Transmission Network Performance Report 2005 - National Grid
Transmission Network Performance Report 2005 - National Grid
Transmission Network Performance Report 2005 - National Grid
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
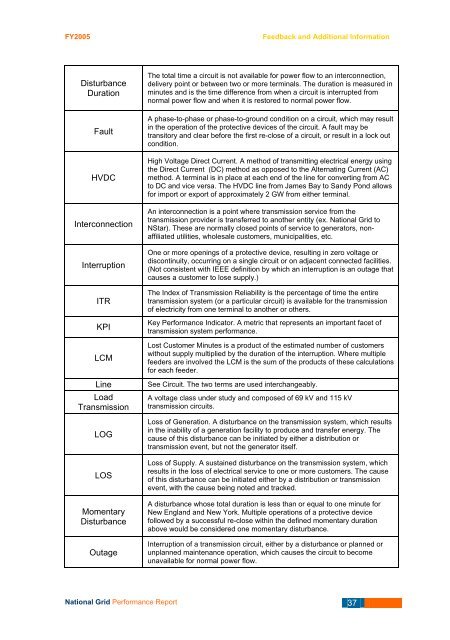
FY<strong>2005</strong>Feedback and Additional InformationDisturbanceDurationFaultHVDCInterconnectionInterruptionITRKPILCMLineLoad<strong>Transmission</strong>LOGLOSMomentaryDisturbanceOutageThe total time a circuit is not available for power flow to an interconnection,delivery point or between two or more terminals. The duration is measured inminutes and is the time difference from when a circuit is interrupted fromnormal power flow and when it is restored to normal power flow.A phase-to-phase or phase-to-ground condition on a circuit, which may resultin the operation of the protective devices of the circuit. A fault may betransitory and clear before the first re-close of a circuit, or result in a lock outcondition.High Voltage Direct Current. A method of transmitting electrical energy usingthe Direct Current (DC) method as opposed to the Alternating Current (AC)method. A terminal is in place at each end of the line for converting from ACto DC and vice versa. The HVDC line from James Bay to Sandy Pond allowsfor import or export of approximately 2 GW from either terminal.An interconnection is a point where transmission service from thetransmission provider is transferred to another entity (ex. <strong>National</strong> <strong>Grid</strong> toNStar). These are normally closed points of service to generators, nonaffiliatedutilities, wholesale customers, municipalities, etc.One or more openings of a protective device, resulting in zero voltage ordiscontinuity, occurring on a single circuit or on adjacent connected facilities.(Not consistent with IEEE definition by which an interruption is an outage thatcauses a customer to lose supply.)The Index of <strong>Transmission</strong> Reliability is the percentage of time the entiretransmission system (or a particular circuit) is available for the transmissionof electricity from one terminal to another or others.Key <strong>Performance</strong> Indicator. A metric that represents an important facet oftransmission system performance.Lost Customer Minutes is a product of the estimated number of customerswithout supply multiplied by the duration of the interruption. Where multiplefeeders are involved the LCM is the sum of the products of these calculationsfor each feeder.See Circuit. The two terms are used interchangeably.A voltage class under study and composed of 69 kV and 115 kVtransmission circuits.Loss of Generation. A disturbance on the transmission system, which resultsin the inability of a generation facility to produce and transfer energy. Thecause of this disturbance can be initiated by either a distribution ortransmission event, but not the generator itself.Loss of Supply. A sustained disturbance on the transmission system, whichresults in the loss of electrical service to one or more customers. The causeof this disturbance can be initiated either by a distribution or transmissionevent, with the cause being noted and tracked.A disturbance whose total duration is less than or equal to one minute forNew England and New York. Multiple operations of a protective devicefollowed by a successful re-close within the defined momentary durationabove would be considered one momentary disturbance.Interruption of a transmission circuit, either by a disturbance or planned orunplanned maintenance operation, which causes the circuit to becomeunavailable for normal power flow.<strong>National</strong> <strong>Grid</strong> <strong>Performance</strong> <strong>Report</strong> 37