33Polyclonal antibodies were prepared for a semipurifiedsuspension of resting spores of P.brassicae. An antibody against resting spores wasused to probe artificially and naturally infested soilby indirect immunofluorescence. The developedmethod enabled to quantify the number of restingspores in soil at a concentration of 104 and 105with sufficient accuracy and its sensitivity was inthe range permissible for a routine test.Methodologies of the rearing and utilisation ofsyrphid flies, Myathropa florea (L.), as pollinatorsin technical isolators and utilisation of in vitrorooting of leaves for testing susceptibility andresistance to P. brassicae were developed. Methodsof breeding of line and hybrid Brassica vegetablecultivars and their seed production were devised.(Vyvadilová M., Kučera V., Klíma M., KudlíkováI., Krátká J., Chytilová V., Havránek P.,Navrátilová B., Horák J.)Study and use of genes and geneticmechanisms controlling importantagronomic characters of bread wheat andproduction of specific lines usingchromosome manipulations (QD 1342)Advanced generations of lines with defined genescontrolling growth and development were alsoproduced in 2004, in the last year of the project.The series of molecular tests of polymorphism ofSSR markers were carried out in the lines withchanged growth habit and their parental varietiesto find markers for Vrn-1 genes and to verify thesubstitutions. In some of the lines with changedgrowth habit, present recombination or lostsubstitutions of the checked chromosomes wererevealed. Thus, the necessity of molecular checks ofthe substitutions was proved.We published the results of a field experimentstudying the effects of substitutions ofhomoeologous group 5 chromosomes carrying genesVrn-A1, Vrn-B1, Vrn-D1 into genetic backgrounds ofwinter wheat varieties Zdar and Košutka withcontrasting photoperiod sensitivity on the growthstages. The differences between the effects ofindividual genes Vrn-1 on growth and developmentwere confirmed as well as the influence on the yieldcomponents of wheat plants that were analysed andsubmitted as a part of the project final report.(Pánková K., Milec, Z., Leišová L.)FHB Ring test (25 varieties in three replications)were also examined for resistance to FHB. In hillplot design a highly pathogenic isolate (B) ofFusarium culmorum was used for inoculation. Thefollowing characters were considered as decisive inexperiments of these types: visual symptom scores,percentage of Fusarium damaged kernels andDON content. Fusarium damaged (scabby) kernelswere calculated as a percentage out of the totalseed number (%FDK). The inclusion of uninfected,control variant enabled to evaluate tolerance tothe infection. The trait %FDK, which providesuseful information about pathogen colonisation ingrain, was found to be closely related to DONcontent (r=0.75). The highest resistance to DONaccumulation, connected with favourableperformance in the other examined resistancetraits, was detected in Sumai 3 and in the lineSG-V NB x MM Sum 3 from Szeged, Hungary, whichincludes Sumai 3 and Nobeoca Bozu in its pedigree.In European Wheat FHB Ring test advanced linesHUS 690, 692, 700 and 702 from BSRCA Freising-Weihenstephan showed high resistance. It isimportant that moderate resistance was alsodetected in advanced lines developed in breedingprograms of SELGEN Company (SG-S 1800-01, SG-S1875-01, SG-U 7029 – winter wheat, SG-S 856-02,SG-U 305B – spring wheat). All these materials aresuitable from agronomic aspects (the line SG-S1875-01 is tested in Official Trials). The resultsindicate that a suitable resistance level can also beobtained in programs that utilise recombinationof resistance genes from adapted germplasm.(Chrpová J., Šíp V., Sýkorová S., Matějová E.)Department of Breeding MethodsResults of testing wheat for resistance toFusarium head blight in the Czech Republic(QD 1311)National tests of resistance to Fusarium headblight (FHB), performed in 2004 (the third year) inRICP and at other three locations of the CzechRepublic, included 84 winter and spring wheatmaterials (potential sources of resistance frominternational cooperation, advanced breedinglines, selected registered cultivars and checkcultivars). In RICP the materials tested in OfficialTrials (57 varieties in three replications) andselected foreign materials from European WheatExamination of resistance to Fusarium head blight in field testsusing hill plot design
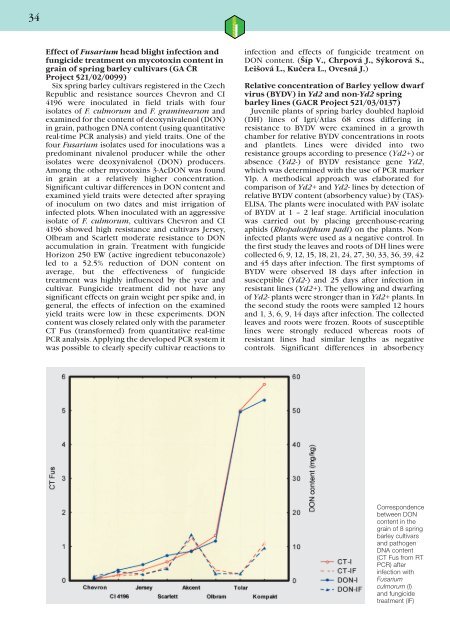
34Effect of Fusarium head blight infection andfungicide treatment on mycotoxin content ingrain of spring barley cultivars (GA ČRProject 521/02/0099)Six spring barley cultivars registered in the CzechRepublic and resistance sources Chevron and CI4196 were inoculated in field trials with fourisolates of F. culmorum and F. graminearum andexamined for the content of deoxynivalenol (DON)in grain, pathogen DNA content (using quantitativereal-time PCR analysis) and yield traits. One of thefour Fusarium isolates used for inoculations was apredominant nivalenol producer while the otherisolates were deoxynivalenol (DON) producers.Among the other mycotoxins 3-AcDON was foundin grain at a relatively higher concentration.Significant cultivar differences in DON content andexamined yield traits were detected after sprayingof inoculum on two dates and mist irrigation ofinfected plots. When inoculated with an aggressiveisolate of F. culmorum, cultivars Chevron and CI4196 showed high resistance and cultivars Jersey,Olbram and Scarlett moderate resistance to DONaccumulation in grain. Treatment with fungicideHorizon 250 EW (active ingredient tebuconazole)led to a 52.5% reduction of DON content onaverage, but the effectiveness of fungicidetreatment was highly influenced by the year andcultivar. Fungicide treatment did not have anysignificant effects on grain weight per spike and, ingeneral, the effects of infection on the examinedyield traits were low in these experiments. DONcontent was closely related only with the parameterCT Fus (transformed) from quantitative real-timePCR analysis. Applying the developed PCR system itwas possible to clearly specify cultivar reactions toinfection and effects of fungicide treatment onDON content. (Šíp V., Chrpová J., Sýkorová S.,Leišová L., Kučera L., Ovesná J.)Relative concentration of Barley yellow dwarfvirus (BYDV) in Yd2 and non-Yd2 springbarley lines (GACR Project 521/03/0137)Juvenile plants of spring barley doubled haploid(DH) lines of Igri/Atlas 68 cross differing inresistance to BYDV were examined in a growthchamber for relative BYDV concentrations in rootsand plantlets. Lines were divided into tworesistance groups according to presence (Yd2+) orabsence (Yd2-) of BYDV resistance gene Yd2,which was determined with the use of PCR markerYlp. A methodical approach was elaborated forcomparison of Yd2+ and Yd2- lines by detection ofrelative BYDV content (absorbency value) by (TAS)-ELISA. The plants were inoculated with PAV isolateof BYDV at 1 – 2 leaf stage. Artificial inoculationwas carried out by placing greenhouse-rearingaphids (Rhopalosiphum padi) on the plants. Noninfectedplants were used as a negative control. Inthe first study the leaves and roots of DH lines werecollected 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42and 45 days after infection. The first symptoms ofBYDV were observed 18 days after infection insusceptible (Yd2-) and 25 days after infection inresistant lines (Yd2+). The yellowing and dwarfingof Yd2- plants were stronger than in Yd2+ plants. Inthe second study the roots were sampled 12 hoursand 1, 3, 6, 9, 14 days after infection. The collectedleaves and roots were frozen. Roots of susceptiblelines were strongly reduced whereas roots ofresistant lines had similar lengths as negativecontrols. Significant differences in absorbencyCorrespondencebetween DONcontent in thegrain of 8 springbarley cultivarsand pathogenDNA content(CT Fus from RTPCR) afterinfection withFusariumculmorum (I)and fungicidetreatment (IF)