You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
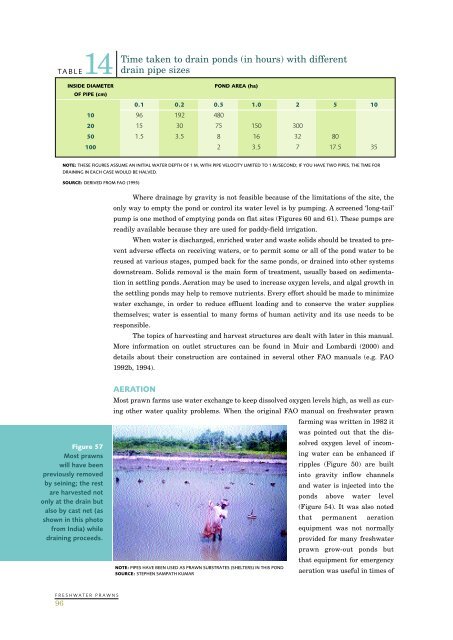
Time taken to drain ponds (in hours) with differentTABLE14 drain pipe sizesINSIDE DIAMETERPOND AREA (ha)OF PIPE (cm)0.1 0.2 0.5 1.0 2 5 1010 96 192 48020 15 30 75 150 30050 1.5 3.5 8 16 32 80100 2 3.5 7 17.5 35NOTE: THESE FIGURES ASSUME AN INITIAL WATER DEPTH OF 1 M, WITH PIPE VELOCITY LIMITED TO 1 M/SECOND; IF YOU HAVE TWO PIPES, THE TIME FORDRAINING IN EACH CASE WOULD BE HALVED.SOURCE: DERIVED FROM FAO (1995)Where drainage by gravity is not feasible because of the limitations of the site, theonly way to empty the pond or control its water level is by pumping. A screened ‘long-tail’pump is one method of emptying ponds on flat sites (Figures 60 and 61). These pumps arereadily available because they are used for paddy-field irrigation.When water is discharged, enriched water and waste solids should be treated to preventadverse effects on receiving waters, or to permit some or all of the pond water to bereused at various stages, pumped back for the same ponds, or drained into other systemsdownstream. Solids removal is the main form of treatment, usually based on sedimentationin settling ponds. Aeration may be used to increase oxygen levels, and algal growth inthe settling ponds may help to remove nutrients. Every effort should be made to minimizewater exchange, in order to reduce effluent loading and to conserve the water suppliesthemselves; water is essential to many forms of human activity and its use needs to beresponsible.The topics of harvesting and harvest structures are dealt with later in this manual.More information on outlet structures can be found in Muir and Lombardi (2000) anddetails about their construction are contained in several other FAO manuals (e.g. FAO1992b, 1994).Figure 57Most <strong>prawns</strong>will have beenpreviously removedby seining; the restare harvested notonly at the drain butalso by cast net (asshown in this photofrom India) whiledraining proceeds.AERATIONMost prawn farms use water exchange to keep dissolved oxygen levels high, as well as curingother water quality problems. When the original FAO manual on <strong>freshwater</strong> prawnfarming was written in 1982 itwas pointed out that the dissolvedoxygen level of incomingwater can be enhanced ifripples (Figure 50) are builtinto gravity inflow channelsand water is injected into theponds above water level(Figure 54). It was also notedthat permanent aerationequipment was not normallyprovided for many <strong>freshwater</strong>prawn grow-out ponds butthat equipment for emergencyaeration was useful in times ofNOTE: PIPES HAVE BEEN USED AS PRAWN SUBSTRATES (SHELTERS) IN THIS PONDSOURCE: STEPHEN SAMPATH KUMARFRESHWATER PRAWNS96