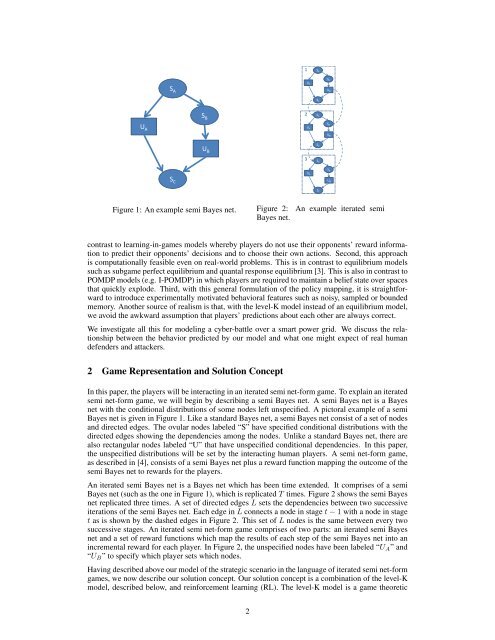
1S AS BS AU BU AS CS B2S AU AU AS BU BU B3S CS AS BS CU BU AS CFigure 1: An example semi Bayes net.Figure 2:Bayes net.An example iterated semicontrast to learning-in-games models whereby players do not use their opponents’ reward informationto predict their opponents’ <strong>decision</strong>s and to choose their own actions. Second, this approachis computationally feasible even on real-world problems. This is in contrast to equilibrium modelssuch as subgame perfect equilibrium and quantal response equilibrium [3]. This is also in contrast toPOMDP models (e.g. I-POMDP) in which players are required to maintain a belief state over spacesthat quickly explode. Third, <strong>with</strong> this general formulation <strong>of</strong> the policy mapping, it is straightforwardto introduce experimentally motivated behavioral features such as noisy, sampled or boundedmemory. Another source <strong>of</strong> realism is that, <strong>with</strong> the level-K model instead <strong>of</strong> an equilibrium model,we avoid the awkward assumption that players’ predictions about each other are always correct.We investigate all this for modeling a cyber-battle over a smart power grid. We discuss the relationshipbetween the behavior predicted by our model and what one might expect <strong>of</strong> real humandefenders and attackers.2 Game Representation and Solution ConceptIn this paper, the players will be interacting in an iterated semi net-form game. To explain an iteratedsemi net-form game, we will begin by describing a semi Bayes net. A semi Bayes net is a Bayesnet <strong>with</strong> the conditional distributions <strong>of</strong> some nodes left unspecified. A pictoral example <strong>of</strong> a semiBayes net is given in Figure 1. Like a standard Bayes net, a semi Bayes net consist <strong>of</strong> a set <strong>of</strong> nodesand directed edges. The ovular nodes labeled “S” have specified conditional distributions <strong>with</strong> thedirected edges showing the dependencies among the nodes. Unlike a standard Bayes net, there arealso rectangular nodes labeled “U” that have unspecified conditional dependencies. In this paper,the unspecified distributions will be set by the interacting human players. A semi net-form game,as described in [4], consists <strong>of</strong> a semi Bayes net plus a reward function mapping the outcome <strong>of</strong> thesemi Bayes net to rewards for the players.An iterated semi Bayes net is a Bayes net which has been time extended. It comprises <strong>of</strong> a semiBayes net (such as the one in Figure 1), which is replicated T times. Figure 2 shows the semi Bayesnet replicated three times. A set <strong>of</strong> directed edges L sets the dependencies between two successiveiterations <strong>of</strong> the semi Bayes net. Each edge in L connects a node in stage t − 1 <strong>with</strong> a node in staget as is shown by the dashed edges in Figure 2. This set <strong>of</strong> L nodes is the same between every twosuccessive stages. An iterated semi net-form game comprises <strong>of</strong> two parts: an iterated semi Bayesnet and a set <strong>of</strong> reward functions which map the results <strong>of</strong> each step <strong>of</strong> the semi Bayes net into anincremental reward for each player. In Figure 2, the unspecified nodes have been labeled “U A ” and“U B ” to specify which player sets which nodes.Having described above our model <strong>of</strong> the strategic scenario in the language <strong>of</strong> iterated semi net-formgames, we now describe our solution concept. Our solution concept is a combination <strong>of</strong> the level-Kmodel, described below, and reinforcement learning (RL). The level-K model is a game theoretic2
solution concept used to predict the outcome <strong>of</strong> human-human interactions. A number <strong>of</strong> studies[1, 2] have shown promising results predicting experimental data in games using this method. Thesolution to the level-K model is defined recursively as follows. A level K player plays as though allother players are playing at level K − 1, who, in turn, play as though all other players are playingat level K − 2, etc. The process continues until level 0 is reached, where the level 0 player playsaccording to a prespecified prior distribution. Notice that running this process for a player at K ≥ 2results in ricocheting between players. For example, if player A is a level 2 player, he plays asthough player B is a level 1 player, who in turn plays as though player A is a level 0 player playingaccording to the prior distribution. Note that player B in this example may not actually be a level 1player in reality – only that player A assumes him to be during his reasoning process.This work extends the standard level-K model to time-extended strategic scenarios, such as iteratedsemi net-form games. In particular, each Undetermined node associated <strong>with</strong> player i in the iteratedsemi net-form game represents an action choice by player i at some time t. We model player i’saction choices using the policy function, ρ i , which takes an element <strong>of</strong> the Cartesian product <strong>of</strong>the spaces given by the parent nodes <strong>of</strong> i’s Undetermined node to an action for player i. Note thatthis definition requires a special type <strong>of</strong> iterated semi-Bayes net in which the spaces <strong>of</strong> the parents<strong>of</strong> each <strong>of</strong> i’s action nodes must be identical. This requirement ensures that the policy function isalways well-defined and acts on the same domain at every step in the iterated semi net-form game.We calculate policies using reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms. That is, we first define a level0 policy for each player, ρ 0 i . We then use RL to find player i’s level 1 policy, ρ1 i , given the level 0policies <strong>of</strong> the other players, ρ 0 −1, and the iterated semi net-form game. We do this for each player iand each level K. 13 Application: Cybersecurity <strong>of</strong> a Smart Power NetworkIn order to test our iterated semi net-form game modeling concept, we adopt a model for analyzingthe behavior <strong>of</strong> intruders into cyber-physical systems. In particular, we consider SupervisoryControl and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems [5], which are used to monitor and control manytypes <strong>of</strong> critical infrastructure. A SCADA system consists <strong>of</strong> cyber-communication infrastructurethat transmits data from and sends control commands to physical devices, e.g. circuit breakers inthe electrical grid. SCADA systems are partly automated and partly human-operated. Increasingconnection to other cyber systems creating vulnerabilities to SCADA cyber attackers [6].Figure 3 shows a single, radial distribution circuit [7] from the transformer at a substation (node1) serving two load nodes. Node 2 is an aggregate <strong>of</strong> small consumer loads distributed along thecircuit, and node 3 is a relatively large distributed generator located near the end <strong>of</strong> the circuit. Inthis figure V i , p i , and q i are the voltage, real power, and reactive power at node i. P i , Q i , r i , andx i are the real power, reactive power, resistance and reactance <strong>of</strong> circuit segment i. Together, thesevalues represent the following physical system [7], where all terms are normalized by the nominalsystem voltage.P 2 = −p 3 , Q 2 = −q 3 , P 1 = P 2 + p 2 , Q 1 = Q 2 + q 2 (1)V 2 = V 1 − (r 1 P 1 + x 1 Q 1 ), V 3 = V 2 − (r 2 P 2 + x 2 Q 2 ) (2)In this model, r, x, and p 3 are static parameters, q 2 and p 2 are drawn from a random distributionat each step <strong>of</strong> the game, V 1 is the <strong>decision</strong> variable <strong>of</strong> the defender, q 3 is the <strong>decision</strong> variable <strong>of</strong>the attacker, and V 2 and V 3 are determined by the equations above. The injection <strong>of</strong> real powerp 3 and reactive power q 3 can modify the P i and Q i causing the voltage V 2 to deviate from 1.0.Excessive deviation <strong>of</strong> V 2 or V 3 can damage customer equipment or even initiate a cascading failurebeyond the circuit in question. In this example, the SCADA operator’s (defender’s) control over q 3is compromised by an attacker who seeks to create deviations <strong>of</strong> V 2 causing damage to the system.In this model, the defender has direct control over V 1 via a variable-tap transformer. The hardware<strong>of</strong> the transformer limits the defenders actions at time t to the following domainD D (t) = 〈min(v max , V 1,t−1 + v), V 1,t−1 , max(v min , V 1,t−1 − v)〉1 Although this work uses level-K and RL exclusively, we are by no means wedded to this solution concept.Previous work on semi net-form games used a method known as Level-K Best-<strong>of</strong>-M/M’ instead <strong>of</strong> RL todetermine actions. This was not used in this paper because the possible action space is so large.3
- Page 1 and 2: The 2nd International Workshop onDE
- Page 3 and 4: The 2nd International Workshop onDE
- Page 5 and 6: Time Title Authors7:30—7:50 Openi
- Page 7: Modeling Humans as Reinforcement Le
- Page 11 and 12: an ɛ-greedy policy parameterizatio
- Page 13 and 14: Automated Explanations for MDP Poli
- Page 15 and 16: V E = ∑ i∈Eλ π∗s 0(sc i )
- Page 17 and 18: Figure 1: User Perception of MDP-Ba
- Page 19 and 20: [9] Warren B. Powell. Approximate D
- Page 21 and 22: information (technological knowledg
- Page 23 and 24: The complete fulfilment of preferen
- Page 25 and 26: References[1] J.O. Berger. Statisti
- Page 27 and 28: (happiness, anger, fear, disgust, s
- Page 30 and 31: David H Wolpert, editors, Decision
- Page 32 and 33: on some of their concepts, we devel
- Page 34 and 35: We assume that they are evaluated t
- Page 36 and 37: AcknowledgmentsResearch supported b
- Page 38 and 39: Bayesian Combination of Multiple, I
- Page 40 and 41: is not in closed form [5], requirin
- Page 42 and 43: where α (k)j is updated by adding
- Page 44 and 45: Figure 3: Prototypical confusion ma
- Page 46 and 47: Artificial Intelligence Designfor R
- Page 48 and 49: the game. Each has its own attribut
- Page 50 and 51: 4.3 Experimental Results and Limita
- Page 52 and 53: Distributed Decision Making byCateg
- Page 54 and 55: q 1a 1 (1) b 1(1)a 2(1)b 2(1)a K(1)
- Page 56 and 57: Bayes risk0.250.20.150.10.05Collabo
- Page 58 and 59:
Decision making and working memory
- Page 60 and 61:
in WM as well as inhibitory tasks [
- Page 62 and 63:
Difficulty level will be automatica
- Page 64 and 65:
Overall, the current literature lea
- Page 66 and 67:
[31] W K Bickel, R Yi, R D Landes,
- Page 68 and 69:
Each time instant, the agents first
- Page 70 and 71:
Figure 2: Two basic decentralized a
- Page 72 and 73:
[11] M. Kárný and T.V. Guy. Shari
- Page 74 and 75:
these results yields a design metho
- Page 76 and 77:
Minimum of (16) is well known from
- Page 78 and 79:
Algorithm 2 VB-DP variant of the di
- Page 80 and 81:
Further simplications can be achiev
- Page 82 and 83:
The basic terms we use are as follo
- Page 84 and 85:
3 Connection to the Bayesian soluti
- Page 86 and 87:
4 ConclusionThis paper brings an im
- Page 88 and 89:
2 Dynamic programming and revisions
- Page 90 and 91:
The possible way how to recognize t
- Page 92 and 93:
The data used for experiment are da
- Page 95:
T.V. Guy, Institute of Information