- Page 1 and 2:
BRAND - Your Partner in the Lab.Wor
- Page 3 and 4:
About the ProductOrdering optionsOu
- Page 5:
About usIdeasPartnering for success
- Page 8 and 9:
About usFactory and ProductionAs th
- Page 10 and 11:
1949 195019571961196319641967197319
- Page 12 and 13:
© Mark Weathers Images/Flicks/Gett
- Page 14 and 15:
© Peter de Rooij/Flickr/Getty Imag
- Page 16 and 17:
Product NewsNew in this Catalog!New
- Page 18 and 19:
Liquid HandlingOne of the most impo
- Page 20 and 21:
Dispensette ® IIIDispensette ® Or
- Page 22 and 23:
Dispensette ® IIIDispensette ® Or
- Page 24 and 25:
Dispensette ® III / OrganicDispens
- Page 26 and 27:
Dispensette ® III / OrganicOrderin
- Page 28 and 29:
Dispensette ® III / OrganicAccesso
- Page 30 and 31:
Dispensette ® TANEW!Liquid Handlin
- Page 32 and 33:
Dispensette ® TAUse and HandlingGe
- Page 34 and 35:
seripettor ®seripettor ® proserip
- Page 36 and 37:
seripettor ® · seripettor ® proA
- Page 38 and 39:
seripettor ® · seripettor ® proO
- Page 40 and 41:
Titrette ® - the first bottle-top
- Page 42 and 43:
Titrette ®Use and HandlingLight-we
- Page 44 and 45:
Titrette ®Comparisonof error limit
- Page 46 and 47:
BRAND offers the ideal pipette for
- Page 48 and 49:
Transferpette ® STransferpette ®
- Page 50 and 51:
Transferpette ® SA Closer Look...A
- Page 52 and 53:
Transferpette ® S -8/-12A Closer L
- Page 54 and 55:
Transferpette ®Transferpette ® -8
- Page 56 and 57:
Transferpette ®Tip ejector capErgo
- Page 58 and 59:
Transferpette ®AccessoriesAccessor
- Page 60 and 61:
Transferpette ® -8/-12Ordering Dat
- Page 62 and 63:
Transferpette ® electronicTransfer
- Page 64 and 65:
Transferpette ® electronicA Closer
- Page 66 and 67:
Transferpette ® -8/-12 electronicA
- Page 68 and 69:
Transferpette ® -12 electronicOrde
- Page 70 and 71:
Pipette Tips and Filter TipsConsist
- Page 72 and 73:
Pipette Tips and Filter Tips5 - 300
- Page 74 and 75:
Pipette Tips and Filter TipsTipRack
- Page 76 and 77:
Pipette Tipssterile and non-sterile
- Page 78 and 79:
Filter Tipssterile and non-sterileF
- Page 80 and 81:
ULR Pipette Tipssterile and non-ste
- Page 82 and 83:
ULR Filter Tipssterile and non-ster
- Page 84 and 85:
The Transferpettor pipette is ideal
- Page 86 and 87:
Transferpettor · Ordering DataAppl
- Page 88 and 89:
Serial pipetting can be quick and e
- Page 90 and 91:
HandyStep ® SUse and Handlingn Inc
- Page 92 and 93:
The HandyStep ® electronic repetit
- Page 94 and 95:
HandyStep ® electronicUse and Hand
- Page 96 and 97:
PD-TipsPD-TipsPrecision Dispenser T
- Page 98 and 99:
Pipetting aids from BRAND excel by
- Page 100 and 101:
accu-jet ® pro Single-handed opera
- Page 102 and 103:
micro · micro-classicmicro Pipette
- Page 104 and 105:
The QuikSip bottle-top aspirator f
- Page 106 and 107:
The most frequent cause of inaccura
- Page 108 and 109:
PLT unitUse and HandlingTesting wit
- Page 110 and 111:
BRAND calibration software is compa
- Page 112 and 113:
EASYCAL 4.0 · Ordering DataQuit c
- Page 114 and 115:
Liquid HandlingBRAND onlineLiquid H
- Page 116 and 117:
Life ScienceResearch - and even rou
- Page 118 and 119:
Life ScienceCleanroom productionBRA
- Page 120 and 121:
Microcentrifuge TubesMicrocentrifug
- Page 122 and 123:
Microcentrifuge Tubes1.5 ml, with l
- Page 124 and 125:
Micro TubesMicro tubesattached scre
- Page 126 and 127:
AccessoriesMicrocentrifuge TubesAcc
- Page 128 and 129:
PCR TubesSingle PCR tubes0.2 ml and
- Page 130 and 131:
PCR Strips · PCR PlatesStrips of 8
- Page 132 and 133:
PCR Plates1Life ScienceLow profileL
- Page 134 and 135:
PCR Sealing Mats andSealing FilmsPC
- Page 136 and 137:
Thermal Cycler Compatibilitycontinu
- Page 138 and 139:
Deep-well PlatesDeep-well PlatesThe
- Page 140 and 141:
Racks · Tubes96 tube rackswith 0.6
- Page 142 and 143:
Cryogenic TubesCryogenic TubesDesig
- Page 144 and 145:
BRANDplates ® MicroplatesBRANDplat
- Page 146 and 147:
BRANDplates ®non-treatedApplicatio
- Page 148 and 149:
BRANDplates ®non-treated384-well M
- Page 150 and 151:
BRANDplates ® MicroplatesBRANDplat
- Page 152 and 153:
BRANDplates ®ImmunoassaysApplicati
- Page 154 and 155:
BRANDplates ®Immunoassays384-well
- Page 156 and 157:
BRANDplates ® MicroplatesBRANDplat
- Page 158 and 159:
BRANDplates ®Cell CulturecellGrade
- Page 160 and 161:
BRANDplates ®Insert SystemNEW!BRAN
- Page 162 and 163:
BRANDplates ®Insert SystemA Closer
- Page 164 and 165:
BRANDplates ®OverviewAt a Glance96
- Page 166 and 167:
CuvettesCuvettesLife ScienceFor mor
- Page 168 and 169:
CuvettesLife ScienceStandard Cuvett
- Page 170 and 171:
Life ScienceBRAND onlineLife Scienc
- Page 172 and 173:
VolumetricInstrumentsPrecision anal
- Page 174 and 175:
CertificatesBLAUBRAND ® Volumetric
- Page 176 and 177:
Bulb PipettesBulb pipettes, 1 markB
- Page 178 and 179:
Graduated PipettesGraduated Pipette
- Page 180 and 181:
Graduated PipettesGraduated pipette
- Page 182 and 183:
Graduated PipettesGraduated pipette
- Page 184 and 185:
Volumetric FlasksVolumetric FlasksB
- Page 186 and 187:
Volumetric FlasksVolumetric flasks,
- Page 188 and 189:
Volumetric FlasksVolumetric flasks,
- Page 190 and 191:
Volumetric Flasksmade of PlasticVol
- Page 192 and 193:
Graduated CylindersGraduated cylind
- Page 194 and 195:
Graduated CylindersDispensers, tilt
- Page 196 and 197:
Plastic Graduated CylindersGraduate
- Page 198 and 199:
BurettesBurettes, lateral stopcockB
- Page 200 and 201:
BurettesBurettes, lateral stopcockS
- Page 202 and 203:
BurettesThe Modular Burette Concept
- Page 204 and 205:
BurettesCompact burettes, 'Economy'
- Page 206 and 207:
Automatic BurettesAutomatic burette
- Page 208 and 209:
Automatic BurettesAutomatic burette
- Page 210 and 211:
Automatic BurettesCompact automatic
- Page 212 and 213:
Spare Burette StopcocksSpare burett
- Page 214 and 215:
Burette AccessoriesBurette clampAll
- Page 216 and 217:
Volumetric InstrumentsBRAND onlineV
- Page 218 and 219:
Temperatureand DensityMeasurementFo
- Page 220 and 221:
Oxygen flasksDensity bottles,uncali
- Page 222 and 223:
Sedimentation ConesASTM centrifuge
- Page 224 and 225:
Racks forSedimentation ConesRack fo
- Page 226 and 227:
HydrometersRange finder hydrometers
- Page 228 and 229:
HydrometersGeneral purpose alcoholo
- Page 230 and 231:
ThermometersThermometerBRAND thermo
- Page 232 and 233:
ThermometersSolid-stem thermometers
- Page 234 and 235:
Thermometers1Precision Anschutz the
- Page 236 and 237:
ThermometersASTM thermometersASTMNo
- Page 238 and 239:
Temperature and DensityBRAND online
- Page 240 and 241:
ClinicalLaboratoryClinical laborato
- Page 242 and 243:
JarsJar with snap-on lidJar PS, sna
- Page 244 and 245:
Disposal Bags · ContainersDisposal
- Page 246 and 247:
Culture TubesCentrifuge TubesCultur
- Page 248 and 249:
TubesSample tubesPS, transparent.Cl
- Page 250 and 251:
Pasteur PipettesDropping PipettesPa
- Page 252 and 253:
Disposable MicropipettesDisposable
- Page 254 and 255:
Counting ChambersCounting ChambersC
- Page 256 and 257:
Counting ChambersThomadouble ruling
- Page 258 and 259:
Haematology · MicroscopyHaemacytom
- Page 260 and 261:
MicroscopyStaining trough, CoplinSo
- Page 262 and 263:
Clinical LaboratoryBRAND onlineClin
- Page 264 and 265:
GeneralLaboratorySuppliesSample pre
- Page 266 and 267:
Erlenmeyer Flasks · BeakersErlenme
- Page 268 and 269:
BeakersGraduated beakers with handl
- Page 270 and 271:
Watch GlassesEvaporating DishesWatc
- Page 272 and 273:
Centrifuge tubes · Test tubesCentr
- Page 274 and 275:
FunnelsFunnelsfluted interiorPP. Fo
- Page 276 and 277:
Separating funnelsSeparating funnel
- Page 278 and 279:
Filter FlasksRubber sleevesRubber (
- Page 280 and 281:
DesiccatorsDesiccatorsPC lid. PP ba
- Page 282 and 283: Gas Wash BottlesWash bottle head wi
- Page 284 and 285: TubingTubingPVC. Particularly high-
- Page 286 and 287: Tubing ConnectorsTubing Connectors
- Page 288 and 289: StopcocksStraight-bore stopcockswit
- Page 290 and 291: Sockets · StoppersSocketswith grip
- Page 292 and 293: StirrersStirrersGood operating char
- Page 294 and 295: Magnetic Stirring BarsCylindrical,
- Page 296 and 297: Magnetic Stirring BarsMagnetic Stir
- Page 298 and 299: Forceps · ScoopsForcepsPMP. Pointe
- Page 300 and 301: BottlesLaboratory bottlesBoro 3.3.
- Page 302 and 303: BottlesWide-mouth bottlesPE-LD, fle
- Page 304 and 305: BottlesWash bottleswithout venting
- Page 306 and 307: ContainersAtomizersPE-HD. By turnin
- Page 308 and 309: ContainersTrays (photographic trays
- Page 310 and 311: Draining RackPipette Trays and Stan
- Page 312 and 313: CleaningCleaningManual Detergents f
- Page 314 and 315: DetergentsMucocit ® -TInstrument d
- Page 316 and 317: General LaboratoryBRAND onlineGener
- Page 318 and 319: TechnicalInformationQuality Managem
- Page 320 and 321: PrecisionPrecisionWhat do "Error Li
- Page 322 and 323: Monitoring ofMeasuring InstrumentsM
- Page 324 and 325: Calculations3. Calculation of the s
- Page 326 and 327: Easy Calibration TechniqueEasy Cali
- Page 328 and 329: Calibration CertificatesDetailed Ca
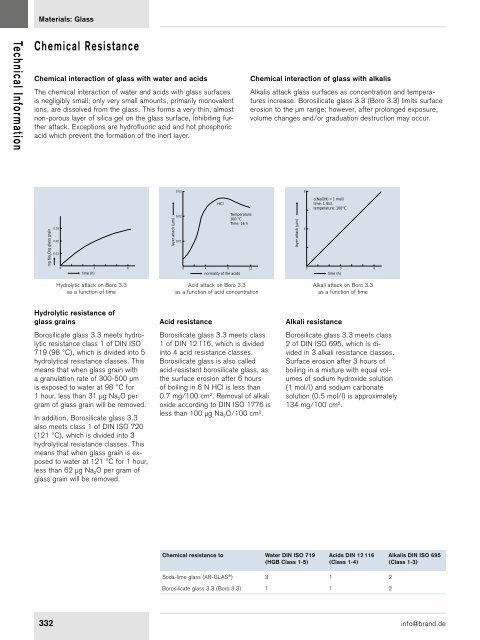
- Page 330 and 331: Monitoring ofMeasuring InstrumentsD
- Page 334 and 335: Materials: GlassMechanical Resistan
- Page 336 and 337: Materials: PlasticPVC Vinyl chlorid
- Page 338 and 339: Materials: PlasticBiological Proper
- Page 340 and 341: Materials: PlasticThe data for the
- Page 342 and 343: Materials: PlasticThe data for the
- Page 344 and 345: Cleaning (Basics)Gentle CleaningFor
- Page 346 and 347: IndexGeneral Terms and ConditionsAl
- Page 348 and 349: Alphabetical IndexDisposablesfilter
- Page 350 and 351: Alphabetical IndexSedimentationcone
- Page 352 and 353: Number IndexCat. No.Page4020 38 - 4
- Page 354: © Patrick Escudero/hemis.fr/Getty