CANDU Safety #22 - Regulatory Requirements for Design - Canteach
CANDU Safety #22 - Regulatory Requirements for Design - Canteach
CANDU Safety #22 - Regulatory Requirements for Design - Canteach
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong><strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>Dr. V.G. SnellDirector<strong>Safety</strong> & Licensing24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 1
Other Sources of <strong>Requirements</strong>λλλλnational standards cover many design aspects– Canadian Standards Association (CSA)– other recognized standards - ANSI, ISO, IEEEAECB participates in CSA Committeesdesigner sets the detailed requirements– submitted to AECB and auditedsome must be <strong>for</strong>mally accepted and need approval ifchanged– <strong>Safety</strong> <strong>Design</strong> Guides24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 3
<strong>Safety</strong> <strong>Design</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> DocumentsλλλλλλλλλλλLicensing BasisQA Programme<strong>Safety</strong> <strong>Design</strong> Guides<strong>Safety</strong> Critical Software Standards and ProceduresCompliance with <strong>Regulatory</strong> DocumentsHuman Factors Engineering Programme Plan<strong>Safety</strong> Analysis Initial Conditions and Standard AssumptionsProbabilistic <strong>Safety</strong> Analysis Methodology<strong>Design</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Safety</strong>-Related SystemsDisposition of Generic Licensing IssuesSevere Accident Programme, etc.
AECB Key Documents <strong>for</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> SystemsλλλλR-7: <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> Containment SystemsR-8: <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> Shutdown SystemsR-9: <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> Emergency Core Cooling SystemsR-10: The Use of Two Shutdown Systems in Reactors24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 6
Common Elements - 1λ minimum allowable per<strong>for</strong>mance standards (MAPS)λ public dose limits <strong>for</strong> accidentsλ environmental qualification– <strong>for</strong> those portions required <strong>for</strong> accident mitigationλ system unavailability < 10 - 3 years / yearλ support system unavailability to meet system unavailabilityλ long-term post accident availabilityλ single component failure criterion– not required <strong>for</strong> components which do not change state andwhich do not depend on safety support equipmentλ fail-safe where practicable24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 7
Common Elements - 2λλλλλλλλknown failed component can be put in safe stateall automatic actions can also be manually initiated fromcontrol roomphysical and operational independence from other safetysystems, no shared equipmentindependence from process systemsseparation of redundant instrument channelsjustification of independent subsystemscall-up of specific CSA Standardsseismic qualification of portions that are credited in safetyanalysis after DBE24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 8
Common Elements - 3λλλλλλno operator action credited until 15 minutes after clear signalin-service component testing to demonstrate availabilitytesting does not impair systemsafety function cannot depend on Class IV power supplyperiodic but infrequent integrated system tests, <strong>for</strong> shutdown& containmentsafety systems cannot be intentionally made unavailable(except under specific conditions - e.g., guaranteed shutdown,backup heat sinks available)24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 9
Example of Goal-Oriented Requirement“<strong>Design</strong> principles <strong>for</strong> separation of redundant instrumentchannels…shall be prepared and shall require approval by theAECB prior to the issuance of a construction approval”– no numbers or acceptance criteria given– designer prepares <strong>Safety</strong> <strong>Design</strong> Guide stating specificseparation requirements– <strong>Safety</strong> <strong>Design</strong> Guide approved by AECB– major exceptions or changes to <strong>Safety</strong> <strong>Design</strong> Guiderequire approval of AECB24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 10
Specific Containment <strong>Requirements</strong> - 1λλλλλdesign pressure set only by accidents which releaseradioactivity (LOCA)must assume failure of dousing in setting design pressure<strong>for</strong> primary and secondary side failures, with or withoutdousing, cannot impair structure so that damage to reactorsystems occurs<strong>for</strong> primary side failures with or without dousing, andsecondary side failures with dousing, no damage tocontainment structuremaximum leakage rate set by value used in safety analysis24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 11
Specific Containment <strong>Requirements</strong> - 3λλtests of penetration and isolatingdevices (no method specified)appendix giving detailedrequirements <strong>for</strong> metal extensionsof the containment envelope24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 13
Specific Shutdown System <strong>Requirements</strong>λλλλλλλλprovision of 2 independent shutdown systemsprevent loss of heat transport system integritymanual operation from main control room and remote locationdiverse designsnormal process system action, or inaction, cannot reduceeffectivenesstwo diverse trip parameters on each shutdown system <strong>for</strong>each accident (unless impracticable or detrimental to safety)re-poising of shutdown systems after tripprocedures <strong>for</strong> guaranteed shutdown but at least oneshutdown system must be available even then24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 14
Diversity & Separation of Flux DetectorsSDS1SDS224/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 15
Specific Emergency Core Cooling System<strong>Requirements</strong>λλλλλλfuel failures prevented <strong>for</strong> small LOCA and secondary sidebreakscoolable geometry in fuel channels <strong>for</strong> all LOCAsno further fuel damage after ECC has re-established established coolinglong-term reliability targets required, defined by designer(typically unavailability in long term < 10 - 2 years/year)leakage collection and control <strong>for</strong> ECC components outsidecontainmentno detrimental safety affect due to inadvertent operation24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 16
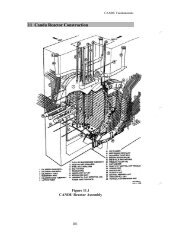
ECC Schematic24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 17
Conclusionsλλλλλregulatory requirements on design are goal-orientedorienteddetailed requirements set by designer & approved by regulatoremphasis on reliability, separation, testabilitystrong tie to accident analysis through MAPSqualification where required24/05/01 <strong>CANDU</strong> <strong>Safety</strong> - <strong>#22</strong> - <strong>Regulatory</strong> <strong>Requirements</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Design</strong>.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 18