Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
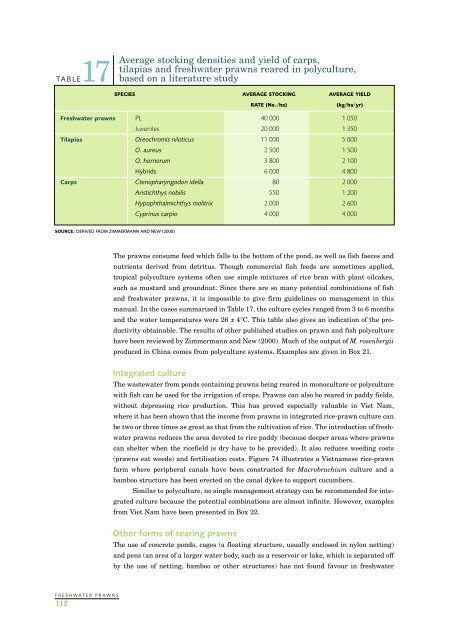
Average stocking densities and yield of carps,tilapias and <strong>freshwater</strong> <strong>prawns</strong> reared in polyculture,TABLE17 based on a literature studySPECIES AVERAGE STOCKING AVERAGE YIELDRATE (No./ha)(kg/ha/yr)Freshwater <strong>prawns</strong> PL 40 000 1 050Juveniles 20 000 1 350Tilapias Oreochromis niloticus 11 000 5 000O. aureus 2 500 1 500O. hornorum 3 800 2 100Hybrids 6 000 4 800Carps Ctenopharyngodon idella 80 2 000Aristichthys nobilis 550 1 200Hypophthalmichthys molitrix 2 000 2 600Cyprinus carpio 4 000 4 000SOURCE: DERIVED FROM ZIMMERMANN AND NEW (2000)The <strong>prawns</strong> consume feed which falls to the bottom of the pond, as well as fish faeces andnutrients derived from detritus. Though commercial fish feeds are sometimes applied,tropical polyculture systems often use simple mixtures of rice bran with plant oilcakes,such as mustard and groundnut. Since there are so many potential combinations of fishand <strong>freshwater</strong> <strong>prawns</strong>, it is impossible to give firm guidelines on management in thismanual. In the cases summarized in Table 17, the culture cycles ranged from 3 to 6 monthsand the water temperatures were 26 ± 4°C. This table also gives an indication of the productivityobtainable. The results of other published studies on prawn and fish polyculturehave been reviewed by Zimmermann and New (2000). Much of the output of M. rosenbergiiproduced in China comes from polyculture systems. Examples are given in Box 21.Integrated cultureThe wastewater from ponds containing <strong>prawns</strong> being reared in monoculture or polyculturewith fish can be used for the irrigation of crops. Prawns can also be reared in paddy fields,without depressing rice production. This has proved especially valuable in Viet Nam,where it has been shown that the income from <strong>prawns</strong> in integrated rice-prawn culture canbe two or three times as great as that from the cultivation of rice. The introduction of <strong>freshwater</strong><strong>prawns</strong> reduces the area devoted to rice paddy (because deeper areas where <strong>prawns</strong>can shelter when the ricefield is dry have to be provided). It also reduces weeding costs(<strong>prawns</strong> eat weeds) and fertilisation costs. Figure 74 illustrates a Vietnamese rice-prawnfarm where peripheral canals have been constructed for Macrobrachium culture and abamboo structure has been erected on the canal dykes to support cucumbers.Similar to polyculture, no single management strategy can be recommended for integratedculture because the potential combinations are almost infinite. However, examplesfrom Viet Nam have been presented in Box 22.Other forms of rearing <strong>prawns</strong>The use of concrete ponds, cages (a floating structure, usually enclosed in nylon netting)and pens (an area of a larger water body, such as a reservoir or lake, which is separated offby the use of netting, bamboo or other structures) has not found favour in <strong>freshwater</strong>FRESHWATER PRAWNS112