Wheat DDGS Feed Guide - Western Canadian Feed Innovation ...
Wheat DDGS Feed Guide - Western Canadian Feed Innovation ...
Wheat DDGS Feed Guide - Western Canadian Feed Innovation ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The manufacturing process for wheat <strong>DDGS</strong> may involve high temperatures which can affect the digestibility<br />
of lysine and other nutrients through the Maillard reaction. Cozannet et al. (2010) showed that energy content,<br />
protein and amino acid digestibility is related to colour as measured by a colour meter and luminance<br />
measurements. A summary of their findings comparing dark versus light is presented in Table 10.<br />
FEEDING STUDIES<br />
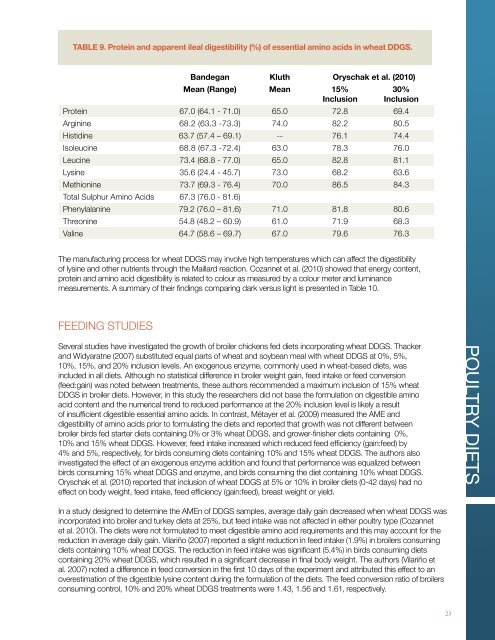
Bandegan Kluth Oryschak et al. (2010)<br />
Mean (Range) Mean 15%<br />
Inclusion<br />
30%<br />
Inclusion<br />
Protein 67.0 (64.1 - 71.0) 65.0 72.8 69.4<br />
Arginine 68.2 (63.3 -73.3) 74.0 82.2 80.5<br />
Histidine 63.7 (57.4 – 69.1) -- 76.1 74.4<br />
Isoleucine 68.8 (67.3 -72.4) 63.0 78.3 76.0<br />
Leucine 73.4 (68.8 - 77.0) 65.0 82.8 81.1<br />
Lysine 35.6 (24.4 - 45.7) 73.0 68.2 63.6<br />
Methionine 73.7 (69.3 - 76.4) 70.0 86.5 84.3<br />
Total Sulphur Amino Acids 67.3 (76.0 - 81.6)<br />
Phenylalanine 79.2 (76.0 – 81.6) 71.0 81.8 80.6<br />
Threonine 54.8 (48.2 – 60.9) 61.0 71.9 68.3<br />
Valine 64.7 (58.6 – 69.7) 67.0 79.6 76.3<br />
Several studies have investigated the growth of broiler chickens fed diets incorporating wheat <strong>DDGS</strong>. Thacker<br />
and Widyaratne (2007) substituted equal parts of wheat and soybean meal with wheat <strong>DDGS</strong> at 0%, 5%,<br />
10%, 15%, and 20% inclusion levels. An exogenous enzyme, commonly used in wheat-based diets, was<br />
included in all diets. Although no statistical difference in broiler weight gain, feed intake or feed conversion<br />
(feed:gain) was noted between treatments, these authors recommended a maximum inclusion of 15% wheat<br />
<strong>DDGS</strong> in broiler diets. However, in this study the researchers did not base the formulation on digestible amino<br />
acid content and the numerical trend to reduced performance at the 20% inclusion level is likely a result<br />
of insufficient digestible essential amino acids. In contrast, Métayer et al. (2009) measured the AME and<br />
digestibility of amino acids prior to formulating the diets and reported that growth was not different between<br />
broiler birds fed starter diets containing 0% or 3% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong>, and grower-finisher diets containing 0%,<br />
10% and 15% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong>. However, feed intake increased which reduced feed efficiency (gain:feed) by<br />
4% and 5%, respectively, for birds consuming diets containing 10% and 15% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong>. The authors also<br />
investigated the effect of an exogenous enzyme addition and found that performance was equalized between<br />
birds consuming 15% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong> and enzyme, and birds consuming the diet containing 10% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong>.<br />
Oryschak et al. (2010) reported that inclusion of wheat <strong>DDGS</strong> at 5% or 10% in broiler diets (0-42 days) had no<br />
effect on body weight, feed intake, feed efficiency (gain:feed), breast weight or yield.<br />
In a study designed to determine the AMEn of <strong>DDGS</strong> samples, average daily gain decreased when wheat <strong>DDGS</strong> was<br />
incorporated into broiler and turkey diets at 25%, but feed intake was not affected in either poultry type (Cozannet<br />
et al. 2010). The diets were not formulated to meet digestible amino acid requirements and this may account for the<br />
reduction in average daily gain. Vilariño (2007) reported a slight reduction in feed intake (1.9%) in broilers consuming<br />
diets containing 10% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong>. The reduction in feed intake was significant (5.4%) in birds consuming diets<br />
containing 20% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong>, which resulted in a significant decrease in final body weight. The authors (Vilariño et<br />
al. 2007) noted a difference in feed conversion in the first 10 days of the experiment and attributed this effect to an<br />
overestimation of the digestible lysine content during the formulation of the diets. The feed conversion ratio of broilers<br />
consuming control, 10% and 20% wheat <strong>DDGS</strong> treatments were 1.43, 1.56 and 1.61, respectively.<br />
23<br />
POULTRY DIETS