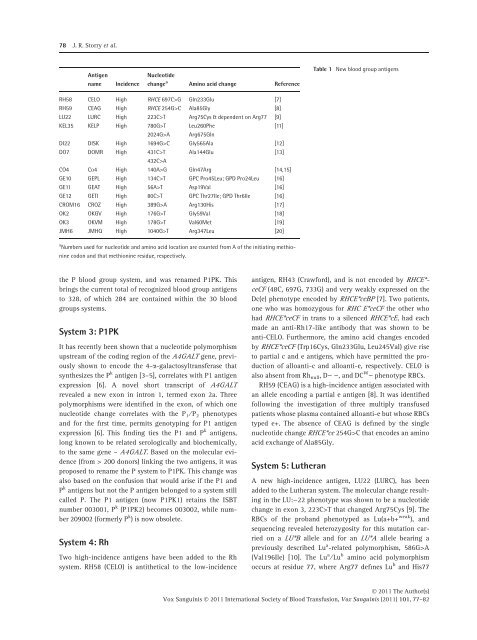
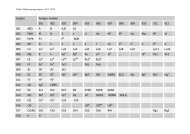
78 J. R. Storry et al.AntigennameIncidenceNucleotidechange a Amino acid change ReferenceTable 1 New blood group antigensRH58 CELO High RHCE 697C>G Gln233Glu [7]RH59 CEAG High RHCE 254G>C Ala85Gly [8]LU22 LURC High 223C>T Arg75Cys & dependent <strong>on</strong> Arg77 [9]KEL35 KELP High 780G>T2024G>ALeu260PheArg675GlnDI22 DISK High 1694G>C Gly565Ala [12]DO7 DOMR High 431C>T Ala144Glu [13]432C>ACO4 Co4 High 140A>G Gln47Arg [14,15]GE10 GEPL High 134C>T GPC Pro45Leu; GPD Pro24Leu [16]GE11 GEAT High 56A>T Asp19Val [16]GE12 GETI High 80C>T GPC Thr27Ile; GPD Thr6Ile [16]CROM16 CROZ High 389G>A Arg130His [17]OK2 OKGV High 176G>T Gly59Val [18]OK3 OKVM High 178G>T Val60Met [19]JMH6 JMHQ High 1040G>T Arg347Leu [20][11]a Numbers used for nucleotide and amino acid locati<strong>on</strong> are counted from A <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the initiating methi<strong>on</strong>inecod<strong>on</strong> and that methi<strong>on</strong>ine residue, respectively.the P blood group system, and was renamed P1PK. Thisbrings the current total <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> recognized blood group antigensto 328, <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> which 284 are c<strong>on</strong>tained within the 30 bloodgroups systems.System 3: P1PKIt has recently been shown that a nucleotide polymorphismupstream <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the coding regi<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the A4GALT gene, previouslyshown to encode the 4-a-galactosyltransferase thatsynthesizes the P k antigen [3–5], correlates with P1 antigenexpressi<strong>on</strong> [6]. A novel short transcript <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> A4GALTrevealed a new ex<strong>on</strong> in intr<strong>on</strong> 1, termed ex<strong>on</strong> 2a. Threepolymorphisms were identified in the ex<strong>on</strong>, <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> which <strong>on</strong>enucleotide change correlates with the P 1 ⁄ P 2 phenotypesand for the first time, permits genotyping for P1 antigenexpressi<strong>on</strong> [6]. This finding ties the P1 and P k antigens,l<strong>on</strong>g known to be related serologically and biochemically,to the same gene – A4GALT. Based <strong>on</strong> the molecular evidence(from > 200 d<strong>on</strong>ors) linking the two antigens, it wasproposed to rename the P system to P1PK. This change wasalso based <strong>on</strong> the c<strong>on</strong>fusi<strong>on</strong> that would arise if the P1 andP k antigens but not the P antigen bel<strong>on</strong>ged to a system stillcalled P. The P1 antigen (now P1PK1) retains the ISBTnumber 003001, P k (P1PK2) becomes 003002, while number209002 (formerly P k ) is now obsolete.System 4: RhTwo high-incidence antigens have been added to the Rhsystem. RH58 (CELO) is antithetical to the low-incidenceantigen, RH43 (Crawford), and is not encoded by RHCE*-ceCF (48C, 697G, 733G) and very weakly expressed <strong>on</strong> theDc(e) phenotype encoded by RHCE*ceBP [7]. Two patients,<strong>on</strong>e who was homozygous for RHC E*ceCF the other whohad RHCE*ceCF in trans to a silenced RHCE*cE, had eachmade an anti-Rh17-like antibody that was shown to beanti-CELO. Furthermore, the amino acid changes encodedby RHCE*ceCF (Trp16Cys, Gln233Glu, Leu245Val) give riseto partial c and e antigens, which have permitted the producti<strong>on</strong><str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> alloanti-c and alloanti-e, respectively. CELO isalso absent from Rh null ,D)), and DC W ) phenotype RBCs.RH59 (CEAG) is a high-incidence antigen associated withan allele encoding a partial e antigen [8]. It was identifiedfollowing the investigati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> three multiply transfusedpatients whose plasma c<strong>on</strong>tained alloanti-e but whose RBCstyped e+. The absence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CEAG is defined by the singlenucleotide change RHCE*ce 254G>C that encodes an aminoacid exchange <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Ala85Gly.System 5: LutheranA new high-incidence antigen, LU22 (LURC), has beenadded to the Lutheran system. The molecular change resultingin the LU:)22 phenotype was shown to be a nucleotidechange in ex<strong>on</strong> 3, 223C>T that changed Arg75Cys [9]. TheRBCs <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the proband phenotyped as Lu(a+b+ weak ), andsequencing revealed heterozygosity for this mutati<strong>on</strong> carried<strong>on</strong> a LU*B allele and for an LU*A allele bearing apreviously described Lu a -related polymorphism, 586G>A(Val196Ile) [10]. The Lu a ⁄ Lu b amino acid polymorphismoccurs at residue 77, where Arg77 defines Lu b and His77Ó 2011 The Author(s)Vox Sanguinis Ó 2011 <str<strong>on</strong>g>Internati<strong>on</strong>al</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Society</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Blood</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Transfusi<strong>on</strong></str<strong>on</strong>g>, Vox Sanguinis (2011) 101, 77–82
Red <strong>cell</strong> immunogenetics and blood group terminology 79defines Lu a . The proximity <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Arg75Cys presumably interruptsand weakens the expressi<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the Lu b antigenencoded by this allele. Furthermore, the occurrence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> theLURC-negative phenotype <strong>on</strong> a heterozygous LU*A ⁄ LU*Bbackground dem<strong>on</strong>strates the reliance <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> LURC <strong>on</strong> the Lu bantigen residue, Arg77 for expressi<strong>on</strong>.System 6: KellAnother high-incidence antigen was added to the Kell system:KEL35 (KELP), defined by an antibody that was n<strong>on</strong>reactive<strong>on</strong>ly with K 0 RBCs and those <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the antibody maker[11]. The patient’s RBCs typed KEL:)1,2–3,4,6,11,)12,22,although sequence analysis did not c<strong>on</strong>firm the K:)12phenotype. However, the proband was homozygous fortwo novel mutati<strong>on</strong>s: 780G>T in ex<strong>on</strong> 8, which encodesLeu260Phe, and 2024G>A in ex<strong>on</strong> 18, encoding Arg675Gln. Leu260Phe is located <strong>on</strong> the Kell glycoprotein at apositi<strong>on</strong> distal from the membrane and modelling p<strong>red</strong>ictsa change in the molecular surface <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Kell. However, aminoacid positi<strong>on</strong> 675 lies close to or in the membrane. Bothmutati<strong>on</strong>s are seemingly unc<strong>on</strong>nected with Arg548 thatdefines K12 and the effect <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> these two novel mutati<strong>on</strong>s <strong>on</strong>K12 expressi<strong>on</strong> remains unresolved.System 8: DuffyFollowing the criteria that an antibody to a blood groupantigen must be extant for that antigen to be recognized,and based <strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong>ly scant original evidence for its existence,FY4 has been made obsolete.System 10: DiegoA high-incidence antigen antithetical to DI9 (Wu) has beenidentified. The new antigen, DI22 (DISK), was characterizedby an apparently naturally occurring, str<strong>on</strong>gly agglutinatingantibody reactive both at 18 and 37°C and by the indirectantiglobulin test [12]. DISK was shown to be sensitive toa-chymotrypsin treatment, but resistant to other comm<strong>on</strong>lyused proteases. Targeted sequence analysis <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> SLC4A1 ex<strong>on</strong>14 revealed homozygosity in the proband and heterozygosityin a sample from her brother, for the mutati<strong>on</strong> 1694G>Cthat encodes Gly565Ala. The RBCs <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> her brother reactedmore weakly with her antibody, suggesting that the anti-DISK exhibits dosage in DI:9,22 individuals.System 14: DombrockDO7 (DOMR) is defined by an antibody to a high-incidenceantigen produced in a patient, homozygous for two adjacentnucleotide changes 431C>A, 432C>A that encode achange <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Ala144Glu [13]. These changes are present with aDO*B-WL allele (DO*793G, DO*323G, DO*350C, DO*547T,DO*898G). The DO*B-WL allele is p<strong>red</strong>icted to encode thephenotype Do(a)b+), Hy+, Jo(a+), DOYA+, however, thepatient’s RBCs typed Do(a)b+), Hy+ w , Jo(a+ w ), DOYA+ w .Her RBCs also typed Gy(a)) with a polycl<strong>on</strong>al antibody butwere reactive with several m<strong>on</strong>ocl<strong>on</strong>al antibodies to theDombrock glycoprotein. Further complexity was dem<strong>on</strong>stratedby the plasma antibody that was n<strong>on</strong>reactive or<strong>on</strong>ly very weakly reactive with six Hy) samples, n<strong>on</strong>reactivewith Gy(a)) RBCs but reactive with Jo(a)) and DOYA)RBCs.System 15: COAn antibody compatible with Co(a)b)) RBCs but weaklyincompatible with Co(a)b+) RBCs was identified in theplasma <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> a patient whose RBCs typed Co(a)b)) [14].Molecular analysis <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> AQP1 revealed homozygosity for140A>G, encoding the amino acid change Gln47Arg, inclose proximity to the Co a ⁄ Co b polymorphism at residue45. Samples from a sec<strong>on</strong>d Co(a)b)) proband homozygousfor the same 140A>G mutati<strong>on</strong> were investigated followingdetecti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> an antibody to a high-incidence antigen initiallyidentified as anti-Co3 [15]. Unexpectedly, her RBCswere shown to have functi<strong>on</strong>al aquaporin 1. Expressi<strong>on</strong>studies with AQP1 encoding Arg47 dem<strong>on</strong>strated a loss <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g>Co a antigen expressi<strong>on</strong> despite the presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the Co a -specific Ala45, c<strong>on</strong>sistent with the observed phenotype.Arnaud et al. [15] also re-evaluated three antisera classifiedas anti-Co3 in their collecti<strong>on</strong> and re-identified <strong>on</strong>e <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> thethree sera as anti-Co4. PCR–RFLP analysis revealed thatthis sample also was homozygous for AQP1 140G. Thus,this polymorphism defines a new high-incidence antigen,CO4, in the Colt<strong>on</strong> blood group system.System 20: GerbichThree novel high-incidence antigens am<strong>on</strong>g four individualshave been added to the Gerbich blood group system:GE10 (GEPL), GE11 (GEAT), GE12 (GETI) [16]. GE10 wasidentified following the investigati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> an individualwhose RBCs typed GE:2,3,4 but whose plasma c<strong>on</strong>tained anapparent alloanti-Ge3. Immunoblotting analysis showedthe presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> both normal GPC ⁄ GPD and two unexpectedbands that were approximately 2 kDa smaller than normal.DNA sequence analysis revealed a single point mutati<strong>on</strong> inGYPC, 134C>T, which encodes an amino acid change Proto Leu at positi<strong>on</strong>s 45 and 24 <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> GPC and GPD, respectively.Anti-Ge11 was n<strong>on</strong>reactive with GE:)2,)3 andGE:)2,)3,)4 RBCs, but dem<strong>on</strong>strated variable reactivitywith GE:)2,3 RBCs. Bands corresp<strong>on</strong>ding to GPC and GPD<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> apparently normal mass were shown by immunoblottingand DNA sequence analysis revealed homozygosity for aÓ 2011 The Author(s)Vox Sanguinis Ó 2011 <str<strong>on</strong>g>Internati<strong>on</strong>al</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Society</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Blood</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Transfusi<strong>on</strong></str<strong>on</strong>g>, Vox Sanguinis (2011) 101, 77–82