CHAPTER 2 BARRIER WARRANTS
CHAPTER 2 BARRIER WARRANTS
CHAPTER 2 BARRIER WARRANTS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
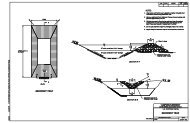
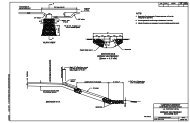
Barrier Warrants ________ November 20052.3.2 Crash HistoryCrash history, if available, can also be of assistance in identifying and evaluatinghazards. In order to identify significant patterns, a history of several years is needed.Three to five years is usually sufficient, but even longer periods are useful for lowvolume roads. There is a certain amount of randomness with roadside crashes.Therefore, a crash analysis should look for patterns of crashes at several sites thatshare common characteristics, such as roadway features and hazard types. Care mustbe taken to avoid overreacting to one severe crash at a specific site when there is noestablished pattern. Otherwise, an expensive corrective action may be constructed tocorrect a problem that may never recur.2.3.3 Innocent Bystander WarrantA final consideration is what is known as the innocent bystander warrant. In this casethe issue is not protecting the occupants of an errant vehicle, but protecting nonmotoristsor sensitive roadside conditions. Examples are a school playground that iswithin the needed clear zone, pedestrian facilities within the clear zone that will be usedfrequently by many pedestrians who may be inattentive to traffic or homes within theclear zone. Application of this warrant is difficult to quantify but it should follow the samegeneral process discussed in this chapter, evaluating both risks and costs of placing ornot placing barriers.________________________________________________________________________2-12 Identify Potential Hazards