- Page 1 and 2:
University of CassinoFaculty of Eng
- Page 3 and 4:
Contents1. INTRODUCTION ...........
- Page 5 and 6:
5.2.1.2. Finite Element Approximati
- Page 7 and 8:
1 INTRODUCTIONScience and technolog
- Page 9 and 10:
The implementations of the model in
- Page 11 and 12:
applications are presented in order
- Page 13 and 14:
2 SHAPE MEMORY ALLOYS2.1 Introducti
- Page 16 and 17:
transformation (M→A), indicated r
- Page 18:
Fig. 2.2: SuperelasticityFig. 2.3:
- Page 21 and 22:
The Differential Scanning Calorimet
- Page 23 and 24:
2.3 Biocompatibility of Shape-Memor
- Page 25 and 26:
only in the angioplasty procedure,
- Page 27 and 28:
micropumps used to unblock blood ve
- Page 29 and 30:
introduction of a multi-well free-e
- Page 31 and 32:
spectral decomposition allowing the
- Page 33 and 34:
Fig. 3.1: Reference and deformed co
- Page 35 and 36:
δ δ = δ and δ δ = δ(3.6)iI iJ
- Page 37 and 38:
and it is a two-point tensor since
- Page 39 and 40:
Furthermore,( ) 2 2Jdet b= det F =
- Page 41 and 42:
3.2.3 Polar DecompositionThe deform
- Page 43 and 44:
which can now be interpreted as fir
- Page 45 and 46:
Fig. 3.2: Representation of the pol
- Page 47 and 48:
ecause, as time progresses, the spe
- Page 49 and 50:
It can be introduced the rotated ra
- Page 51 and 52:
traction vector. For the Cauchy’s
- Page 53 and 54:
Nt per unit area acting on the boun
- Page 55 and 56:
transforms according to a= Qa. Velo
- Page 57 and 58:
∂∂t=−∂F∂t−1 −1 −1F
- Page 59 and 60:
where the direct dependency upon X
- Page 61 and 62:
3.4.2 Isotropic Hyperelasticity - M
- Page 63 and 64:
such phenomena as the Bauschinger e
- Page 65 and 66:
superposed to intermediate configur
- Page 67 and 68:
whereΨerepresents the elastic stra
- Page 69 and 70:
( )( ) E 1 ( )Ψ = h ω β T − M
- Page 71 and 72:
4.2.2 Clausius-Duhem InequalityIn o
- Page 73 and 74:
−1∂Ψe−TS− 2FtFt= 0∂Ce(4.
- Page 75 and 76:
qφ = T : dt− ⋅gradT≥0(4.30)T
- Page 77 and 78: fact the values of ϕ andenergy usu
- Page 79 and 80: 4.2.5 Final Format of the Constitut
- Page 81 and 82: 1 ( C )*1t−1α = ( β T − M ( )
- Page 83 and 84: 5 FINITE STRAIN CONSTITUTIVE MODEL:
- Page 85 and 86: 2 3ζ 2 ζ 3exp( ζ g) = 1+ ζ g+ g
- Page 87 and 88: where d is a user-defined parameter
- Page 89 and 90: ⎡R R Rt⎢⎢RR Rt⎢⎣R R RtC C
- Page 91 and 92: γ• R,Ct=12EEtt(5.28)• R γ ,
- Page 93 and 94: The spatial virtual work equation s
- Page 95 and 96: [ E E E 2 E 2 E 2 E ]δE = δ δ δ
- Page 97 and 98: ˆNLB = B + B (5.51)a a ain whichBa
- Page 99 and 100: Kirchhoff stress and converting int
- Page 101 and 102: DF( φ)[ u]d=dεε = 0( φ εu)∂
- Page 103 and 104: In terms of the linear strain tenso
- Page 105 and 106: 6.2 3D Constitutive Model for Stres
- Page 107 and 108: T − Mf Tη = η0− ⎡⎣h( ω)
- Page 109 and 110: assumed to be ruled by the limit fu
- Page 111 and 112: ♦The limit function is assumed fu
- Page 113 and 114: 6.3.1.1 Time Integration of the 3D
- Page 115 and 116: ⎧∂f∂ ε⎪ C ⎡⎤⎣ ⎦⎪
- Page 117 and 118: RRRRRRRR*( f )2 2 2Xd, X= I+ hΔ ζ
- Page 119 and 120: If equation (6.42) is considered as
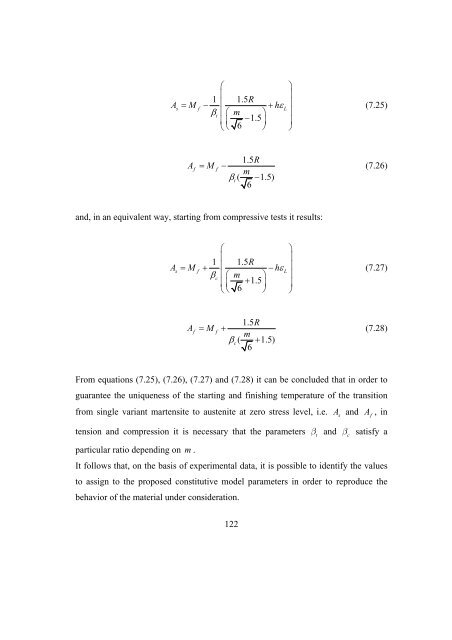
- Page 121 and 122: 7 3D-1D Constitutive Model with 1D
- Page 123 and 124: *∂f6 3σ9 3 2 2 T Ml− hϑ+mz β
- Page 125 and 126: ⎡⎤⎢1 0 0 ⎥⎢⎥1ε t= ϑ
- Page 127: (7.21)σ3 1.5R=− βc( T − Mf)+2
- Page 131 and 132: It can be noted that equations (7.3
- Page 133 and 134: The inelastic step is solved by the
- Page 135 and 136: For brevity, only the saturated pha
- Page 137 and 138: Fig. 7.2. Timoshenko’s beam theor
- Page 139 and 140: NNNv1v2v3N θ1= ξξ ( − 1)21= ξ
- Page 141 and 142: to analyze the two-dimensional elem
- Page 143 and 144: 300 N . A regular mesh characterize
- Page 145 and 146: 8.1.1.3 Superelastic and Shape-Memo
- Page 147 and 148: 200180T=285 K160140120Force [N]1008
- Page 149 and 150: 8.1.2 Comparison between 3D and 3D-
- Page 151 and 152: PhLFig. 8.7: Geometry and boundary
- Page 153 and 154: 250200150100Axial force [N]500-50-1
- Page 155 and 156: 908070Bending moment [Nmm]605040302
- Page 157 and 158: The arch is subjected to tension-co
- Page 159 and 160: 10864Axial force [N]20-2-4-6-8beam
- Page 161 and 162: Some parameters characterizing the
- Page 163 and 164: 9876Applied load [N]54321Numerical
- Page 165 and 166: The proposed constitutive models se
- Page 167 and 168: REFERENCESAdler P.H., Yu W., Pelton
- Page 169 and 170: Auricchio F., Taylor R., A return-m
- Page 171 and 172: Ciarlet P.G., The Finite Element Me
- Page 173 and 174: Huang M.S., Brinson L.C., A multiva
- Page 175 and 176: Raniecki B., Lexcellent Ch., Thermo
- Page 177: Taylor G.I., Plastic strain in meta