You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
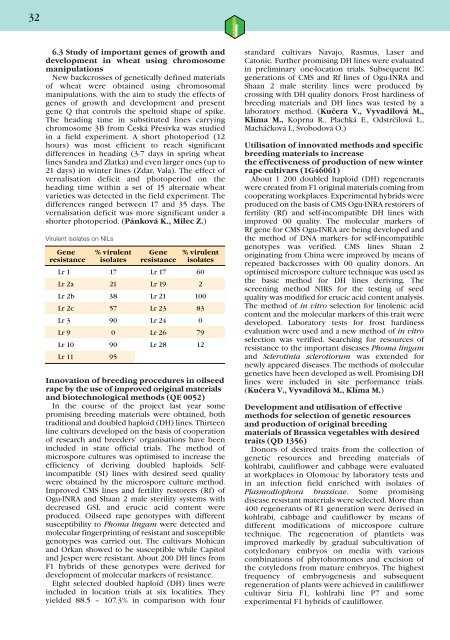
326.3 Study of important genes of growth anddevelopment in wheat using chromosomemanipulationsNew backcrosses of genetically defined materialsof wheat were obtained using chromosomalmanipulations, with the aim to study the effects ofgenes of growth and development and presentgene Q that controls the speltoid shape of spike.The heading time in substituted lines carryingchromosome 3B from Česká Přesívka was studiedin a field experiment. A short photoperiod (12hours) was most efficient to reach significantdifferences in heading (3-7 days in spring wheatlines Sandra and Zlatka) and even larger ones (up to21 days) in winter lines (Zdar, Vala). The effect ofvernalisation deficit and photoperiod on theheading time within a set of 15 alternate wheatvarieties was detected in the field experiment. Thedifferences ranged between 17 and 35 days. Thevernalisation deficit was more significant under ashorter photoperiod. (Pánková K., Milec Z.)Virulent isolates on NILsGene % virulent Gene % virulentresistance isolates resistance isolatesLr 1 17 Lr 17 60Lr 2a 21 Lr 19 2Lr 2b 38 Lr 21 100Lr 2c 57 Lr 23 83Lr 3 90 Lr 24 0Lr 9 0 Lr 26 79Lr 10 90 Lr 28 12Lr 11 95Innovation of breeding procedures in oilseedrape by the use of improved original materialsand biotechnological methods (QE 0052)In the course of the project last year somepromising breeding materials were obtained, bothtraditional and doubled haploid (DH) lines. Thirteenline cultivars developed on the basis of cooperationof research and breeders’ organisations have beenincluded in state official trials. The method ofmicrospore cultures was optimised to increase theefficiency of deriving doubled haploids. Selfincompatible(SI) lines with desired seed qualitywere obtained by the microspore culture method.Improved CMS lines and fertility restorers (Rf) ofOgu-INRA and Shaan 2 male sterility systems withdecreased GSL and erucic acid content wereproduced. Oilseed rape genotypes with differentsusceptibility to Phoma lingam were detected andmolecular fingerprinting of resistant and susceptiblegenotypes was carried out. The cultivars Mohicanand Orkan showed to be susceptible while Capitoland Jesper were resistant. About 200 DH lines fromF1 hybrids of these genotypes were derived fordevelopment of molecular markers of resistance.Eight selected doubled haploid (DH) lines wereincluded in location trials at six localities. Theyyielded 88.5 – 107.3% in comparison with fourstandard cultivars Navajo, Rasmus, Laser andCatonic. Further promising DH lines were evaluatedin preliminary one-location trials. Subsequent BCgenerations of CMS and Rf lines of Ogu-INRA andShaan 2 male sterility lines were produced bycrossing with DH quality donors. Frost hardiness ofbreeding materials and DH lines was tested by alaboratory method. (Kučera V., Vyvadilová M.,Klíma M., Koprna R., Plachká E., Odstrčilová L.,Macháčková I., Svobodová O.)Utilisation of innovated methods and specificbreeding materials to increasethe effectiveness of production of new winterrape cultivars (1G46061)About 1 200 doubled haploid (DH) regenerantswere created from F1 original materials coming fromcooperating workplaces. Experimental hybrids wereproduced on the basis of CMS Ogu-INRA restorers offertility (Rf) and self-incompatible DH lines withimproved 00 quality. The molecular markers ofRf gene for CMS Ogu-INRA are being developed andthe method of DNA markers for self-incompatiblegenotypes was verified. CMS lines Shaan 2originating from China were improved by means ofrepeated backcrosses with 00 quality donors. Anoptimised microspore culture technique was used asthe basic method for DH lines deriving. Thescreening method NIRS for the testing of seedquality was modified for erucic acid content analysis.The method of in vitro selection for linolenic acidcontent and the molecular markers of this trait weredeveloped. Laboratory tests for frost hardinessevaluation were used and a new method of in vitroselection was verified. Searching for resources ofresistance to the important diseases Phoma lingamand Sclerotinia sclerotiorum was extended fornewly appeared diseases. The methods of moleculargenetics have been developed as well. Promising DHlines were included in site performance trials.(Kučera V., Vyvadilová M., Klíma M.)Development and utilisation of effectivemethods for selection of genetic resourcesand production of original breedingmaterials of Brassica vegetables with desiredtraits (QD 1356)Donors of desired traits from the collection ofgenetic resources and breeding materials ofkohlrabi, cauliflower and cabbage were evaluatedat workplaces in Olomouc by laboratory tests andin an infection field enriched with isolates ofPlasmodiophora brassicae. Some promisingdisease resistant materials were selected. More than400 regenerants of R1 generation were derived inkohlrabi, cabbage and cauliflower by means ofdifferent modifications of microspore culturetechnique. The regeneration of plantlets wasimproved markedly by gradual subcultivation ofcotyledonary embryos on media with variouscombinations of phytohormones and excision ofthe cotyledons from mature embryos. The highestfrequency of embryogenesis and subsequentregeneration of plants were achieved in cauliflowercultivar Siria F1, kohlrabi line P7 and someexperimental F1 hybrids of cauliflower.