View - Jurnal Mekanikal - UTM
View - Jurnal Mekanikal - UTM
View - Jurnal Mekanikal - UTM
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
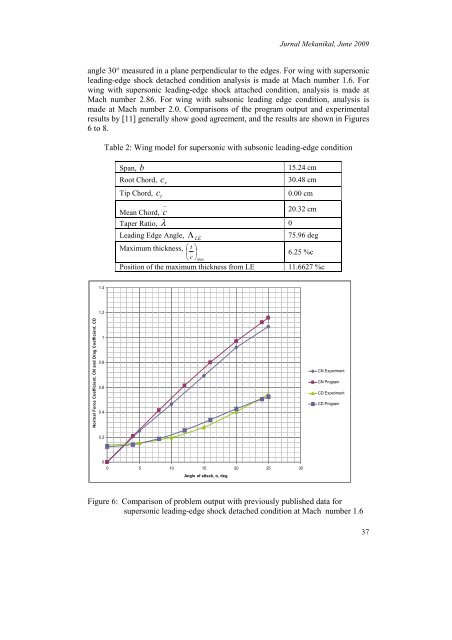
<strong>Jurnal</strong> <strong>Mekanikal</strong>, June 2009angle 30° measured in a plane perpendicular to the edges. For wing with supersonicleading-edge shock detached condition analysis is made at Mach number 1.6. Forwing with supersonic leading-edge shock attached condition, analysis is made atMach number 2.86. For wing with subsonic leading edge condition, analysis ismade at Mach number 2.0. Comparisons of the program output and experimentalresults by [11] generally show good agreement, and the results are shown in Figures6 to 8.Table 2: Wing model for supersonic with subsonic leading-edge conditionSpan, bRoot Chord,Tip Chord, ctcr_15.24 cm30.48 cm0.00 cmMean Chord, c20.32 cmTaper Ratio, λ 0Leading Edge Angle, Λ 75.96 degLEMaximum thickness, ⎛ t ⎞⎜ ⎟⎝ c ⎠max6.25 %cPosition of the maximum thickness from LE 11.6627 %c1.41.2Normal Force Coefficient, CN and Drag Coefficient, CD10.80.60.4CN ExperimentCN ProgramCD ExperimentCD Program0.200 5 10 15 20 25 30Angle of attack, α, degFigure 6: Comparison of problem output with previously published data forsupersonic leading-edge shock detached condition at Mach number 1.637