The Why, What, How & Who Of Maintenance - AMMJ
The Why, What, How & Who Of Maintenance - AMMJ
The Why, What, How & Who Of Maintenance - AMMJ
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
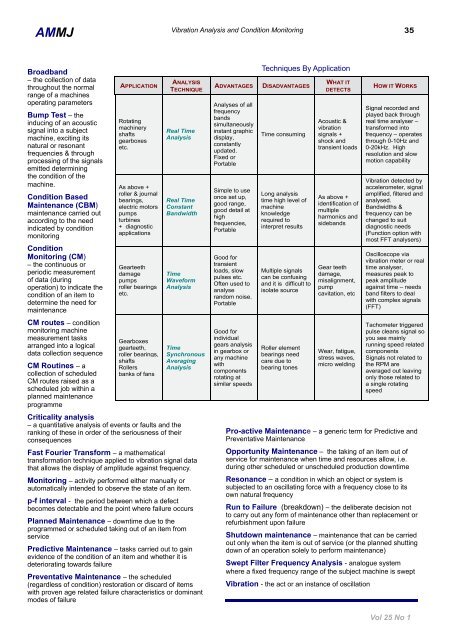
<strong>AMMJ</strong>Vibration Analysis and Condition Monitoring 35Broadband– the collection of datathroughout the normalrange of a machinesoperating parametersBump Test – theinducing of an acousticsignal into a subjectmachine, exciting itsnatural or resonantfrequencies & throughprocessing of the signalsemitted determiningthe condition of themachine.Condition Based<strong>Maintenance</strong> (CBM)maintenance carried outaccording to the needindicated by conditionmonitoringConditionMonitoring (CM)– the continuous orperiodic measurementof data (duringoperation) to indicate thecondition of an item todetermine the need formaintenanceCM routes – conditionmonitoring machinemeasurement tasksarranged into a logicaldata collection sequenceCM Routines – acollection of scheduledCM routes raised as ascheduled job within aplanned maintenanceprogrammeAPPLICATIONRotatingmachineryshaftsgearboxesetc.As above +roller & journalbearings,electric motorspumpsturbines+ diagnosticapplicationsGearteethdamagepumpsroller bearingsetc.Gearboxesgearteeth,roller bearings,shaftsRollersbanks of fansCriticality analysis– a quantitative analysis of events or faults and theranking of these in order of the seriousness of theirconsequencesANALYSISTECHNIQUEReal TimeAnalysisReal TimeConstantBandwidthTimeWaveformAnalysisTimeSynchronousAveragingAnalysisFast Fourier Transform – a mathematicaltransformation technique applied to vibration signal datathat allows the display of amplitude against frequency.Monitoring – activity performed either manually orautomatically intended to observe the state of an item.p-f interval - the period between which a defectbecomes detectable and the point where failure occursPlanned <strong>Maintenance</strong> – downtime due to theprogrammed or scheduled taking out of an item fromservicePredictive <strong>Maintenance</strong> – tasks carried out to gainevidence of the condition of an item and whether it isdeteriorating towards failurePreventative <strong>Maintenance</strong> – the scheduled(regardless of condition) restoration or discard of itemswith proven age related failure characteristics or dominantmodes of failureADVANTAGESAnalyses of allfrequencybandssimultaneouslyinstant graphicdisplay,constantlyupdated.Fixed orPortableSimple to useonce set up,good range,good detail athighfrequencies,PortableGood fortransientloads, slowpulses etc.<strong>Of</strong>ten used toanalyserandom noise.PortableGood forindividualgears analysisin gearbox orany machinewithcomponentsrotating atsimilar speedsTechniques By ApplicationDISADVANTAGESTime consumingLong analysistime high level ofmachineknowledgerequired tointerpret resultsMultiple signalscan be confusingand it is difficult toisolate sourceRoller elementbearings needcare due tobearing tonesWHAT ITDETECTSAcoustic &vibrationsignals +shock andtransient loadsAs above +identification ofmultipleharmonics andsidebandsGear teethdamage,misalignment,pumpcavitation, etcWear, fatigue,stress waves,micro weldingPro-active <strong>Maintenance</strong> – a generic term for Predictive andPreventative <strong>Maintenance</strong>Opportunity <strong>Maintenance</strong> – the taking of an item out ofservice for maintenance when time and resources allow, i.e.during other scheduled or unscheduled production downtimeResonance – a condition in which an object or system issubjected to an oscillating force with a frequency close to itsown natural frequencyRun to Failure (breakdown) – the deliberate decision notto carry out any form of maintenance other than replacement orrefurbishment upon failureShutdown maintenance – maintenance that can be carriedout only when the item is out of service (or the planned shuttingdown of an operation solely to perform maintenance)Swept Filter Frequency Analysis - analogue systemwhere a fixed frequency range of the subject machine is sweptVibration - the act or an instance of oscillationHOW IT WORKSSignal recorded andplayed back throughreal time analyser –transformed intofrequency – operatesthrough 0-10Hz and0-20kHz. Highresolution and slowmotion capabilityVibration detected byaccelerometer, signalamplified, filtered andanalysed.Bandwidths &frequency can bechanged to suitdiagnostic needs(Function option withmost FFT analysers)Oscilloscope viavibration meter or realtime analyser,measures peak topeak amplitudeagainst time – needsband filters to dealwith complex signals(FFT)Tachometer triggeredpulse cleans signal soyou see mainlyrunning speed relatedcomponentsSignals not related tothe RPM areaveraged out leavingonly those related toa single rotatingspeedVol 25 No 1