You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
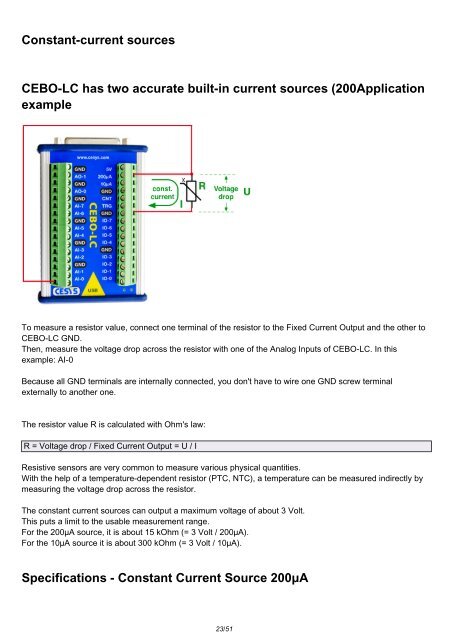
Constant-current sources<br />
<strong>CEBO</strong>-<strong>LC</strong> has two accurate built-in current sources (200Application<br />
example<br />
To measure a resistor value, connect one terminal of the resistor to the Fixed Current Output and the other to<br />
<strong>CEBO</strong>-<strong>LC</strong> GND.<br />
Then, measure the voltage drop across the resistor with one of the Analog Inputs of <strong>CEBO</strong>-<strong>LC</strong>. In this<br />
example: AI-0<br />
Because all GND terminals are internally connected, you don't have to wire one GND screw terminal<br />
externally to another one.<br />
The resistor value R is calculated with Ohm's law:<br />
R = Voltage drop / Fixed Current Output = U / I<br />
Resistive sensors are very common to measure various physical quantities.<br />
With the help of a temperature-dependent resistor (PTC, NTC), a temperature can be measured indirectly by<br />
measuring the voltage drop across the resistor.<br />
The constant current sources can output a maximum voltage of about 3 Volt.<br />
This puts a limit to the usable measurement range.<br />
For the 200µA source, it is about 15 kOhm (= 3 Volt / 200µA).<br />
For the 10µA source it is about 300 kOhm (= 3 Volt / 10µA).<br />
Specifications - Constant Current Source 200µA<br />
23/51