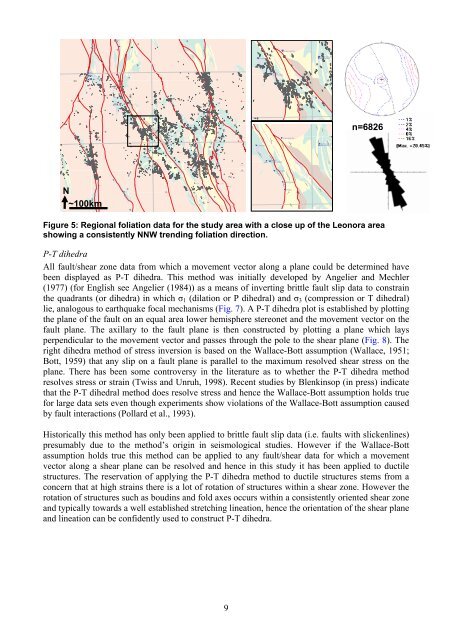
n=6826N~100kmFigure 5: Regional foliation data for <strong>the</strong> study area with a close up <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Leonora areashowing a consistently NNW trending foliation direction.P-T dihedraAll fault/shear zone data from which a movement vector along a plane could be determined havebeen displayed as P-T dihedra. This method was initially developed by Angelier <strong>and</strong> Mechler(1977) (for English see Angelier (1984)) as a means <strong>of</strong> inverting brittle fault slip data to constrain<strong>the</strong> quadrants (or dihedra) in which σ 1 (dilation or P dihedral) <strong>and</strong> σ 3 (compression or T dihedral)lie, analogous to earthquake focal mechanisms (Fig. 7). A P-T dihedra plot is established by plotting<strong>the</strong> plane <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> fault on an equal area lower hemisphere stereonet <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> movement vector on <strong>the</strong>fault plane. The axillary to <strong>the</strong> fault plane is <strong>the</strong>n constructed by plotting a plane which laysperpendicular to <strong>the</strong> movement vector <strong>and</strong> passes through <strong>the</strong> pole to <strong>the</strong> shear plane (Fig. 8). Theright dihedra method <strong>of</strong> stress inversion is based on <strong>the</strong> Wallace-Bott assumption (Wallace, 1951;Bott, 1959) that any slip on a fault plane is parallel to <strong>the</strong> maximum resolved shear stress on <strong>the</strong>plane. There has been some controversy in <strong>the</strong> literature as to whe<strong>the</strong>r <strong>the</strong> P-T dihedra methodresolves stress or strain (Twiss <strong>and</strong> Unruh, 1998). Recent studies by Blenkinsop (in press) indicatethat <strong>the</strong> P-T dihedral method does resolve stress <strong>and</strong> hence <strong>the</strong> Wallace-Bott assumption holds truefor large data sets even though experiments show violations <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Wallace-Bott assumption causedby fault interactions (Pollard et al., 1993).Historically this method has only been applied to brittle fault slip data (i.e. faults with slickenlines)presumably due to <strong>the</strong> method’s origin in seismological studies. However if <strong>the</strong> Wallace-Bottassumption holds true this method can be applied to any fault/shear data for which a movementvector along a shear plane can be resolved <strong>and</strong> hence in this study it has been applied to ductilestructures. The reservation <strong>of</strong> applying <strong>the</strong> P-T dihedra method to ductile structures stems from aconcern that at high strains <strong>the</strong>re is a lot <strong>of</strong> rotation <strong>of</strong> structures within a shear zone. However <strong>the</strong>rotation <strong>of</strong> structures such as boudins <strong>and</strong> fold axes occurs within a consistently oriented shear zone<strong>and</strong> typically towards a well established stretching lineation, hence <strong>the</strong> orientation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> shear plane<strong>and</strong> lineation can be confidently used to construct P-T dihedra.9