an innovative algorithm for key frame extraction in video ...
an innovative algorithm for key frame extraction in video ...
an innovative algorithm for key frame extraction in video ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
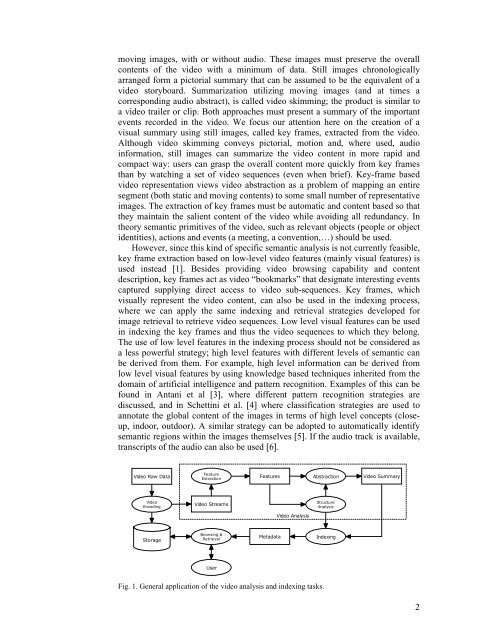
mov<strong>in</strong>g images, with or without audio. These images must preserve the overallcontents of the <strong>video</strong> with a m<strong>in</strong>imum of data. Still images chronologicallyarr<strong>an</strong>ged <strong>for</strong>m a pictorial summary that c<strong>an</strong> be assumed to be the equivalent of a<strong>video</strong> storyboard. Summarization utiliz<strong>in</strong>g mov<strong>in</strong>g images (<strong>an</strong>d at times acorrespond<strong>in</strong>g audio abstract), is called <strong>video</strong> skimm<strong>in</strong>g; the product is similar toa <strong>video</strong> trailer or clip. Both approaches must present a summary of the import<strong>an</strong>tevents recorded <strong>in</strong> the <strong>video</strong>. We focus our attention here on the creation of avisual summary us<strong>in</strong>g still images, called <strong>key</strong> <strong>frame</strong>s, extracted from the <strong>video</strong>.Although <strong>video</strong> skimm<strong>in</strong>g conveys pictorial, motion <strong>an</strong>d, where used, audio<strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation, still images c<strong>an</strong> summarize the <strong>video</strong> content <strong>in</strong> more rapid <strong>an</strong>dcompact way: users c<strong>an</strong> grasp the overall content more quickly from <strong>key</strong> <strong>frame</strong>sth<strong>an</strong> by watch<strong>in</strong>g a set of <strong>video</strong> sequences (even when brief). Key-<strong>frame</strong> based<strong>video</strong> representation views <strong>video</strong> abstraction as a problem of mapp<strong>in</strong>g <strong>an</strong> entiresegment (both static <strong>an</strong>d mov<strong>in</strong>g contents) to some small number of representativeimages. The <strong>extraction</strong> of <strong>key</strong> <strong>frame</strong>s must be automatic <strong>an</strong>d content based so thatthey ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> the salient content of the <strong>video</strong> while avoid<strong>in</strong>g all redund<strong>an</strong>cy. Intheory sem<strong>an</strong>tic primitives of the <strong>video</strong>, such as relev<strong>an</strong>t objects (people or objectidentities), actions <strong>an</strong>d events (a meet<strong>in</strong>g, a convention,…) should be used.However, s<strong>in</strong>ce this k<strong>in</strong>d of specific sem<strong>an</strong>tic <strong>an</strong>alysis is not currently feasible,<strong>key</strong> <strong>frame</strong> <strong>extraction</strong> based on low-level <strong>video</strong> features (ma<strong>in</strong>ly visual features) isused <strong>in</strong>stead [1]. Besides provid<strong>in</strong>g <strong>video</strong> brows<strong>in</strong>g capability <strong>an</strong>d contentdescription, <strong>key</strong> <strong>frame</strong>s act as <strong>video</strong> “bookmarks” that designate <strong>in</strong>terest<strong>in</strong>g eventscaptured supply<strong>in</strong>g direct access to <strong>video</strong> sub-sequences. Key <strong>frame</strong>s, whichvisually represent the <strong>video</strong> content, c<strong>an</strong> also be used <strong>in</strong> the <strong>in</strong>dex<strong>in</strong>g process,where we c<strong>an</strong> apply the same <strong>in</strong>dex<strong>in</strong>g <strong>an</strong>d retrieval strategies developed <strong>for</strong>image retrieval to retrieve <strong>video</strong> sequences. Low level visual features c<strong>an</strong> be used<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dex<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>key</strong> <strong>frame</strong>s <strong>an</strong>d thus the <strong>video</strong> sequences to which they belong.The use of low level features <strong>in</strong> the <strong>in</strong>dex<strong>in</strong>g process should not be considered asa less powerful strategy; high level features with different levels of sem<strong>an</strong>tic c<strong>an</strong>be derived from them. For example, high level <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation c<strong>an</strong> be derived fromlow level visual features by us<strong>in</strong>g knowledge based techniques <strong>in</strong>herited from thedoma<strong>in</strong> of artificial <strong>in</strong>telligence <strong>an</strong>d pattern recognition. Examples of this c<strong>an</strong> befound <strong>in</strong> Ant<strong>an</strong>i et al [3], where different pattern recognition strategies arediscussed, <strong>an</strong>d <strong>in</strong> Schett<strong>in</strong>i et al. [4] where classification strategies are used to<strong>an</strong>notate the global content of the images <strong>in</strong> terms of high level concepts (closeup,<strong>in</strong>door, outdoor). A similar strategy c<strong>an</strong> be adopted to automatically identifysem<strong>an</strong>tic regions with<strong>in</strong> the images themselves [5]. If the audio track is available,tr<strong>an</strong>scripts of the audio c<strong>an</strong> also be used [6].Video Raw DataFeatureExtractionFeaturesAbstractionVideo SummaryVideoEncod<strong>in</strong>gVideo StreamsStructureAnalysisVideo AnalysisStorageBrows<strong>in</strong>g &RetrievalMetadataIndex<strong>in</strong>gUserFig. 1. General application of the <strong>video</strong> <strong>an</strong>alysis <strong>an</strong>d <strong>in</strong>dex<strong>in</strong>g tasks.2