B. Tech. Production & Industrial Engineering - Shiats.edu.in
B. Tech. Production & Industrial Engineering - Shiats.edu.in
B. Tech. Production & Industrial Engineering - Shiats.edu.in
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
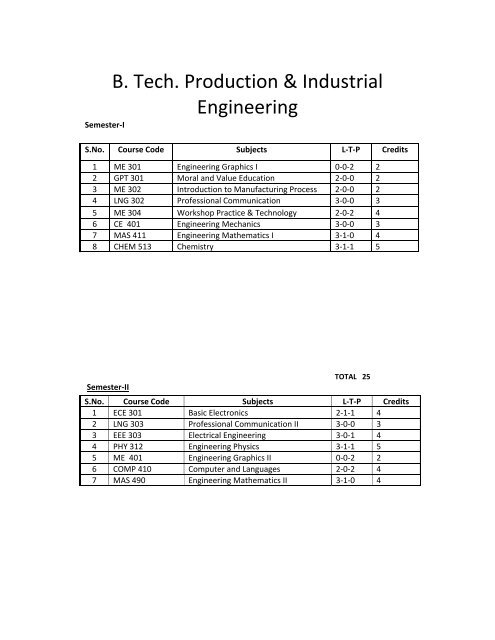
B. <strong>Tech</strong>. <strong>Production</strong> & <strong>Industrial</strong><strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>Semester‐IS.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 ME 301 <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Graphics I 0‐0‐2 22 GPT 301 Moral and Value Education 2‐0‐0 23 ME 302 Introduction to Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Process 2‐0‐0 24 LNG 302 Professional Communication 3‐0‐0 35 ME 304 Workshop Practice & <strong>Tech</strong>nology 2‐0‐2 46 CE 401 <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mechanics 3‐0‐0 37 MAS 411 <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics I 3‐1‐0 48 CHEM 513 Chemistry 3‐1‐1 5Semester‐IITOTAL 25S.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 ECE 301 Basic Electronics 2‐1‐1 42 LNG 303 Professional Communication II 3‐0‐0 33 EEE 303 Electrical <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> 3‐0‐1 44 PHY 312 <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Physics 3‐1‐1 55 ME 401 <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Graphics II 0‐0‐2 26 COMP 410 Computer and Languages 2‐0‐2 47 MAS 490 <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics II 3‐1‐0 4
Semester‐IIITOTAL 26S.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 ME 403 Mach<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g and Computer Aided 0‐0‐2 2Draft<strong>in</strong>g2 ME 404 Applied Thermodynamics 3‐1‐1 53 CE 406 Fluid Mechanics 3‐0‐1 44 CE 408 Strength of Materials 3‐0‐0 35 ME 410 Material Science and Test<strong>in</strong>g 3‐0‐1 46 SES 415 Environmental Studies 2‐0‐0 27 COMP 510 Foundation of Information <strong>Tech</strong>nology 2‐1‐2 58 MAS 590 <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics III 3‐1‐0 4TOTAL 29Semester‐IVS.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 EEE 404 Electrical Mach<strong>in</strong>es 3‐0‐1 42 ME 405 Measurement and Metrology 2‐1‐1 43 ME 407 K<strong>in</strong>ematics of Mach<strong>in</strong>es 3‐1‐0 44 ME 411 <strong>Industrial</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> 3‐1‐0 45 ME 412 Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Science I 3‐0‐1 46 ME 416 Management Information System 3‐0‐0 37 MAS 491 Computer Based Numerical &Statistical 2‐0‐1 3<strong>Tech</strong>niquesTOTAL 26Semester‐VS.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 BAM 315 Elements of Economics and Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of 3‐1‐0 4Management Science2 ME 409 Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design I 2‐0‐2 43 ME 503 Heat and Mass Transfer 3‐0‐1 44 ME 504 Dynamic of Mach<strong>in</strong>es 3‐0‐1 45 ME 506 Product Development and Design 2‐1‐0 36 ME 507 Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Science II 3‐0‐1 47 ME 508 IC Eng<strong>in</strong>e 3‐1‐0 4TOTAL 27Semester‐VIS.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 ME 501 Tool Design 3‐0‐1 42 ME 505 Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design II 3‐0‐1 43 ME 509 Project Management 2‐1‐0 34 EEE 509 Automatic Controls 2‐1‐0 35 ME 510 Quality <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> 3‐0‐1 4
6 ME 516 Energy Management 3‐1‐0 47 ME 580 Sem<strong>in</strong>ar I 0‐0‐2 28 CE 516 Fluid Mach<strong>in</strong>ery 2‐1‐1 4TOTAL 28Note: Four Weeks Practical summer tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g‐2 after VI Semester (to be evaluated <strong>in</strong> VIISemester)Semester‐VIIS.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 ME 518 Design aga<strong>in</strong>st Fatigue and Failure 3‐1‐0 42 ME 601 Computer Aided Design 3‐0‐2 53 ME 602 Computer aided Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g 3‐0‐2 54 ME 603 Automobile <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> 2‐1‐1 45 ME 604 <strong>Industrial</strong> Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g 0‐0‐1 16 ME 680 Sem<strong>in</strong>ar II 0‐0‐2 27 ME 699a Project 0‐0‐2 2Semester‐VIIITOTAL 23S.No. Course Code Subjects L‐T‐P Credits1 ME 606 Mechanical System Design 3‐1‐0 42 ME 665‐679 Electives ‐1 3‐0‐0 33 ME 665‐679 Electives ‐2 3‐0‐0 34 ME 665‐679 Electives ‐3 3‐0‐0 35 ME 699b Project (Execution and Report ) 0‐0‐6 6TOTAL 19
SyllabusENGINEERING GRAPHICS ICourse Code ME‐301 CREDIT : 2 (0-0-2)1. Introduction: Graphics as a tool to communicate ideas, eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>struments andits uses. Letter<strong>in</strong>g and dimension<strong>in</strong>g, scales, layouts of draw<strong>in</strong>g sheets Construction ofgeometrical figures like pentagon and hexagon.2. Orthographic Projection: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of orthographic projections, Pr<strong>in</strong>cipal and auxiliaryplanes, First and Third angle projections. Projection of po<strong>in</strong>ts. Pictorial view.Projection ofl<strong>in</strong>es parallel to both the planes. Parallel to one and <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ed to other, Incl<strong>in</strong>ed to both theplanes. Application to practical problems. Projection of solid <strong>in</strong> simple position, Axis or slantedge <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ed to one and parallel to other Plane, Solids ly<strong>in</strong>g on a face or generator on a plane.Section<strong>in</strong>g of solids ly<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> various positions, True shape of the section.Development oflateral surfaces, sheet metal draw<strong>in</strong>g.3. Isometric Projection: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of isometric projection, Isometric projection us<strong>in</strong>g box andoffset methods.References:1. Bhatt N.D.: Elementary <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Draw<strong>in</strong>g, Charothar Publish<strong>in</strong>g.2. Laxmi Narayan V & Vaish W.: A Text Book of Practical Geometry on GeometricalDraw<strong>in</strong>g.MORAL AND VALUE EDUCATIONCourse Code GPT-301 CREDIT : 2 (2-0-0)My country and my people, the many Indians, be<strong>in</strong>g and becom<strong>in</strong>g an Indian, nationalism and<strong>in</strong>ternationalism.Some life issues- love, sex and marriage, men and money-value of time, mean<strong>in</strong>g of work,human communication, human suffer<strong>in</strong>g, addiction, ecology, women’s issues.Understand<strong>in</strong>g one’s neighbour, neibhourhood groups: their structure and functions,Patterns of social <strong>in</strong>teraction of group dynamics.Preparation for a career, choice of vocation, motivation for study and research. The present<strong>edu</strong>cational system: curriculum and syllabus, teach<strong>in</strong>g methods, exam<strong>in</strong>ation and workexperience.Def<strong>in</strong>ition of value <strong>edu</strong>cation, moral and ethics, laws and morale based on ten commandmentsand two great commandments.Discovery of self, self-awareness, growth of <strong>in</strong>tellect- man’s spiritual nature emotions, will,respect, the rights of life, liberty, property, truth and reputation.
S<strong>in</strong>, orign of s<strong>in</strong>, manifestation of s<strong>in</strong>, the results of s<strong>in</strong>, the remedy of s<strong>in</strong>, s<strong>in</strong> as an act, S<strong>in</strong> asa state, s<strong>in</strong> as a nature.Conscience- as def<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> oxford dictionary and W<strong>in</strong>ston dictionary. Types of consciousness(such as Evil, convicted, purged, pure, weak, good, void of offence).INTRODUCTION TO MANUFACTURING PROCESSCourse Code ME-302 CREDIT : 2 (2-0-0)1. Introduction to eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g materials- Metals & alloys- composition-properties and uses2. Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Process – Classification, mechanization, Automation , Inter-changeability,computers <strong>in</strong> manufactur<strong>in</strong>g ,CAD,CAM,CIM,MRP, GT3. Metal Form<strong>in</strong>g- Brief <strong>in</strong>troduction to press work<strong>in</strong>g, cast<strong>in</strong>g, plastic process<strong>in</strong>g ,Smithyoperations.4. Mach<strong>in</strong>e Tools-Introduction to lathe mach<strong>in</strong>es , Drill<strong>in</strong>g, Shaper, Slotter, Planer , Bor<strong>in</strong>gmach<strong>in</strong>es.5. Mach<strong>in</strong>e Operation-Turn<strong>in</strong>g, Thread<strong>in</strong>g, Bor<strong>in</strong>g, Drill<strong>in</strong>g.6. Plastic Process<strong>in</strong>gPROFESSIONAL COMUNICATION ICourse Code LNG-302 CREDIT : 3(3-0-0)1. Study of selected Literacy Texts.I.Collection of short essays.II.Collection of short stories.2. Test<strong>in</strong>g Written Comprehension Ability.: Comprehension Passages of 500 words MultipleChoice Questions.3. Composition & Grammar.4.Report Writ<strong>in</strong>g: Characteristics of Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Reports. Structure of reports: Front Matter, Ma<strong>in</strong>Body, and Back Matter Style of Reports: Def<strong>in</strong>ition, the Scientific Attitude, Readability ofReports, Choice of Words and Phrases, Construction and length of sentences, Constructionand length of Paragraphs. The l<strong>in</strong>eout or break up of a format report Blank Form Report,Frogen Report, Memoranda Form Report, Periodic Report, Miscellaneous Report.5. Speech Drills:Us<strong>in</strong>g the language laboratory to develop Speak<strong>in</strong>g Communication Skills.(i) Word Accent: <strong>Production</strong> of correct accentual patterns <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g two and three syllabiwords.(j) Rhythm: Stress-tone rhythm <strong>in</strong> sentences.(k) Intonation: Ris<strong>in</strong>g Tone and Talk<strong>in</strong>g Tone Ear Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and <strong>Production</strong> Tests.References:1. Close R.A.: A University Grammar of English Workbook.
Longman, London, 1998.2. Jones, Daniel: English Pronounc<strong>in</strong>g Dictionary, ELBS, and London, 1999.3. Sharma S.D: A Textbook of Spoken and Written English, Vikas, 1994.4. Alvarez, Joseph A.: The Elements of <strong>Tech</strong>nical Writ<strong>in</strong>g, New York: Harcourt, 1998.5. 5.Bansal, R.K.: Spoken English For India, Orient Longman, 1993.WORKSHOP PRACTICE AND TECHNOLOGYCourse Code ME-304 CREDIT : 4(2-0-2)I. Introduction to tools- Description , applications of tools used <strong>in</strong> different shops2. Carpentry- Classification of tools-mark<strong>in</strong>g and measur<strong>in</strong>g-hold<strong>in</strong>g and support<strong>in</strong>gplann<strong>in</strong>g-cutt<strong>in</strong>g-bor<strong>in</strong>g –strik<strong>in</strong>g-miscellaneous-etc.3. Fitt<strong>in</strong>g shop-Mark<strong>in</strong>g & measur<strong>in</strong>g, hold<strong>in</strong>g, cutt<strong>in</strong>g tools etc4. Smithy- hold<strong>in</strong>g and support<strong>in</strong>g tools, cutt<strong>in</strong>g tools , strik<strong>in</strong>g tools5. Sheet metal1.Weld<strong>in</strong>gII Properties of metals- Strength, elasticity , plasticity, Malleability , hardness, brittleness etc.III.Timber- Introduction-selection of timbers-season<strong>in</strong>g of timbers – timber defectsIV.Brief <strong>in</strong>troduction to jo<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g process-Nuts& bolts-Screw- Screws-rivets & rivet<strong>in</strong>g- weld<strong>in</strong>gelectricarc-gas weld<strong>in</strong>g- TIG-MIG weld<strong>in</strong>g –threadsV.Extrusion-Classification-process geometry- Geometrical relationship- analysis of extrusionstresses-load – power – maximum r<strong>edu</strong>ction possible-work<strong>in</strong>g and application of <strong>in</strong>directextrusion- hydrostatic extrusion- defects <strong>in</strong> extruded parts.VI . Forg<strong>in</strong>g – classification- strip sand disc forg<strong>in</strong>g- Process geometry-geometrical relationship-Analysis - defects <strong>in</strong> forged products .VII. Roll<strong>in</strong>g – classification-process geometry-geometrical relationship analysis-roll<strong>in</strong>g pressure &roll<strong>in</strong>g separat<strong>in</strong>g force.2)ENGINEERING MECHANICSCourse Code CE-401 CREDIT : 4 (2-0-1. force and equilibriumBasic concepts, force, moment and couple, pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of transmissibility, verigonon’s theorem,resultant of force systems, concurrent and non-concurrent coplanar forces, funicular polygon, andfree body diagram.1. TrussesPlane structures, various methods of analysis of trusses, method of jo<strong>in</strong>ts, method of sections andgraphical method.2. Moment of <strong>in</strong>ertia
Center of gravity, centroids of l<strong>in</strong>e, area, volume and composite Bodies, area moment of <strong>in</strong>ertiaand mass moment of <strong>in</strong>ertia for plane figures and bodies <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g composite bodies, productmoment of <strong>in</strong>ertia, parallel axis theorem, pr<strong>in</strong>cipal moment of <strong>in</strong>ertia.3. FrictionIntroduction, dry friction, co-efficient of static friction, friction cone, screw jack and beltfriction.4. BeamsBend<strong>in</strong>g moment and shear force diagrams for statically determ<strong>in</strong>ate beams.5. K<strong>in</strong>ematics of Rigid BodiesPlane motion, absolute motion, relative motion, translat<strong>in</strong>g axes and rotat<strong>in</strong>g axes.6. K<strong>in</strong>etics of Rigid BodiesPlane motion, force Mass and Acceleration, Work and energy, Impulse and momentum,pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of energy conservation, Pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of virtual work, D’AleMbert’s pr<strong>in</strong>cipal anddynamic equilibrium.References:1. Beer F.p and Johnston F.R: mechanics for eng<strong>in</strong>eers, McGraw hill.2. Meriam, J.L: Statistics, John Wiley.3. Meriam, J.L: Dynamics, John Wiley.4. Shames I.H: <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mechanics, Prentice Hall of India.5. Dayaratnam, P: Statistics, Tata Mc Graw Hill.6. Timeshenko, S.and Ypung D: <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mechanics, Mc Graw Hill.ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS - ICourse Code MAS-411 CREDIT : 4 (3-1-0)1. Matrices :Elementary row and column transformations, L<strong>in</strong>ear dependence, Rank ofmatrix, Consistency of system of l<strong>in</strong>ear equations and solution of l<strong>in</strong>ear equations,Characteristic equation, and Caley-Hamilton theorem, Eigen values and eigen vectors,Diagonalisation, Complex and unitary matrices.2. Differential Calculus-I:Leibnitz theorem, Partial differentiation, Euler’s theorem,Asymptotes, Curve trac<strong>in</strong>g, Change of Variables, expansion of functions of one andseveral variables. Cyl<strong>in</strong>drical and spherical coord<strong>in</strong>ate systems3. Differential Calculus-II:Jacobian, Approximation of errors, Extrema of function ofseveral variables, Lagrange’s method of multipliers (simple applications).4. Multiple <strong>in</strong>tegrals:Double and triple <strong>in</strong>tegrals, change of order, change of variables,Gamma & Beta functions,application to area, volume, Disrichlet’s <strong>in</strong>tegral and itsapplications.5. Vector Calculus:Po<strong>in</strong>t functions, Gradient, divergence and curl of a vector and theirphysical <strong>in</strong>terpretations, l<strong>in</strong>e, surface & volume <strong>in</strong>tegrals, Gauss divergence theorem andGreens & Stokes theorem.References:1. Shanti Narayan: A Text Book of matrices, S.Chand & Co.2. Thomas/F<strong>in</strong>ney: Calculus and Analytic Geometry, Narosa Pub. House.3. J. N. Kapur: Mathematical Statistis, S. Chand &Co.4. C. Prasad: Mathematics for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers, Prasad Mudranalaya.5. B.S. Grewal: Higher <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics, Khanna Publishers.6. Jaggi & Mathur : Advanced <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics, Khanna Publishers.7. Piskunov, N.: Differential & Integral Calculus, Moscow Peace Pub.
8. H.K. Das, <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics.9. Vijai Shankar Verma & Sanjeev Kumar, <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics.10. Rakesh Dubey, <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> MathematicsCHEMISTRYCourse Code CHEM-513 CREDIT : 5 (3-1-1)1. General Chemistry:Advanced Theory of Chemical Bond<strong>in</strong>g: Valence bond and molecularorbital theory. Structure of NH 3 , H 2 O, SO 3 , PCl 5 , XeO 2 molecules. Theories of bond<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>metals and semiconductors,n-type and p-type semi-conductors, Imperfections <strong>in</strong> materials.Born-Haber cycle, Bragg’s conditions.2. Physical Chemistry:Equilibrium on Reactivity: Bronsted and Lewis Acids, pH, pka, pkbScale, Buffer solution. Stereochemistry of organic compounds, Co-ord<strong>in</strong>ation chemistry,Nomenclature, Valence Bond and crystal field theory.Chemical K<strong>in</strong>etics & Catalysis: Rate law, Order of reactions, Parallel and reversiblereactions, Catalysis, Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis, Characteristics ofcatalytic reaction, Catalytic promoters and poi-sons, Auto catalysis and negativecatalysis, Intermediate compound formation theory and absorption theory.3. Environment Chemistry:Atmospheric Chemistry & Air Pollution: Environment andEcology, Environmental segments, Structure and composition of atmosphere, RadiationBalance of Earth and Green House Effect, Formation and depletion of Ozone layer,Chemical and photochemical reactions of various species <strong>in</strong> atmosphere, Air pollution –sources, reactions and s<strong>in</strong>ks for pollutants, Acid ra<strong>in</strong>s and Smog formation. Pollutioncontrol methods.Corrosion and Lubrication: Introduction, causes of corrosion, Theories of corrosion,Factors <strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g Corrosion, Corrosion <strong>in</strong>hibitors, passivity, Types of corrosion,Protection from corrosion and protective coat<strong>in</strong>gs. Theory, Classification and mechanismof Lubrication.4. Applied Chemistry:Water and Waste Water Chemistry: Introduction, Hardness ofwater, characteristics imparted by impurities, Analysis of contam<strong>in</strong>ants, Treatment ofWater by Zeolite, L-S process, Boiler feed water, Waste water treatment.5. Chemistry of <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Materials:Fuels & Combustion: Classification of fuels, Nonconventional Energy, Biogas, Biomass and solar energy. Calorific value- gross and net,characteristics of good fuel, Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of calorific value, Solid fuels, Analysis of coal,Liquid fuels.Instrumentation: IR, UV, NMR, MASS AND ASS.6. <strong>Industrial</strong> Chemistry:Polymer Chemistry: Classification of Polymers, Includ<strong>in</strong>gBiopolymers condensation and addition polymers and their applications. <strong>Industrial</strong>Application and mechanism of chemical reaction, Beckman, Hoffman, Reimer Tiemann,Cunnizzaro, Diels Alder and Skraup synthesis.References:1. Puri and Sharma/Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Physical Chemistry.2. Manas Chandra/Atomic Structure and Chemical Bond.3. Bahl and Tuli /<strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Chemistry.4. Ja<strong>in</strong> and Ja<strong>in</strong>/A Text-Book of <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Chemistry5. S.S Dara/Environmental Chemistry and Pollution Control.6. S.S Dara /Environmental Chemistry.7. A.K De/Environmental Chemistry.LIST OF EXPERIMENTS (ANY TEN):1. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the percentage of available chlor<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> the supplied sample of Bleach<strong>in</strong>gpowder.
2. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the Ferrous content <strong>in</strong> the supplied sample of iron ore by titrimetric analysisaga<strong>in</strong>st standard K Cr solution us<strong>in</strong>g K, Fe(CN) g as external <strong>in</strong>dicator.3. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the chloride content <strong>in</strong> supplied water sample us<strong>in</strong>g Mohr’s method.4. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the constituents and amount of alkal<strong>in</strong>ity of the supplied water sample.5. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the Temporary and Permanent hardness of water sample by Coplexometry.6. To f<strong>in</strong>d the Chemical Oxygen Demand of a waste water sample us<strong>in</strong>g Potassium dichromate.7. To determ<strong>in</strong>e iron concentration <strong>in</strong> the sample of water by spectrophotometric method.8. To f<strong>in</strong>d out the Velocity constant for the <strong>in</strong>version of cane sugar <strong>in</strong> acidic medium and toshow that <strong>in</strong>version follows the first order k<strong>in</strong>etics.9. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the Molecular weight of a polystyrene sample by us<strong>in</strong>g Viscometer method.10. To determ<strong>in</strong>e pH of a solution us<strong>in</strong>g a pH-meter and titration of such a solution pHmetrically.11. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the calorific value of a fuel sample by us<strong>in</strong>g a Bomb Calorimeter.12. Analysis of a coal sample by proximate analysis method.References:1. Vogel’s Qualitative Chemical Analysis: Ed. By Jaffery Bassette et. al. (ELBS).2. Applied Chemistry- Theory and Practice, 2 nd Ed. By Virmani and Narula (New AgeInternational Pub.).3. Experiments <strong>in</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Chemistry, Ed. By Masood Alam (Maktaba Jamia Limited).BASIC ELECTRONICS1-1)Course Code ECE-301 CREDIT : 4 (2-1. Energy Bands <strong>in</strong> Solids: Energy band theory of solids, Concept of forbidden gap, Insulators,Metals and Semiconductors.2. Transport Phenomenon <strong>in</strong> Semiconductors: Mobility and conductivity, electrons and holes <strong>in</strong>an <strong>in</strong>tr<strong>in</strong>sic semiconductor, Donor and acceptor impurities, Fermi level, carrier densities <strong>in</strong>semiconductor, electrical properties of semiconductor, Hall effect, Diffusion.3. Junction Diode:P-N junction, depletion layer, V-I characteristics, diode resistance,capacitance, switch<strong>in</strong>g time, diode application as a rectifier (half wave and full wave), diodecircuits (clipper, clamper, voltage multipliers) Breakdown mechanism, Zener & Avalanche,breakdown characteristics, Zener diode and its applications.4. Bi-junction Transistor:Bipolar junction Transistor, CE, CB and CC configuration,characteristic curves (cut off, active and saturation region), Requirement of bias<strong>in</strong>g, bias<strong>in</strong>g typesand bias<strong>in</strong>g analysis, stability.5. Transistor as an Amplifier:Graphical analysis of CE amplifier, concept of voltage ga<strong>in</strong>,current ga<strong>in</strong> and power ga<strong>in</strong>, h-parameter (low frequency), computation of A v , R I , R o andapproximate formulae.6. Operational Amplifiers:Concepts of ideal op-amp, <strong>in</strong>vert<strong>in</strong>g, non-<strong>in</strong>vert<strong>in</strong>g and unity ga<strong>in</strong>amplifiers, adders, difference amplifiers. , Integrators.
7. Switch<strong>in</strong>g Theory & Logic Gates: Number systems, conversion of bases, Boolean algebra,Logic Gates, concept of universal gate, canonical forms, and m<strong>in</strong>imization us<strong>in</strong>g K-map.8. Electronic Instruments: Multimeter, CRO and its Applications.References:1. Boylestad & Nashelsky/Electronic Devices & Circuits/ PHI.2. Morris Mano/Digital Computer Design/ PHI.3. Milliman, J. Halkias/Integrated Electronics/TMH.4. Malv<strong>in</strong>o & Leach/Digital Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples & Application/List of Experiments:1. Study of Diode characteristics.2. Study of Common Base Transistor characteristics.3. Study of Common Emitter Transistor characteristics.4. Study of Half Wave Rectifier with effect of Capacitor and also calculate the ripple factor.5. Study of Full- Wave Rectifier with effect of Capacitor and also calculate the ripple factor.6. Study of Various Logic Gates.7. Study of Clipp<strong>in</strong>g and clamp<strong>in</strong>g Circuits.8. Study of C.R.O., Function generator, Multimeter.PROFESSIONAL COMMUNICATION IICourse Code LNG-303 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-0)1. <strong>Tech</strong>nical Written Communication(a) Nature, orig<strong>in</strong> and development of technical written communication.(b) Salient Features.(c) Difference between technical writ<strong>in</strong>g and general writ<strong>in</strong>g.2. Pre-requisites of Scientific and <strong>Tech</strong>nical Communication(a) Fragment sentences.(b) Parallel comparisons.(c) Elements of a series.(d) Squ<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g construction and split <strong>in</strong>f<strong>in</strong>itive.(e) Modifiers, connectives, antecedents and clause subord<strong>in</strong>ation.(f) Dangl<strong>in</strong>g participles and gerunds.(g) Ellipsis.(h) Coherence, Unity, Chronological method, spatial method, <strong>in</strong>ductive method, l<strong>in</strong>earmethod, d<strong>edu</strong>ctive method, <strong>in</strong>terrupted method.3. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Correspondence(a) General pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of bus<strong>in</strong>ess correspondence.(b) Ramifications of bus<strong>in</strong>ess letters.(c) Letters giv<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>structions, <strong>in</strong>quiries and answers to enquiries, compla<strong>in</strong>ts andadjustments, letters urg<strong>in</strong>g action, employment letters, application and resumes.4. Proposal Writ<strong>in</strong>g(a) Proposal: Def<strong>in</strong>itions and k<strong>in</strong>ds.(b) Division of format proposals (front matter, title page, summary/ abstract, Table ofcontents etc.)(c) Statement of request, body- statement of problem, background, scope, methodology,Advantages and disadvantages.5. Writ<strong>in</strong>g Scientific and Semi-technical Articles(a) Source material, topic sentence, literature review.(b) Tables, figures, footnotes, bibliography.
6. Study of Scientific and General Texts.(A). Prescribed text books for detailed study Arora, V.N (et. al.), Improve your writ<strong>in</strong>g (Delhi: Oxford University Press, 1981.2 Lesson No. 1.2, 1.6, 2.4, 3.5, 4.1, 4.3, 5.1, 5.4, 6.2.(B). For extended Read<strong>in</strong>g (any one of the follow<strong>in</strong>g) Orwell George, N<strong>in</strong>eteen Eighty Four (New York: Pengu<strong>in</strong>, 1984)2 Hem<strong>in</strong>gway, Ernest, The old man and the Sea, (Oxford: 1990)7.Listen<strong>in</strong>gComprehension(a).Ear-tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g.(b). Uses of latest scientific techniques (AVR Comprehension tra<strong>in</strong>er,SRA Comprehension tra<strong>in</strong>er, SRA Comprehension Accelerator, AVR ComprehensionReteometer.)8.Read<strong>in</strong>gComprehension.(a) Scann<strong>in</strong>g method.(b) Skimm<strong>in</strong>g method.9. Phonetic Transcription10. Stresses and Intonation.References1. Sherman, Theodore A. (et al) Modern <strong>Tech</strong>nical Writ<strong>in</strong>g, New Jersey, Prentice Hall, 1991.2. Legget, Glenn (et al) Essentials of grammar and composition, Macmillan, Delhi 1994.3. Strunk, Jr. William (et al), The elements of style, Macmillan, 1987.4. Sharma, S.D A Text Book of Scientific and <strong>Tech</strong>nical Writ<strong>in</strong>g, Vikas, Delhi, 1990.ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGCourse Code EEE-303 CREDIT : 4 (3-0-1)1. S<strong>in</strong>usoidal Steady State Circuit Analysis:Voltage, Current, S<strong>in</strong>usoidal & Phasorrepresentation.1-Phase A.C. Circuit-behavior of resistance, Inductance and Capacitance andtheir comb<strong>in</strong>ations, impedance, concept of power, power factor, series & parallel resonancebandwidthand quality factor.2. Network Theory:Introduction to basic physical laws, Network theory: Superposition,Theven<strong>in</strong>, Norton, Maximum Power transfer theorems, Star-delta transformation, Circuit theoryConcepts: Mesh and Nodal analysis.3. Three Phase Supply:Star/delta connections, l<strong>in</strong>e and phase voltage/current relations, Threephasepower and its measurement.4. Basic Instruments:Instruments for measurement of voltage, Current, power and energy:Construction, pr<strong>in</strong>ciple and application.5. Magnetic Circuit and Transformer:Magnetic circuit concept, theory and work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>cipleof s<strong>in</strong>gle-phase transformer.6. Rotat<strong>in</strong>g Mach<strong>in</strong>es:Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of energy conversion, Basic concepts of rotat<strong>in</strong>g mach<strong>in</strong>es,DC mach<strong>in</strong>es, Different types and their characteristics & applications. Elementary idea ofoperation of synchronous and <strong>in</strong>duction mach<strong>in</strong>es. S<strong>in</strong>gle-phase <strong>in</strong>duction & stepper motors,Applications.7. Power Systems:Introduction, Elements, L<strong>in</strong>e diagram, Supply systems, Power factorimprovement.Reference:1. V. Del Toro/ Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Electrical <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>/ PHI.2. W.H Hayt & J.E Kennedy/ <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Circuit Analysis/ McGraw Hill.
3. I.J Nagrath/ Basic Electrical <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>/ Tata McGraw Hill.4. A.E Fitzgerald/ Electronic Instruments & Measurement <strong>Tech</strong>niques/ PHI.5. Higg<strong>in</strong>botham L.Grabel/Basic Electrical <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>/ McGraw Hill.LIST OF PRACTICALSA m<strong>in</strong>imum of 10 experiments from the follow<strong>in</strong>g:1. Verification of Theven<strong>in</strong>’s Theorem.2. Verification of Superposition Theorem.3. Verification of Norton’s Theorem4. Verification of Kirchoff’s Law.5. To measure the value of impedance and power factor <strong>in</strong> RLC series A.C. circuit.6. To measure the value of impedance and power factor <strong>in</strong> RLC parallel A.C.circuit.7. To study resonance by frequency variation <strong>in</strong> series RLC circuit.8. To calibrate the given energy meter with the help of a standard wattmeter.9. To f<strong>in</strong>d the relation between l<strong>in</strong>e current and phase current and l<strong>in</strong>e voltage and phase voltage<strong>in</strong> Star – Delta connections.10. To perform open circuit and short circuit test and draw the equivalent circuit of a s<strong>in</strong>glephasetransformer.11. To measure three phase power by two-wattmeter method.12. To draw the magnetiz<strong>in</strong>g characteristic of a s<strong>in</strong>gle-phase transformer.Additional experiments may be added based on contents of syllabi.ENGINEERING PHYSICSCourse Code PHY-312 CREDIT :5 (3-1-1)1. Special Theory of Relativity:Michelson Morley experiment, Inertial frames of reference,Postulates of special theory of relativity, Lorentz transformation equation of space and time,length contraction, time dilaton, addition of velocities, variation of mass with velocity, massenergyequivalence.2. Optics :Interference: Coherent sources, Conditions of <strong>in</strong>terference, Fresnel’s bi-prismexperiment, displacement of fr<strong>in</strong>ges, <strong>in</strong>terference <strong>in</strong> th<strong>in</strong> films, wedge shaped film,Newton’s r<strong>in</strong>gs.Diffraction: S<strong>in</strong>gle slit and double slit diffraction, diffraction grat<strong>in</strong>g, Reyleigh’s criterion oflimit of resolution, resolv<strong>in</strong>g power of telescope, microscope and grat<strong>in</strong>g.Polarization: Polarization of light, Pictorial representation of polarized light, Brewster’s law,Malus law, Phenomena of double refraction, Geometry of calcite crystal, Optical activity,Specific rotation, Polarimeter.3. Fields: Scalar and vector fields, Gradient of a scalar field, divergence and curl of a vector field,l<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong>tegral, conservative vector field, Gauss’ Divergence theorem, Stoke’s theorem.4. Electrostatics: Gauss’ law and its applications, Poisson and Laplace equations. Maxwell’sequations, Basic Concepts of Electromagnetic waves and its solution <strong>in</strong> free space.5. Magnetic Properties of Materials:Para, dia, ferro, antiferro and ferro-magnetic materials,hysteresis, Methods of plott<strong>in</strong>g hysteresis curve of a ferro-magnetic material and their uses,magnetic circuits.
6. X-Rays: Orig<strong>in</strong> of X-rays, Cont<strong>in</strong>uous and characteristic X-Ray spectra, Moseley’s law,Absorption of X-rays, Diffraction of X-rays, Bragg’s law, Bragg’s spectrometer, Practicalapplication of X-rays, Compton effect.7. Quantum Theory:Wave particle duality, De Broglie concept of matter waves, Davisson andGermer experiment, Heissenberg’s uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty pr<strong>in</strong>ciple, Schrod<strong>in</strong>ger wave equation and itsapplications.8. LaserSpontaneous and stimulated emission of radiation, E<strong>in</strong>ste<strong>in</strong>’s coefficients, Ma<strong>in</strong> components of alaser, types of lasers and their applications.References:1. Arthur Beiser: Concepts Of Modern Physics, TMH.2. Subramanyam & Brij Lal: A Text Book of Optics, S. Chand & Co.3. K.K. Tiwari: Electricity & Magnetism, S. Chand & Co.4. Brij Lal & Subramanyam: Electricity & Magnetism.5. Wehr, Richardo & Adair: Physics of the Atom.List Of Experiments (Any Ten)1. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the wavelength of monochromatic light by Newton’s r<strong>in</strong>g.2. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the wavelength of monochromatic light with the help of Fresnel’s biprism.3. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the focal length of two lenses by nodal slide and locate the position of card<strong>in</strong>al po<strong>in</strong>ts.4. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the specific rotation of cane sugar solution us<strong>in</strong>g half shade polarimeter.5. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the wavelength of spectral l<strong>in</strong>es us<strong>in</strong>g plane transmission grat<strong>in</strong>g.6.To determ<strong>in</strong>e the specific resistance of the material of given wire us<strong>in</strong>g Carey Foster’sbridge.7. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the variation of magnetic field along the axis of a current carry<strong>in</strong>g coil andthen to estimate the radius of the coil.8. To verify Stefan’s Law by electrical method.9. To calibrate the given ammeter and voltmeter.10. To study the Hall Effect and determ<strong>in</strong>e Hall coefficient, carrier density and mobility of agiven semiconductor material us<strong>in</strong>g Hall Effect set up.11. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the energy band gap of a given semiconductor material.12. To determ<strong>in</strong>e E.C.E of copper us<strong>in</strong>g Tangent or Helmholtz galvanometer.13. To draw hysteresis curve of a given sample of ferromagnetic material and from this todeterm<strong>in</strong>e magnetic susceptibility and permeability of the given specimen.14. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the ballistic constant of a ballistic galvanometer.15. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the viscosity of a liquid.16. To determ<strong>in</strong>e refractive <strong>in</strong>dex of the material of prism us<strong>in</strong>g spectrometer.ENGINEERING GRAPHICS IICourse Code ME-401CREDIT:2(0-0-2)1. Introduction: Graphic language, Classification of draw<strong>in</strong>gs, Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of draw<strong>in</strong>g: IS codesfor Mach<strong>in</strong>e draw<strong>in</strong>g, L<strong>in</strong>es, Sections, Dimension<strong>in</strong>g, Standard abbreviation.2. Orthographic Projections: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of first and third angle projections, draw<strong>in</strong>g andsketch<strong>in</strong>g of mach<strong>in</strong>e elements <strong>in</strong> orthographic projections, spac<strong>in</strong>g of views.3. Screwed (Threaded) Fasteners: Introduction, Screw thread nomenclature, Forms of threads,Thread series, Thread designation. Representation of threads, Bolted jo<strong>in</strong>ts, Lock<strong>in</strong>garrangements for nuts, Foundation bolts.4. Keys and Cotters: Keys, Cotter jo<strong>in</strong>ts.5. Shaft Coupl<strong>in</strong>gs: Introduction, Rigid and flexible coupl<strong>in</strong>g.
6. Riveted Jo<strong>in</strong>ts: Introduction, Rivets and rivet<strong>in</strong>g, Rivet heads, Classification of rivetedjo<strong>in</strong>ts.7. Assembly Draw<strong>in</strong>g: Introduction, Eng<strong>in</strong>e parts, Stuff<strong>in</strong>g box etc.8. Free Hand Sketch<strong>in</strong>g:Need for free hand sketch<strong>in</strong>g, Free hand sketch<strong>in</strong>g of some threadedfasteners and simple mach<strong>in</strong>e components.References:1. N. Siddeshwar, P. Kannaiah, V.V.S Shastri: Mach<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g, TMH, New Delhi.2. K.L Narayana, P. Kannaiah, K. VenkatReddy: Mach<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g, New Age InternationalPublications, 2 nd edition.3. <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> draw<strong>in</strong>g practice for schools and colleges, SP 46-1998(BIS).COMPUTER AND LANGUAGESCourse Code COM-410 CREDIT : 4(2-0-2)1 Computer hardware components and their functions2 Basic operat<strong>in</strong>g system concepts3 MS-DOS and gett<strong>in</strong>g to know DOS commands4 Familiariz<strong>in</strong>g with WINDOWS environment5 Gett<strong>in</strong>g started with UNIX6 Files and Directories and their use <strong>in</strong> different Operat<strong>in</strong>g System Environments7 Gett<strong>in</strong>g to know different editors like edit & vi8 Introduction to Internet9 Gett<strong>in</strong>g familiar with Web Browsers like Netscape Navigator & Internet Explorer10 Send<strong>in</strong>g & receiv<strong>in</strong>g mail over Internet11 Introduction to PINE and /or ELM12 Need of programm<strong>in</strong>g languages.13 Language translators.14 Introduction to “C” language15 Data types operators and expressions.16 Conditional & loop<strong>in</strong>g statements.17 Function & Arrays.18 Introduction to Po<strong>in</strong>ters & Structures.References:1. DOS the complete reference by Kris Jamsa, Tata- McGraw Hill Publication.2. UNIX POWER TOOLS by J.Peek Tim O’reilly & M. Locekides, BPB Publication.3. The ‘C’ Programm<strong>in</strong>g Language by B.W Kernighan & D.M Ritchie, Prentice Hall of India.4. Us<strong>in</strong>g LINUX- Latest Edition by Jade Tackett & David Ganter, Prentice Hall of India.LIST OF PRACTICALS1. Basic Internal and External DOS Commands.2. Write a simple batch program.3. Giv<strong>in</strong>g exposure to W<strong>in</strong>dows environment.4. File and program management <strong>in</strong> w<strong>in</strong>dows.5. Practice of basic UNIX commands.6. Write simple shell script.7. Introduction to word process<strong>in</strong>g.8. Exposure to advance feature supported by some editors.9. Net Surf<strong>in</strong>g.10. Creation and check<strong>in</strong>g of E-mail account.
11. Write C program to demonstrate each of the follow<strong>in</strong>g:1 Conditional statements.2 Loop<strong>in</strong>g statements.3 User def<strong>in</strong>ed functions.4 Arrays.5 Po<strong>in</strong>ters and structures.12. Familiariz<strong>in</strong>g mail account us<strong>in</strong>g PINE, delet<strong>in</strong>g, creat<strong>in</strong>g folder/mail-messages, add<strong>in</strong>gsignature, creat<strong>in</strong>g director of addresses.ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS IICourse Code MAS-490 CREDIT : 4 (3-1-0)1. Differential Equations:Ord<strong>in</strong>ary differential equations of first order, exact differentialequations, L<strong>in</strong>ear differential equations of 1st order with constant coefficients,Complementary functions and particular <strong>in</strong>tegrals, Simultaneous l<strong>in</strong>ear differentialequations, Solution of second order differential equation by chang<strong>in</strong>g dependent and<strong>in</strong>dependent variables, Method of variation of parameters, Applications to eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>gproblems(without derivation).2. Series Solution & Special Functions:Series solutions of ODE of 2nd order with variablecoefficients with special emphasis to the differential of legendre and Bessel.Legendre’s polynomials, bessel’s functions and their properties.3. LaplaceTransform:Laplace transform, Existence theorem, Laplace transform derivativesand <strong>in</strong>tegrals, Inverse Laplace transform, Unit-step function, Dirac Delta function,Laplace transform of periodic functions, convolution theorem Applications to solvesimple l<strong>in</strong>ear and simultaneous differential equations.4. Fourier Series And Partial Differential Equations :Periodic functions,Trignometricseries, Fourier series of functions with period 2n, Eulers formulae, functions hav<strong>in</strong>garbitrary period, even and odd functions, change of <strong>in</strong>terval, half range s<strong>in</strong>e and cos<strong>in</strong>eseries.Introdution to partial differtial equations, l<strong>in</strong>ear partial differential equation with constantcoefficients of 2nd order and their classifications, parabolic, elliptic & hyperbolic withillustrative examples.5. Application of Partial Differential EquationsMethod of separation of variables for solv<strong>in</strong>g partial differential equation, Waveequation up to two dimension, Laplace equation <strong>in</strong> two dimension, Heat conductionequations up to two dimension, Equation of transmission L<strong>in</strong>es.References:1. E. Kreyszig: Advanced <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics, Wiley Eastern Ltd.2. B.S Grewal: Higher <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics, Khanna Publishers.3. Jaggi & Mathur: Advanced <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics, Khanna Publishers.
4. C. Prasad: Advanced Mathematics for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers, Prasad Mudranalaya.MACHINE DRAWING & COMPUTER AIDED DRAFTING LABCourse Code ME-403 CREDIT : 2 (0-0-2)Review (1 Class)Orthographic projection, miss<strong>in</strong>g l<strong>in</strong>es, <strong>in</strong>terpretation of views and section<strong>in</strong>g.Part and Assembly Draw<strong>in</strong>g (2 Classes):Introduction, assemblies draw<strong>in</strong>g of stuff<strong>in</strong>g box, steam eng<strong>in</strong>e cross head, air valves, lathetailstock, gate valve, screw jack, connect<strong>in</strong>g rods, spark plug, tool post, safety valves etc. Draw<strong>in</strong>gexercise.Specification of Materials:<strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> materials, code designation of steels, copper and alum<strong>in</strong>um and its alloys.Limits, Tolerance and fits: (1 Class)Introduction, Limit systems, tolerance fits, draw<strong>in</strong>gs and exercises.Surface Roughness:Introduction, surface roughness, mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g symbols, <strong>in</strong>dication of surfaceroughness, draw<strong>in</strong>g exercises.<strong>Production</strong> Draw<strong>in</strong>g:Introduction to develop<strong>in</strong>g and read<strong>in</strong>g or production draw<strong>in</strong>g of simplemach<strong>in</strong>e elements like helical gear, bevel gear, flange, p<strong>in</strong>ion shaft, connect<strong>in</strong>g rot, crankshaft,belt pulley, piston details etc. Idea about tool draw<strong>in</strong>g.Computer Aided Draft<strong>in</strong>g:Introduction, <strong>in</strong>put, output devices, <strong>in</strong>troduction to draft<strong>in</strong>g softwarelike Auto CAD, basic commands and development of simple 2D and 3D draw<strong>in</strong>gs.References:1. Mach<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g by Narayana, et.all, New Age.2. <strong>Production</strong> Draw<strong>in</strong>g by Narayana, et.all. New Age.3. Auto CAD 14 for <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Draw<strong>in</strong>g by P. Nageswara Rao, TMH.APPLIED THERMODYNAMICSCourse Code ME-404 CREDIT : 5 (3-1-1)Review of Thermodynamics: Brief review of basic laws of thermodynamics, Helmholtz & Gibb’sfunction, Mathematical conditions for exact deferential. The Maxwell Relations, Clapeyron Equation, Joule– Thompson coefficient curve, Availability & Irreversibility.Steam Boilers: Brief review of properties of steam, use of steam table and Mollier chart, Steamgenerators- classifications, work<strong>in</strong>g of fire-tube and water tube boilers, boiler mount<strong>in</strong>gs & accessories, Airpreheater, Feed water heater, Superheater, Boiler efficiency, Equivalent evaporation, Heat balance. Boilerdraught.Steam Eng<strong>in</strong>es:Rank<strong>in</strong>e and modified Rank<strong>in</strong>e cycles, Work<strong>in</strong>g of eng<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong>dicator diagram.Nozzle: Flow through nozzle, variation of velocity, area and specific volume, Nozzle efficiency, Criticalcondition.
Steam Turb<strong>in</strong>es: Classification, impulse and reaction turb<strong>in</strong>es, Compound<strong>in</strong>g, Velocity diagram,workdone, Reaction, Efficiency, Bleed<strong>in</strong>g, Comparison with steam eng<strong>in</strong>es, Reheat factor, Govern<strong>in</strong>g ofturb<strong>in</strong>es, Velocity diagram, Work done, Efficiencies of reaction and impulse turb<strong>in</strong>es.IC Eng<strong>in</strong>es: Classification, Constraction details. Application of four stroke and two stroke eng<strong>in</strong>es,Review of Otto, diesel and Dual cycles, Work done, Efficiencies, Indicator diagram, Valve tim<strong>in</strong>g diagram.EfficienciesGas Turb<strong>in</strong>es: Review of Bryaton cycle, Thermal ref<strong>in</strong>ement of a gas turb<strong>in</strong>e cycle, Comparison with ICEng<strong>in</strong>e and steam turb<strong>in</strong>e.Refrigeration and Heat Pump Cycles: Def<strong>in</strong>ition, Types, Carnot refrigerat<strong>in</strong>g cycle, Bell Coleman cycle. Unit ofrefrigeration. Description of simple vapour compression and vapour absorption systems. Introduction to aircondition<strong>in</strong>g.Compressors: Reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g compressor, Construction details and work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciple, Efficiency, Power<strong>in</strong>put, Intercool<strong>in</strong>g , Work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of centrifugal and axial flow compressor, Power <strong>in</strong>put calculation.Reference:1. Heat <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> by V.P. Vasandani & D. S. Kumar Publisher Metropolition Book Co. (P)Ltd.2. Thermal Engg. By P.L. Blallaney, Khanna Publishers.3. Theory of Steam Turb<strong>in</strong>e by W. J. Kearton4. Applied Thermodynamics by R. Yadav 6 th edn, CPH, Allahabad.5. Thermal Engg., By R. K. Rajput, Laxmi Publication.6. Turb<strong>in</strong>e Compressors & Fans by S. M. Yahya, HMT7. Thermal Engg. By S .K. kulshrestha, Vicars, Pub. House Ltd.8. Fundamental of Engg. Thermodynamics by R. Yadav 7 th edn, CPH, Allahabad9. Engg. Thermodynamics by Nag10. Engg. Thermodynamics by C .P. AroraFLUID MECHANICSCourse Code CE-406 CREDIT : 4 (3-0-1)I. Introduction: Fluids and cont<strong>in</strong>uum Physical properties of fluids, ideal and real fluids, Newtonian andNon-Newtorian fluids, measurement of surface tension.II. K<strong>in</strong>ematics of Fluid flow:Steady and unsteady, uniform and nonuniform, lam<strong>in</strong>ar and turbulent flows,one, two and three dimensional flows, streaml<strong>in</strong>es, streak l<strong>in</strong>es and path l<strong>in</strong>es, cont<strong>in</strong>uity equation,rotation and circulation, elementary explanation of stream function and velocity potential, graphical andexperimental methods of draw<strong>in</strong>g flow nets.III. Fluid Statics: Pressure-density-height relationship, manometers, pressure on plane and curved surfacescenter of pressure, buoyancy stability of immersed and float<strong>in</strong>g bodies, fluid masses subjected touniform accelerations, measurement of pressure.IV. Dynamics of fluid flow:Euler’s equation of motion along a streaml<strong>in</strong>e and its <strong>in</strong>tegration, Bernoulli’sequation and its applications-Pitot tube, flow through orifices, mouthpieces, nozzles, notches & weirs,sluice gates under free and submerged flow conditions, Aeration of nappe, cavitation, free and forcevortex momentum equation and its application of energy and momentum equations, flow measurements,determ<strong>in</strong>ation of Cd, Cc, and Cv, energy loss.V. Dimensional Analysis and Hydraulic Similitude: Dimensional analysis, Buck<strong>in</strong>gham’s Theorem,important dimensionless numbers and their significance, geometric, K<strong>in</strong>ematic and dynamicsimilarity, model studies.VI. Lam<strong>in</strong>ar and Turbulent flow through pipes, stoke’s law, flow between parallel plates, flowthrough porous media, fluidisation, measurement of viscosity, transition form lam<strong>in</strong>ar to turbulentflwo, turbulent flow, equation for turbulent flow, eddy viscosity, mix<strong>in</strong>g length concept andvelocity distribution <strong>in</strong> turbulent flow, Hot-wire anemometer and LDA.
VII. Boundary Layer Analysis:Boundary layer thicknesses boundary layer over a flat plate,lam<strong>in</strong>ar boundary layer, application of momentum equation, turbulent boundary layer, lam<strong>in</strong>ar sublayer,smooth and rough boundaries, atmospheric boundary layer, local and average frictioncoefficient, separation and its control, measurement of shear.VIII. Pipe flow:Nature of turbulent flow <strong>in</strong> pipes, equation for velocity distribution over smoothand rough surfaces, resistance coefficient and its variation, flow <strong>in</strong> sudden expansion, contraction,diffusers, bends, valves and siphons, concept of equivalent length, branched pipes, pipes <strong>in</strong> seriesand parallel, simple networks.IX. Flow past Submerged Bodies:Drag and lift, drag on a sphere, cyl<strong>in</strong>der and disc, lift, Magnuseffect and circulation.X. Compressibility Effects <strong>in</strong> pipe Flow:Transmission of pressure waves <strong>in</strong> rigid and elasticpipes, water hammer, analysis of simple surge tank exclud<strong>in</strong>g friction.References:1. Som & Biswas: Introduction of fluid mechanics & Mach<strong>in</strong>es, TMH.2. S.K. Agrawal: Fluid Mechanics & Mach<strong>in</strong>ery, TMH3. Garde, R.J. and A.G. Mirajgaoker, “<strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Fluid Mechanics” (<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g HydraulicMach<strong>in</strong>es), Second Ed. Nemchand & Bros, Roorkee, 19834. Garde, R.J. “Fluid Mechanics through Problems”, Wiley Eastern Limited, New Delhi, 19895. Hunter Rouse, “Elementary Mechanics of Fluids”, John Wiley & Sons, Omc. 19466. L.H. Shames, “Mechanics of Fluids”, McGraw Hill, Int. Student, Education.7. Fluid Mechanics by Jagdish Lal8. Vijay Gupta and S.K. Gupta, “Fluid Mechanics and its Applications”, Villey Eastern Ltd.9. Fluid Mechanics by Modi & Seth.FLUID MECHANICS LAB1. To determ<strong>in</strong>e experimentally the metacentric height of ship model.2. To verify the momentum equation experimentally.3. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the coefficient of discharge of an orifice (or a mouth piece) of a given shape. Also todeterm<strong>in</strong>e the coefficient of velocity and the coefficient of contraction of the orifice (or the mouthpiece)4. To plot the flow net for a given model us<strong>in</strong>g the concept of electrical analogy.5. To measure surface tension of a liquid.6. To calibrate an orifice meter and study the variation of the coefficient of discharge with theReynolds number.7. To verify Darcy’s law and to f<strong>in</strong>e out the coefficient of permeability of the given medium.8. To study the transition from lam<strong>in</strong>ar to turbulent flow and to determ<strong>in</strong>e the lower criticalReynolds number.9. To study the velocity distribution <strong>in</strong> a pipe and also to compute the discharge by <strong>in</strong>tegrat<strong>in</strong>g thevelocity profile.10. To study the variation of friction factor, “f” for turbulent flow <strong>in</strong> smooth and rough commercialpipes.11. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the loss coefficients for the pipe fitt<strong>in</strong>gs.12. To study the flow behavior <strong>in</strong> a pipe bend and to calibrate the pipe bend for deschargemeasurement.13. To study the boundary layer velocity profile and to determ<strong>in</strong>e boundary layer thickness anddisplacement thickness. Also to determ<strong>in</strong>e the exponent <strong>in</strong> the power law of velocity distribution.STRENGTH OF MATERIALS0)Course Code CE-408 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-Introduction: Brief review, concept of stress, stra<strong>in</strong>, ductility, toughness, elastic constants,hardness, brittleness, tension, compression, shear, Brief review of Mohr’s circle for compoundstresses & for pr<strong>in</strong>cipal stresses.
Theories of Failure:Various theories of failure and its comparison.Review of Bend<strong>in</strong>g and Torsion:Brief review of bend<strong>in</strong>g of beams and shear force & bend<strong>in</strong>gmoment diagram. Review of torsion of circular shaft and comb<strong>in</strong>ed bend<strong>in</strong>g & torsion. Shear<strong>in</strong>gstresses <strong>in</strong> beams section.Deflection of Beams: Deflection of beams, Integration method, Macaulay’s method, Area momentmethod, Unit load method.Columns and Struts: Theory of columns & Struts, Eulers and Rank<strong>in</strong>e formulae.Th<strong>in</strong> Cyl<strong>in</strong>ders: Theory of th<strong>in</strong> cyl<strong>in</strong>ders subjected to pressure. Expression for hoop stress andlongitud<strong>in</strong>al stress. Design of th<strong>in</strong> cyl<strong>in</strong>ders.Thick Cyl<strong>in</strong>ders and Spherical Shells:Stresses and stra<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> thick shells/cyl<strong>in</strong>der subjected topressures. Compound cyl<strong>in</strong>ders press fits on solid shaft.Fracture, Fatique and Creep:Stress concentration, Grifith’s formula. Fatigue load<strong>in</strong>g, endurancelimit, Creep.References:1. Strength of Materials by Ryder2. Strength of Materials by S<strong>in</strong>ger3. Strength of Materials by Oimoshenko4. Engg. Mechanics of Solids by Popov5. Mechanics of Materials by Bear Johnson6. Strength of Materials by R.K. Rajput7. Strength of Materials by Ramamrutham & Nara<strong>in</strong>.MATERIAL SCIENCE & TESTINGCourse Code ME-410 CREDIT :4(3-0-1)In troduction: Historical perspective, importance of materials, Brief review of modern & atomicconcepts <strong>in</strong> Physics and Chemistry. Atomic models, Periodic table, Chemical bond<strong>in</strong>gs.Crystallography and Imperfections: Concept of unit cell space lattice, Bravais lattices, commoncrystal structures, Atomic pack<strong>in</strong>g factor and density. Miller <strong>in</strong>dices. X-ray crystallography techniques.Imperfections, Defects & Dislocations <strong>in</strong> solids.Mechanical Properties and Test<strong>in</strong>g: Stress stra<strong>in</strong> diagram, Ductile & brittle material, Stress VsStrength. Toughness, Hardness, Fracture, Fatigue and Creep. Test<strong>in</strong>g such as Strength test<strong>in</strong>gs,Hardness test<strong>in</strong>g, Impact test<strong>in</strong>gs, Fatigue Test<strong>in</strong>g Creep test<strong>in</strong>g, Non-destructive test<strong>in</strong>g (NDT)Microstructural Exam: Microscope pr<strong>in</strong>ciple and methods. Preparation of samples and microstructureexam and gra<strong>in</strong> size determ<strong>in</strong>ation. Comparative study of microstructure of various metals & alloyssuch as Mild steel, CI, Brass.Phase Diagram and Equilibrium Diagram: Unitary and B<strong>in</strong>ary diagrams, Phase rules, Types ofequilibrium diagrams: Solid solution type, eutectic type and comb<strong>in</strong>ation type. Iron-carbon equilibriumdiagram.Ferrous Materials: Iron and steel manufacture, furnaces. Various types of carbon steels alloy steelsand cast irons, its properties and uses.Heat Treatment: Various types of heat treatment such as Anneal<strong>in</strong>g, Normaliz<strong>in</strong>g Quench<strong>in</strong>g,Temper<strong>in</strong>g and case harden<strong>in</strong>g. Time Temperature Transformation (TTT) diagrams.Non-Ferrous metals and alloys:Non-ferrous metals such as Cu, Al, Zn, Cr, Ni, etc. and itsapplications. Various type Brass, Bronze, bear<strong>in</strong>g materials, its properties and uses. Alum<strong>in</strong>um alloyssuch as Duralum<strong>in</strong>. Other advanced materials/alloys.Magnetic Properties: Concept of magnetism-Dia, para, ferro Hysteresis. Soft and har magneticstorages.Electric Properties: Energy ban concept of conductor, <strong>in</strong>sulator and semiconductor. Intr<strong>in</strong>sic &extr<strong>in</strong>sic semi-conductors, P-n junction and transistors. Basic devices and its application. Superconductivity and its applications. Messier effect. Type I & II Superconductors. High TeSuperconductors.
Ceramics: Structure types and properties and applications of ceramics. Mechanical/Electricalbehaviour and process<strong>in</strong>g of plastic.Plastics: Various types of polymers/plastics and its applications. Mechanical behaviors andprocess<strong>in</strong>g of plastics. Future of plastics.Other Materials: Brief description of other material such as concrete, wood, glass etc. and its uses.Performance of materials <strong>in</strong> Service: Brief theoretical consideration of fracture, Fatigue, Creep andCorrosion and its control.References:1. W.D. Callister, Jr.-Material Science & <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Addition Wesly Publish<strong>in</strong>g Co.2. Van Vlash- Elements of Material Science & <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> John Wiley & Sons.3. V. Raghvan- Material Science, Prentice Hall of India4. Narual- Material Science, TMH5. Srivastava, Sr<strong>in</strong>ivasan – Science of Materials <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Newage.MATERIAL SCIENCE AND TESTING LABA. Material Science Lab Experiments: (at least 5 of the follow<strong>in</strong>g)1. Mak<strong>in</strong>g a plastic mould for small metallic specimen.2. Specimen preparation for micro structural exam<strong>in</strong>ation – cutt<strong>in</strong>g, gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g, polish<strong>in</strong>g, etch<strong>in</strong>g.ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES-1Course Code SES-415 CREDIT 2(2 – 0 - 0)1: The Multidiscipl<strong>in</strong>ary Nature of Environmental Studies.Def<strong>in</strong>ition, Scope and Importance.(i) Ecosystems.Concept of an Ecosystem.Structure and function of an Ecosystem.Producers,consumers and decomposers.Energy flow <strong>in</strong> he ecosystem.Ecological successsion.Food cha<strong>in</strong>s,food webs and ecological pyramids.Introduction,types,Characteristics features,structures and function of the follow<strong>in</strong>g ecosystem:(a) Forest Ecosystem.(b) Grassland Ecosystem.(c) Desert Ecosystem.(d) Aquatic Ecosystem (Ponds,streams,lakes,rivers,oceans,estuaries).(ii) Social Issues and the EnvironmentFrom unsusta<strong>in</strong>able to susta<strong>in</strong>able development.Urban problems related to energy.Water conservation, ra<strong>in</strong> water harvest<strong>in</strong>g, water shed management.Resettlement and rehabilitation of people; its problems and concerns case studies.Environmental ethics: Issues and possible solutions.Climate change, global warm<strong>in</strong>g, acid ra<strong>in</strong>, ozone layer depletion, nuclear accidents andholocaust,Case studiesWasteland reclamation.Consumerism and waste products.
Environment Protection act.Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) ActVisit to local polluted site-Urban/Rural/<strong>in</strong>dustrial/Agricultural.Study of Common plants, <strong>in</strong>sects, birds.Study of simple ecosystems-ponds, river. Hillslopes etc(Field work equal to 5 lecture hours).Issues <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> enforcement of environmental legislation; public awareness.FOUNDATIONS OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYCourse Code COMP-510 CREDIT :5 (2-1-2)Fundamental Concept of InformationInformation Concept and Process<strong>in</strong>g: Def<strong>in</strong>ition of Information, Need of Information, Quality ofInformation, Value of Information, Concept of Information, Entropy Category and Level of <strong>in</strong>formation<strong>in</strong> Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Organization, Data concepts and Data Process<strong>in</strong>g, Data Representation.Information Representation: Information Contents, Introduction to <strong>in</strong>formation representation <strong>in</strong>Digital Media, Text, Images, Graphics, Animation, Audio, Video, Elementary concepts <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>formationPreservence, Data compression, Huffman Cod<strong>in</strong>g, Shannon Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, Adaptive Compression, LZWCod<strong>in</strong>g, Images Compression, Introduction to Jpeg, Mpeg, Mheg.Compute Programm<strong>in</strong>gComputer Appreciation: Def<strong>in</strong>ition of Electronic computer, History, Generations, Characteristic andapplication of computers, classification of computers, RAM/ROM, Computer Hardware, CPU, Various I/ODevices, Peripherals, Storage Media, Software Def<strong>in</strong>ition.Programm<strong>in</strong>g Language Classification & Program Methodology: Computer Languages, Generations ofLanguages, Introduction to 4 GLS, Software Development Methodology, Life Cycles, Software Cod<strong>in</strong>g,Test<strong>in</strong>g, Ma<strong>in</strong>tenance, Industry Standards, Introduction to ISO, SEI-CMM Standards for IT Industry.Digital Devices and basic Network Concepts: Digital Fundamentals: Various Codes, Decimal, B<strong>in</strong>ary, HexDecimal Conversion, Float<strong>in</strong>g Numbers, Gates, Flip Flops, M<strong>in</strong>imization adder, Multiplexers.Computer Networks and Communication: Need For Data Transmission Over Distances, Types of DataTransmission, Media for Data Transmission, Network<strong>in</strong>g of Computers-Introduction of Lan and WAN,Network Topologies, basic Concepts <strong>in</strong> Computer Networks, Client-Server Architecture, Introduction toAdvanced Communication <strong>Tech</strong>niques, ISDN, ATM, Token Based Protocol, CSMA/CD, MobileCommunication.Internet and Web <strong>Tech</strong>nologiesInternet & World Wide Web: Hypertext Markup Language, DHJML, WWW, Gopher, FTP, Telnet, WebBrowsers, Net Surf<strong>in</strong>g Search Eng<strong>in</strong>es, E-mail, Basic concepts <strong>in</strong> E-Commerce, EDI, Electronic Payments,Digital Signatures, Network, Security, Fireball.Web <strong>Tech</strong>nologies: Elementary Concepts <strong>in</strong>, Object Oriented Programm<strong>in</strong>g, Corba, Com/Dcom, WirelessApplication Protocol, ASP Script<strong>in</strong>g, HTML, Java, Java Applets, WAP, WML, JSP, EJB, XML.Advanced Concepts <strong>in</strong> Information <strong>Tech</strong>nology:IT Industry Trends, Careers and Applications <strong>in</strong> India: Scientific, Bus<strong>in</strong>ess, Educational andenterta<strong>in</strong>ment applications, Industry Automation, Weather forecast<strong>in</strong>g awareness of ongo<strong>in</strong>g IT projects <strong>in</strong>India, NICNET ernet, Application of IT to E Commerce, Electronic Governance, Multimedia, Enterta<strong>in</strong>ment.Suggested Text Books & References:1. Curt<strong>in</strong>, “Information <strong>Tech</strong>nology: Break<strong>in</strong>g News”, Tm + 12. Raja Raman, V. “Introduction to Computers”3. Bajpai, Kushwaha & Yadav, “Intrduction to Computer & C Programm<strong>in</strong>g”, New Age.4. Nelson, “Data Compression”, BPB5. Bharohoke, “Fundamentals of Information <strong>Tech</strong>nology”, Excel6. Peter Nortans “Introduction to Computers”, TM +17. Leon & Leon “Fundamental of Information <strong>Tech</strong>nology”, Vikas Publish<strong>in</strong>g House
8. Kanter, “manag<strong>in</strong>g Information System”9. Lehngart, “Internet 101”, Addision Wesley10. Cistems “Internet, An Introduction”, Tata McGray Hill.IT LABWrite Programs <strong>in</strong> C for the follow<strong>in</strong>g.1. Conversion of B<strong>in</strong>ary to Hexadecimal, Decimal to BCD and vice versa2. LOGIC Design<strong>in</strong>g of gates and flip flops.3. For M<strong>in</strong>imization methods4. Introduction to <strong>in</strong>formation representation <strong>in</strong> digi8tal media text, Images, Graphics, Animations,Audio, Video.5. Dataflow diagram for generation of Prime Numbers6. Demonstrate Different Lan TopologiesWorld Wide Web,File Transfer Protocol,Goffer,Telenet,Web browsers, Search eng<strong>in</strong>e ,Email SitesCreate your own email address us<strong>in</strong>g any of the eng<strong>in</strong>es Ex. ID @ eng<strong>in</strong>e.com7.Institutions may add 4 more experiments as per the availability of expertise available with them.ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-IIICourse Code MAS –590 Credit (3-1-0) 41. Ord<strong>in</strong>ary Y. Differential Difference Equations: ODE of 2 nd order with constant coefficientsboth homogeneous and non- homogeneous Types with applications to electrical and mechanicalsystems. Difference equations and their Solutions by z transform. Series solutions of ODE of 2 ndorders with variable Coefficients with special emphasis to the differential equations ofLegendre, Bessel and Chebyshev. Legendre’s polynomials, Chabyshev polynomials andBessel’s functions and Their properties.2. Integral Transforms: Fourier transform and <strong>in</strong>tegral Hanker transforms and Hilberttransforms and their Properties, some simple applications. Partial Differential Equations:L<strong>in</strong>ear PDE with constant coefficients of 2 nd order and their classifications, PDE of Parabolic,elliptic and hyperbolic type with illustrative examples. Separation of variables Method forsolv<strong>in</strong>g PDE. Such as two dimensional heat equations, wave equations and Laplace equations.3. Functions of a Complex variable: Analytic (functions, Gauchy- Riemam equations, harmonicfunctions l<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong>tegral <strong>in</strong> the Complex plane, caucry’s Integral theorem cauchy’s <strong>in</strong>tegralformula derivatives of analytic Functions, Liouvilles Theorem, fundamental theorem of Algebrarepresentation of a Function py power series, Taylor’s series and Laurent’s Series, poles,S<strong>in</strong>gularities and Zeros. Residue theorem, evaluation of <strong>in</strong>tegrals us<strong>in</strong>g. Residue theorem.Conformal” Mapp<strong>in</strong>g, l<strong>in</strong>ear fractional transformations, special l<strong>in</strong>ear fractional transformations.Reference:Kreyszig, E. (1993): Advanced Engg. Mathematics 7 th Edition, John Willey & sons <strong>in</strong>c.Paopoulis: Signal Analysis 3 rd Edition (1988) Me Graw Hill .ELECTRICAL MACHINESCourse Code EEE-404 Credit 4(3-0-1)D.C. Mach<strong>in</strong>es:Constructional features and pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of operation of shunt, series and compoundgenerators and motors <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g EMF equation and armature reaction, Performance characteristicsof generators and motors, start<strong>in</strong>g, Speed control and brak<strong>in</strong>g of motors. Two Quadrant and FourQuadrant operation of motors, choice of DC motors for different applications, Losses and efficiency.
Transformers:Construction, EMF equation, Pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of operation, Phasor diagram on no-load,dffect of load, equivalent circuit, Voltage regulation, Losses and efficiency, Tests on transformers,Prediction of efficiency and regulation, Autotransformers, Instrument transformers, Three phasetransformers.Induction Motors:Rotat<strong>in</strong>g magnetic fields, pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of operation, Equivalent circuit, Torque-slipcharacteristic, Starters foe cage and wound rotor type <strong>in</strong>duction motors, Speed control and brak<strong>in</strong>g,S<strong>in</strong>gle Phase <strong>in</strong>duction motors and methods of start<strong>in</strong>g.Synchronous Mach<strong>in</strong>es:Construction, EMF equation, Effect of pitch and distribution, Armaturereaction and determ<strong>in</strong>ation of regulation of synchronous generators, Pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of motor operation,effect of excitation on l<strong>in</strong>e currents (V-curves), methods of synchronization, typical applications ofAC motors <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustries.Reference:1. Hughes Edward, Electrical <strong>Tech</strong>nology, Addision Wesley Longman Ltd.2. Nagrath I.J. & Kothari D.P., Electrical Mach<strong>in</strong>es, TMH3. Cotton H., Advanced Electrical <strong>Tech</strong>nology, Wheeler & Co.4. Fitzgerald, K<strong>in</strong>gsley. Kusko, Dumas-Electrical Mach<strong>in</strong>es TMH5. Kosow L.L., electrical Mach<strong>in</strong>ery and Transformers, PHI6. Parker Smith, Electrical <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Problems, CBS.Course Code (ME-405MEASUREMENT & METROLOGYCredit4(2-1-1)1. Mechanical MeasurementsIntroduction: Introduction to Measurement and Measur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>struments, Generalized Measur<strong>in</strong>gsystem and functional elements, units of Measurement, static and dynamic performancecharacteristics of Measurement devices, calibration, concept of error, sources of error, statisticalanalysis of errors.Sensors and Transducers: Types of Sensors, types of transducers and their characteristics.Time and Transducers: Counters, Stroboscope, frequency measurement by direct comparisonMeasurement of pressure: Gravitational, direct act<strong>in</strong>g, elastic and <strong>in</strong>direct type pressuretransducers. Measurement of very low pressures.Measurements of Force and Torque: Different types of load cells elastic transducers, Pneumatic& Hydraulic systems.Temperature Measurement: By thermometers, bimetallic, thermocouples, thermostats andpyrometers. Vibration and Noise MeasurementSeismic <strong>in</strong>struments, vibration pick ups and decibel meters, vibrometers accelerometers.Data Acquisition system: Introduction to data acquisition systems, s<strong>in</strong>gle and multi-channelsystem, microprocessors and PC based data acquisition systems. Input-output devices.Signal Transmission and Process<strong>in</strong>g: Devices and Systems.METROLOGYII. Metrology and Inspection: Standards of l<strong>in</strong>ear measurement, l<strong>in</strong>e and end standards. Limit, fitsand tolerances. Interchangeability and standardization.L<strong>in</strong>ear and angular measurements devices and systems.Limit gauges classification, Taylor’s Pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of Gauge Design.Measurement of geometric forms like straightness, flatness, roundness and circularity.Tool makers microscope, profile project autocollimator.
III Interferometer: pr<strong>in</strong>ciple and use of <strong>in</strong>terferometry, optical flat and <strong>in</strong>terferometers, laser<strong>in</strong>terferometers. Measurement of screw threads and gears.Surface texture: quantitative evaluation of surface roughness and its measurement.Suggested Text Books & References:1. Beckwith Thomas G., Mechanical Measurements, Narosa Publish<strong>in</strong>g House, N. Delhi.2. Doeble<strong>in</strong> E.O., “Measurement Systems, Application Design”, McGraw Hill, 19903. Kumar D.S. “Mechanical Measurements and Control”, Metropolitan, N.Delhi.4. Hume K.J., “<strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Metrology”, Mac Donaldd & Co. 1963.5. Gupta, I.C., “<strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Metrology”, Dhanpat Rai & Sons, New Delhi, 1994.6. Sirohi, “Mechanical Measurement”, New Age Publishers7. Ja<strong>in</strong>, R.K., “<strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Met5rology ” Khanna Publishers8. Ja<strong>in</strong> R.K., “Mechanical Measurement” Khanna PublishersKINEMATICS OF MACHINES0)Course Code ME-407 Credit 4(3-1-1. Introduction: L<strong>in</strong>ks, k<strong>in</strong>ematics pairs, l<strong>in</strong>kage mechanisms, <strong>in</strong>versions of slider crank cha<strong>in</strong> anddouble slider crank cha<strong>in</strong>, four bar l<strong>in</strong>kage, mechanisms compound cha<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> brief.2. Velocity and Acceleration I Mechanisms:Velocity of po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>in</strong> mech., relative velocity method,<strong>in</strong>stantaneous center method, Kennedy’s theorem acc-diagram, acc-centers, Correolis componentsacc., Kle<strong>in</strong>’s construction for slider crank and four bar mech. Analytical method for slider crankmech.3. Mechanism with Lower Parts.:Pantograph straight l<strong>in</strong>e motion mechanisms, Peucellier’sMechanism, hart’s straight l<strong>in</strong>e mech., Scort Rusel mech., analysis of hook’s jo<strong>in</strong>t, <strong>in</strong>troduction tothe analysis of complex mech., Davis and Ackermann steer<strong>in</strong>g gears.4. K<strong>in</strong>ematic Synthesis of Planner L<strong>in</strong>kages: L<strong>in</strong>kages, geometrical methods, 3 position synthesisof coupl<strong>in</strong>g rod, analytical method, fredenstem equation for functions generation.5. Cam s:Classification & term<strong>in</strong>ology law of gear<strong>in</strong>g, geometric & k<strong>in</strong>ematic characteristic of<strong>in</strong>volute, under cutt<strong>in</strong>g & <strong>in</strong>terference, gear tra<strong>in</strong>s (simple, compound & planetary)Books & reference:1. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es Thomas Bevan2. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es and Mechanisms-Shigley.3. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es and Mechanisms – Ghosh and Mullick4. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es & mechanism – Dukhipati.INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERINGCourse Code ME-411Credit4(3-1-0)1. Productivity: Introduction, def<strong>in</strong>ition, measurement, productivity <strong>in</strong>dex, ways to improveproductivity.2. Work study: Mean<strong>in</strong>g and benefits of work study, time and motion study Micromotion studyP.M.T.S. man mach<strong>in</strong>e Diagram flow chart. Motion economy, Method study, work measurement,work sampl<strong>in</strong>g standard time.3. Job Evaluation & Merit Rat<strong>in</strong>g: Job analysis, job description job simplification and job evaluationmethods & description, merit rat<strong>in</strong>g, wage <strong>in</strong>centive plans.4. Plant layout and Materials Handl<strong>in</strong>g: Plant location type of layout, pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of facility layoutpr<strong>in</strong>ciples of material handl<strong>in</strong>g, Material handl<strong>in</strong>g empts.
5. <strong>Production</strong> Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Control: Objectives, function, steps <strong>in</strong> PPC. Plann<strong>in</strong>g rout<strong>in</strong>e,sch<strong>edu</strong>l<strong>in</strong>g, Dispatch<strong>in</strong>g & Follow-up, Effectiveness of PPC.6. Replacement Analysis: Depreciation causes, obsolescence, service life of assets, Replacement ofitems.7. Inventory Control: Inventory, function, cost, determ<strong>in</strong>istic models.8. Introduction to MRP & JIT quality control: Introduction, process control, Control Charts, S<strong>in</strong>gledouble and sequential sampl<strong>in</strong>g, Introduction to TQM & bench mark<strong>in</strong>g.9. Organization: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of organization, Development of Organizational charts like l<strong>in</strong>e, staff, l<strong>in</strong>eand staff & functional types.10. <strong>Industrial</strong> Ownership: Proprietorship, partnership, Jo<strong>in</strong>t stock & co-operative stores.11. Manpower Plann<strong>in</strong>g: Resources, Human relationship.12. Factory Legislation India: Factory acts, payment of wages, workmen compensation, E.S.I. Salesmanagement & forecast<strong>in</strong>g cost account<strong>in</strong>g, Budgetary control.13. Project management & CPM/PERT: Methods of draw<strong>in</strong>g networks and computations of varioustimes, updat<strong>in</strong>g resources a location, project management.14. Break Even Analysis: Introduction, Assumption, Stepsion BEA, purpose, fixed & variable costs,marg<strong>in</strong> of safety, Angle of <strong>in</strong>cidence profit volume graph.15. Operation Research: Brief outl<strong>in</strong>es of problems, l<strong>in</strong>ear programm<strong>in</strong>g, transportation problems.Graphical methods.References:1.Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of management, An analysis of management functions-H, Koontz & C.O. Donnel, TataMcGraw-Hill Co.2. Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Management- J Moore Prentice Hall Englewoon Cliffs: New Jersey.3. Modrn <strong>Production</strong> Operations Management- Buffam E.S. Wiley Eastern.4. <strong>Industrial</strong> Engg. & Management by O.P. Khanna5. <strong>Industrial</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> by Ravi Shanker6. <strong>Industrial</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> by Mahajan.MANUFACTURING SCIENCE -1Course Code (ME 412 ) Credit 4(3-0-1)Introduction:Importance of manufactur<strong>in</strong>g, economic & <strong>Tech</strong>nological consideration <strong>in</strong> manufactur<strong>in</strong>g. Survey ofManufactur<strong>in</strong>g Process. Materials & manufactur<strong>in</strong>g process for common items.Metal Form<strong>in</strong>g Process:Elastic & Plastic deformation, yield criteria. Hot work<strong>in</strong>g Vs cold work<strong>in</strong>g, Load required toaccomplish metal form<strong>in</strong>g operation.Analysis (equilibrium equation method) of form<strong>in</strong>g process with slid<strong>in</strong>g friction stick<strong>in</strong>g friction andmixed condition for slab and disc. Work required for forg<strong>in</strong>g.Analysis of Wire/Strip draw<strong>in</strong>g and max. R<strong>edu</strong>ction, Tube draw<strong>in</strong>g, Extrusion and its applicationCondition for roll<strong>in</strong>g force and power <strong>in</strong> roll<strong>in</strong>g. Roll<strong>in</strong>g mills.Design, lubrication and defects <strong>in</strong> metal form<strong>in</strong>g processes.Sheet Metal Work<strong>in</strong>g:Die & assembly and press work methods and processes. Cutt<strong>in</strong>g mechanism, blank<strong>in</strong>g Vs pierc<strong>in</strong>g.Compound Vs. progress<strong>in</strong>g die. Flat faces Vs <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ed face punch.Analysis of form<strong>in</strong>g process like cup/deep draw<strong>in</strong>g and bend<strong>in</strong>g.Unconventional Metal Form<strong>in</strong>g Processes:Unconventional Metal form<strong>in</strong>g Processes such as explosive form<strong>in</strong>g, electro-magnetic, electrohydraulicform<strong>in</strong>g.Powder Metallurgy:Powder metallurgy manufactur<strong>in</strong>g processes. The process, advantage and applications.Cast<strong>in</strong>g:
Basic pr<strong>in</strong>ciple & survey of cast<strong>in</strong>g Process. Types of patterns and allowances. Types and properties ofmould<strong>in</strong>g sand. Element of mould and design considerations, gatt<strong>in</strong>g, riser, runner, core. Solidificationof cast<strong>in</strong>g, theory and analysis. Sand cast<strong>in</strong>g, defect and remedies and <strong>in</strong>spection. Cupola furnace.Die cast<strong>in</strong>g centrifugal cast<strong>in</strong>g, Investment cast<strong>in</strong>g.Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Of Plastic Components:Plastic and its past, present & future uses. Injection mould<strong>in</strong>g. Extrusion of plastic section. Weld<strong>in</strong>g ofplastics. Future of plastic & application.Jigs & Fixtures:Locat<strong>in</strong>g and clamp<strong>in</strong>g devices/pr<strong>in</strong>ciple. Jigs and fixtures and its application.Books:1. Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g science by Ghosh and Mallik.2. <strong>Production</strong> Engg. Science by P.C Pandey3. <strong>Production</strong> technology by R.K.Ja<strong>in</strong>.4. Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g technology by P.N.Rao5. Material and manufactur<strong>in</strong>g by Paul Degarmo.MANUFACTURING SCIENCE-1 LABEXPERIMENTS:Say M<strong>in</strong>imum 8 Experiments out of Follow<strong>in</strong>g (Or Such Experiment)1. Design of pattern for a desired cast<strong>in</strong>g (conta<strong>in</strong>g hole).2. Pattern mak<strong>in</strong>g.3. Mak<strong>in</strong>g a mould (with core) and cast<strong>in</strong>g.4. Sand test<strong>in</strong>g (at least one such as of gra<strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>eness number determ<strong>in</strong>ation).5. Injection mould<strong>in</strong>g of plastic.6. Forg<strong>in</strong>g by hand forg<strong>in</strong>g processes.MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMCourse Code ME 416 Credit 3(3-0-0)Part I: Organizations, Management and the Networked Enterprise Information Systems <strong>in</strong> GlobalBus<strong>in</strong>ess TodayGlobal E-Bus<strong>in</strong>ess: How Bus<strong>in</strong>esses Use Information Systems Information Systems, Organizations, andStrategy Ethical and Social Issues <strong>in</strong> Information SystemsPart II: Information <strong>Tech</strong>nology Infrastructure IT Infrastructure and Emerg<strong>in</strong>g <strong>Tech</strong>nologiesFoundations of Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementTelecommunications, the Internet and Wireless <strong>Tech</strong>nology Secur<strong>in</strong>g Information SystemsPart III: Key System Applications for the Digital AgeAchiev<strong>in</strong>g Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise ApplicationsE-Commerce: Digital Markets, Digital Goods Manag<strong>in</strong>g Knowledge Enhanc<strong>in</strong>g Decision Mak<strong>in</strong>gCOMPUTER BASED NUMERICAL & STATISTICAL TECHNIQUESCourse Code (MAT-491) CREDIT 3 (3-1-1)Introduction: Errors <strong>in</strong> Numerical Computation, Mathematical Prelim<strong>in</strong>aries, Errors and their Analysis,Mach<strong>in</strong>e Computations, Computer Software.Algebraic & Transcendental Equation: Bisection Method, Iteration Method, Method of False Position,Rate of Convergence, Method for Complex Root, Muller’s Method, Quotient Difference Method, NewtonRaphson Method.
Interpolation:Introduction, Errors <strong>in</strong> Polynomial Interpolation, F<strong>in</strong>ite Differences, Decision of Errors,Newton’s Formulae for Interpolation, Gauss, Stirl<strong>in</strong>g, Bessel’s, Everett’s Formulae, Interpolation byUnevenly Spaced Po<strong>in</strong>ts, Lagrange’s Interpolation Formula, Divided Difference, Newton’s GeneralInterpolation Formula.Curve Fitt<strong>in</strong>g, Cubic Spl<strong>in</strong>e & Approximation:Introduction, Method of Least Square Curve Fitt<strong>in</strong>gProc<strong>edu</strong>res, Fitt<strong>in</strong>g a Straight L<strong>in</strong>e, Curve Fitt<strong>in</strong>g by Sum of Exponentials, Data Fitt<strong>in</strong>g with CubicSpl<strong>in</strong>es, Approximation of functions.Numerical Integration & Differentiation: Introduction, Numerical differentiation, NumericalIntegration, Trapezoidal Rule, Simpson 1/3 Rule, Simpson 3/8 Rule, Boole's and Weddle's Rule, Eular—Maclariaun Formula, Gaussian Formula, Numerical Evaluation of S<strong>in</strong>gular Integrals.Statistical Computation: Frequency Chart, Regression Analysis, Least Square Fit, Polynomial Fit,L<strong>in</strong>ear & Non L<strong>in</strong>ear Regression, Multiple Regressions, Statistical Quality Control Methods.References:1. Ja<strong>in</strong>, Iyengar, Ja<strong>in</strong>, “Numerical Methods for Scientific & <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Computation”, New AgeInternational.2. Balaguruswamy, “Numerical Methods”, TMH.3. Sastry, “Introductory Method of Numerical Analysis”, PHI.4. Gerald & Wheatly, “Applied Numerical Analysis”, Addision Wesley.5. Probability & Statistic, Schaum Series.6. Hulquit, “Numerical Method for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers & Computer Scientist”, Addision Wesley.7. Flowers, “Numerical Methods In C++”, Oxford University Press.8. Vedamurthy, “Numerical Methods”, Vikas.List of Experiments:Write Programs <strong>in</strong> C1. To d<strong>edu</strong>ce errors <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> polynomial Interpolation.2. Algebraic and transcendental equations us<strong>in</strong>g Bisection, Iterative method of false position, alsogive rate of conversions of roots <strong>in</strong> tabular form for each of these methods.3. To implement Bessel’s functions, Newton’s, Sterl<strong>in</strong>g, Languages.4. To implement method of least square curve fitt<strong>in</strong>g.5. Implement numerical differential us<strong>in</strong>g trapezoidal, Simpson 3/8 rules.6.To show frequency chart, regression analysis, L<strong>in</strong>ear Square fit and polynomial fitELEMENTS OF ECONOMICS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCECourse Code (BAM-315) CREDIT 4(3-1-0)<strong>Industrial</strong> Economics;1. Introduction: -Nature and significance of economics, mean<strong>in</strong>g of science, <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> andtechnology and their relationship with economic development.2. Basic concept: - The concept of demand and supply, <strong>in</strong>difference curve analysis, price effect,<strong>in</strong>come effect and substitution effect.3. Money and bank<strong>in</strong>g: - Function of money, value of money, <strong>in</strong>flation and measure to control it.Brief idea function of bank<strong>in</strong>g system, viz; commercial and central bank<strong>in</strong>g, bus<strong>in</strong>essfluctuation.Management:
4. Introduction: Def<strong>in</strong>ition, nature and significance of management, evaluation of managementthought, contribution of Max Weber, Taylor and Fayol.5. Human behaviour: Factors of <strong>in</strong>dividuals’ behaviour, perception. Learn<strong>in</strong>g and personalitydevelopment, <strong>in</strong>ter personal relationship and group behaviour.References:4. Dewett, K.K./Modern Economics Theory.5. Luthers, Fred / Organizational Behaviours.6. Prasad L.M/ Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Management7. A.W. Stonier &D.C Hergne/ A Text Book of Economics Theory /Oxford Publish<strong>in</strong>g House Pvt LtdMACHINE DESIGN – I0-2)Course Code (ME-409)Credit4(2-Introduction, Def<strong>in</strong>ition, Methods, Standards <strong>in</strong> design & selection of preferred size Selection ofmaterials, BIS system of designation of steels, steel & alloys, plastics & rubbers.Design aga<strong>in</strong>st static loadModes of failure, Factor of safety, stress-stra<strong>in</strong> relationship, pr<strong>in</strong>cipal stresses, theories of failure,endurance limit, design for f<strong>in</strong>ite & <strong>in</strong>f<strong>in</strong>ite life, Soderberg & Goodman criteriaDesign aga<strong>in</strong>st Fluctuat<strong>in</strong>g LoadJo<strong>in</strong>ts Riveted jo<strong>in</strong>ts, welded jo<strong>in</strong>t, screwed jo<strong>in</strong>ts, eccentric load<strong>in</strong>g of above jo<strong>in</strong>ts, design forfatigue load<strong>in</strong>g.Shaft, Keys & coupl<strong>in</strong>g.Design aga<strong>in</strong>st static load, strength & rigidity design, design of square & flat keys & spl<strong>in</strong>es, rigid &flexible coupl<strong>in</strong>gs.Mechanical Spr<strong>in</strong>gs.Helical spr<strong>in</strong>g, stress equation, deflection equation, design aga<strong>in</strong>st static & fatigue load<strong>in</strong>g, Multileafspr<strong>in</strong>g, Nippl<strong>in</strong>g, Design, spiral spr<strong>in</strong>gs.Power ScrewsForm of threads, square threads, trapezoidal threads, stresses <strong>in</strong> screw, design of screw jack.Reference:1. Mach<strong>in</strong>e design: Sharma & Agarwal, Kataria2. Design of M/c Elements: Bhandari TMH3. M/c Design : Maleev & Hariharan4. Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design SI edition by Shegley, McGray Hill5. Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design by black & Adams, McGray Hill6. Design of mach<strong>in</strong>e elements by Sprots.MECHINE DESIGN – I LAB1. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of Riveted jo<strong>in</strong>ts for given operat<strong>in</strong>g conditions2. Design of an eccentrically loaded welded, riveted or bolted jo<strong>in</strong>t3. Design of bolted jo<strong>in</strong>t for fluctuat<strong>in</strong>g loads4. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of a cotter jo<strong>in</strong>t.5. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of a Knuckle jo<strong>in</strong>ts.6. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of a simple screw jack7. Design of shaft for different load<strong>in</strong>g conditions8. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of rigid coupl<strong>in</strong>g (flanged type)9. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of a flexible coupl<strong>in</strong>g (p<strong>in</strong>-bush type)10. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of a leaf spr<strong>in</strong>g for and automobile11. Design & draw<strong>in</strong>g of a helical spr<strong>in</strong>g for a given application
Note-1. Students may be advised to use design data book for design2. Draw<strong>in</strong>g shall be made wherever necessary on small draw<strong>in</strong>g sheetsHEAT & MASS TRANSFERCourse Code (ME-503 ) Credit 4(3-0-1)General: Modes of heat transfer Conduction Convection- Radiation, scope and application of heattransfer, pr<strong>in</strong>ciples <strong>in</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Practice.Conduction:Fourier law-Thermal conductivity of solids, liquids and gases, factors affect<strong>in</strong>gthermal conductivity General differential equation for conductions. One dimensional steady stateconduction through homogeneous and composite surface-Plane, cyl<strong>in</strong>drical and spherical walls-Effect of variable thermal conductivity Shape factor, Overall heat transfer coefficient-Criticalradius of <strong>in</strong>sulation solution of multi dimensional steady state problems us<strong>in</strong>g relaxation method.Transient heat conduction based on lumped parameter method.Convection:Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of dimensional analysis-pi theorem, Application of dimensional analysis tofree and forced convection. Empirical relations for flat plate and tubular geometry. Forcedconvection from tubes & tube bundles <strong>in</strong> cross flow. Simple application to straight, rectangularand triangular f<strong>in</strong>s effectiveness of f<strong>in</strong>s. Fundamentals of boil<strong>in</strong>g heat transfer, pool boil<strong>in</strong>g, Heattransfer <strong>in</strong> condensation: drop wise and film condensation: empirical equations.Radiation:Nature of thermal-radiation-Def<strong>in</strong>itions and concepts Monochromatic and totalemissive power-Absorptivitiy – Reflectivity-Black, gray and real surfaces-concept of a blackbody-Planck’s distribution law-Configuration of geometrical factor Heat exchange by radiationbetween black surfaces-Large parallel black plates, equal parallel and opposite black squares,black rectangles perpendicular to each other hav<strong>in</strong>g a common edge-heat exchange by radiationbetween large parallel planes of different emissivity. Radiation shields Electrical network methodof solv<strong>in</strong>g radiation problems. Solar radiation & Collectors.Heat Exchangers:Tubes of heat exchangers- Parallel flow, Counter flow evaporator andcondenser, Log mean temperature difference, effectiveness, NTU method, Introduction to compactheat exchangers.Ficks law of diffusion, Diffusion coefficient, steady state diffusion through stationary media,steady state diffusion through a stagnant gas films, steady state, equivocal counter diffusion.References:1. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Heat Transfer Frnak Kreith McGray Hill Book Co. Heat and Mass Transfer C-DBennett and J-E-M years, Tata McGraw-Hill (19975)2. Fundamental of moment and heat transfer-Wetly3. Heat and mass Transfer – Eckert & Drake, McGraw Hill Book Co.4. <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Heat Transfer J.P. Homan, McGraw Hill Book Co.5. Heat Transfer by Pitts ane Sission, Schaum series.6. Heat Mass Transfer by R. Yadav7. Heat Mass Transfer by C.P.Gupta8. Heat and Mass Transfer by Domkundvar9. Heat & Mass transfer by R.C. Chandra10.Heat & Mass Transfer by Vijay Gupta11.Heat & Mass Transfer by D.S. KumarHEAT & MASS TRANSFER –LAB1- Conduction- Composite wall experiment2- Conduction- Composite cyl<strong>in</strong>der experiment3- Convection- Pool Boil<strong>in</strong>g experiment4- Convection- Experiment on heat transfer from tube-natural convection.5- Convection- Heat Pipe experiment
6- Convection- Heat transfer through f<strong>in</strong>-natural convection.7- Convection- Heat transfer through tube/f<strong>in</strong>-forced convection.8- Any experiment- Such as on Stefan’s Law9- Any experiment on radiation-Such as on solar collector.10- Heat exchanger- Parallel flow experiment11- Heat exchanger- Counter flow experiment12- Any other suitable exp. Such as on critical <strong>in</strong>sulation thickness.DYNAMICS OF MACHINES.0-1)Course Code ( ME-504) Credit 4(3-1. Force Analysis. Turn<strong>in</strong>g moment & Fly Wheel: Static force analysis of l<strong>in</strong>kages, Equivalentoffset <strong>in</strong>ertia force, Dynamic analysis of slider crank and 4 Bar mechanism. Piston and crankeffort, <strong>in</strong>ertia, torque Turn<strong>in</strong>g moment diagrams, fluctuation of energy, fly wheel.2. Balanc<strong>in</strong>g of Mach<strong>in</strong>es: Static and dynamic balanc<strong>in</strong>g, balanc<strong>in</strong>g of rotat<strong>in</strong>g and reciprocationmasses, Primary and secondary forces and couples.3. Friction:Pivot and collar friction, friction circle, s<strong>in</strong>gle plate, multiple and cone clutches,centrifugal clutches, Michele & K<strong>in</strong>gs burros thrust bear<strong>in</strong>g and roll<strong>in</strong>g contact bear<strong>in</strong>g, Beltsand pulleys, flat and V-Belts, design and selection.4. Brakes and Dynamometers: External and <strong>in</strong>ternal shoe brakes, band and block brakes, hydraulicbrakes, and absorption and transmission dynamometers.5. Governors:Dead weight and spr<strong>in</strong>g loaded governors, sensitivity, stability, hunt<strong>in</strong>g, isochronism’s,effort and power, friction and <strong>in</strong>sensitivity, gyroscopic couple and rection.6. Gyroscopic Motion: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, Gyroscopic acceleration, gyroscopic couple and reaction.7.Mechanical Vibration: S<strong>in</strong>gle degree free & forced, undamped and damped vibrations, Criticalspeeds.Book & Preferences1. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es: Thomas Bevan (ELBS/CBS pub., New Delhi)2. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es: S.S. Rattan (TMH)3. Mechanisms & Dynamic of Mach<strong>in</strong>es- Mabie4. Theory of mach<strong>in</strong>es: Sh<strong>in</strong>glay5. Theory of mach<strong>in</strong>es – R.K. Bansal (Laxmi Publication)6. Mechanisms and Mach<strong>in</strong>e Theory – A.K. Ambekar Ja<strong>in</strong> Bros.7. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es – W.T. Green8. Mechanism & Mach<strong>in</strong>e Theory- Rao & Dukhipati (New Age)9. Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>e and Mechanism- Ghsoh & Mullick10.Theory of Mach<strong>in</strong>es – P.L. Ballaney (Khanna Pub.)PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT & DESIGNCourse Code(ME-506)Credit3(2-1-0)Product, Def<strong>in</strong>ition, Scope, Term<strong>in</strong>ology: Design def<strong>in</strong>itions, Old and new design methods, design byevolution, examples such as evolution bicycle, safetyrazor etc. Need based developments, <strong>Tech</strong>nologybased developments, Physical reliability & Economic feasibility of design concepts.Morphology of design, Divergent, transformation and convergent phases of product disigh, Identificationof need, Analysis of need.Design for what? Design, criteria, functional aesthetic, ergonomics, form, shape, size, colour.
Mental blocks, Removal blocks, Ideation techniques, creativity, checklist, transformations, bra<strong>in</strong> storm<strong>in</strong>gand syneerics, Morphological techniques.Utility concept, Utility value, Utility <strong>in</strong>dex, Decision mak<strong>in</strong>g under multiple criteria. Economic aspectsfixed and variable costs, Break-even analysis.Reliability considerations, Bath tub curve, reliability of systems <strong>in</strong> series and parallel, failure rte, MTTFand MTBF, Optimum spares from reliability considerations.Design of displays and controls, Man-mach<strong>in</strong>e Interface, compatibility of displays and controlsErgonomic Aspects, Anthropometrics data and its importance <strong>in</strong> design.Application of Computers <strong>in</strong> product design.Book References:1. Product Design & Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g – A.K. Chitat & R.C. Gupta, PHI (EEE)2. The <strong>Tech</strong>nology of Creation Th<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g- R.P. Gewford- Ph.D.3. The Art of thought- Grohem Wallas- Brev & Co., New York.4. Product Design & Dection Therory – M.K. Starr, PH5. Engg. Product Design – C.D. La<strong>in</strong>, Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Book6. <strong>Industrial</strong> Design for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers – W.H. Mayall Hiffe7. Human Factor Engg. – Mccormic E.J., McGraw Hill8. <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>, An Introduction to creative Profession- G.C. Beabley & HW Leach, Mc MillanMANUFACTURING SCIENCE – IICourse Code (ME-507)Metal Cutt<strong>in</strong>g and Mach<strong>in</strong>e Tools Metal Cutt<strong>in</strong>gCredit4(3-0-1)Lathe: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciple, types, operations, Turret/Capstan, Semi/Automatic, Tool layout. Shaper, slotterplaner: Operation, drive.Mill<strong>in</strong>g: Mill<strong>in</strong>g cutter, Up & Down mill<strong>in</strong>g, Divid<strong>in</strong>g head, <strong>in</strong>dex<strong>in</strong>g. Max chip thickness, powerrequired.Drill<strong>in</strong>g and bor<strong>in</strong>g: Drill<strong>in</strong>g, bor<strong>in</strong>g, ream<strong>in</strong>g tools. Geometry of twist drillGr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g: Gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g wheel, abrasive, cutt<strong>in</strong>g action. Gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g wheel specification. Gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g wheelwear attritious wear, fracture wear. Dress<strong>in</strong>g and true<strong>in</strong>g. Maxchip thickness and Guest criteria. Flatand cyl<strong>in</strong>drical gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g. Centerless gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g. Super f<strong>in</strong>ish<strong>in</strong>g: Hon<strong>in</strong>g, lapp<strong>in</strong>g, polish<strong>in</strong>g. MetalJo<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gWeld<strong>in</strong>g :Survey of weld<strong>in</strong>g and allied processes. Gas weld<strong>in</strong>g and cutt<strong>in</strong>g, process and equipment. Arcweld<strong>in</strong>g: Power sources and consumables. TIG & MIG processes and their parameters. Resistanceweld<strong>in</strong>g- spot, seam projection.Other weld<strong>in</strong>g processes such as atomic hydrogen, submerged are, electroslag, friction weld<strong>in</strong>g.Thermodynamic and Metallurgical aspects <strong>in</strong> weld<strong>in</strong>g and weld. Shr<strong>in</strong>kage/residual stresses <strong>in</strong>welds. Defects <strong>in</strong> weld and remedies. Weld decay <strong>in</strong> HAZ.Non conventional Mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and Non-conventional Weld<strong>in</strong>gBenefits, application and work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of non-conventional mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g process. Introduction toNon-conventional Mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and weld<strong>in</strong>g (EDM,ECM, LBM, EBM, USM, AJM) similarly, nonconventionalweld<strong>in</strong>g processes such as LBW, USW, EBW, Plasma arc weld<strong>in</strong>g, explosive weld<strong>in</strong>g.Books:
1. Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g science by Ghosh and Mullick2. Fundamentals of Metal Cutt<strong>in</strong>g and Mach<strong>in</strong>e Tools by Boothroyd3. <strong>Production</strong> <strong>Tech</strong>nology, by R.K. Ja<strong>in</strong>4. <strong>Production</strong> <strong>Tech</strong>nology-HMT5. <strong>Production</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Science by P.C. Pandey6. Modern Mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g by P.C. Pandey7. Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g by Degarmo8. Fundamentals of metal cutt<strong>in</strong>g & mach<strong>in</strong>e tools- Juneja & Shekho<strong>in</strong>9. Process & materials of manufactur<strong>in</strong>g- L<strong>in</strong>d burg10.Advanced mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g process by V.K. Ja<strong>in</strong>MANUFACTURING SCIENCE –II LAB1. Shear-angle determ<strong>in</strong>ation (us<strong>in</strong>g formula) with tube cutt<strong>in</strong>g (for orthogonal) on lathe mach<strong>in</strong>e.2. Bolt (thread) mak<strong>in</strong>g on Lathe mach<strong>in</strong>e3. Tools gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g (to provide tool angles) on tool-gr<strong>in</strong>der mach<strong>in</strong>e.4. Gear cutt<strong>in</strong>g on mill<strong>in</strong>g mach<strong>in</strong>e.5. Mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g a block on shaper mach<strong>in</strong>e.6. F<strong>in</strong>ish<strong>in</strong>g of a surface on surface-gr<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g mach<strong>in</strong>e.7. Drill<strong>in</strong>g holes on drill<strong>in</strong>g mach<strong>in</strong>e and study of twist-drill8. Study of different types of tools and its angles & materials.9. Experiment on tool wear and tool life10. Experiment on jigs/Fixtures and its uses11. Gas weld<strong>in</strong>g experiment12. Arc weld<strong>in</strong>g experiment13. Resistance weld<strong>in</strong>g experiment14. Solder<strong>in</strong>g & Braz<strong>in</strong>g experiment15. Experiment on <strong>in</strong> conventional mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g16. Experiment on unconventional weld<strong>in</strong>g17. Experiment on TIG/MIG Weld<strong>in</strong>g18. Macro and microstructure of weld<strong>in</strong>g jo<strong>in</strong>ts, HAZ.I.C. ENGINESCourseCode:ME508 Credit 4(3-1-0)Introduction: Review Classification, Application, Constructions details, Work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciple,Valve tim<strong>in</strong>gs, Environment friendly eng<strong>in</strong>es. List of auxiliary system.Gas Cycle & Processes: Review of Otto, Diesel and Dual Cycles, Comparison, Sterl<strong>in</strong>g andBryaton Cycle, Improvement of Performance by modification of gas turb<strong>in</strong>e cycles, Fuel air cycle,Actual cycle.Combustion <strong>in</strong> SI & CI Eng<strong>in</strong>es: Stiochiometric air fuel, Combustion theory, Combustionphenomena. Eng<strong>in</strong>e variables on ignition delay and flame Speed Abnormoral Combustion,Detonationor Knock, Variable affect<strong>in</strong>g knock, Effects of knock, Methods to r<strong>edu</strong>ce detonation, Combustorchambers design.Fuels for I. C. Eng<strong>in</strong>e: Types, Chemical Structure, Petroleum ref<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g process, Properties of SI,CI and aviation fuels, Knock<strong>in</strong>g rat<strong>in</strong>g of SI and CI fuels, Non- petroleum fuels, Alternative fuelsfor I.C eng<strong>in</strong>e. Stiochiometric air – fuel ratio.
Carburetion and gasol<strong>in</strong>e Injection: Intake and exhaust system, Eng<strong>in</strong>e air-fuel requirement,Simple carburetor, Complete carburetor and its elements, Types, Fuel pump, Fuel system, Multipo<strong>in</strong>tfuel <strong>in</strong>jection system. Govern<strong>in</strong>g of SI eng<strong>in</strong>es.C.I. Fuel Injection System: Requirements of <strong>in</strong>jection system, Types, Injection pump, Govern<strong>in</strong>g,Fuel <strong>in</strong>jector, Injector nozzle.Ignition System: Requirements, Types – Battery and Magneto ignition system, Spark plug, Contactbreaker, Dual angle, Fir<strong>in</strong>g order , Spark advance mechanism , Electronic ignition systemsEng<strong>in</strong>e Friction and Lubrication: Total eng<strong>in</strong>e friction, Factors affect<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>e friction,Lubrication, Mechanism of lubrication, Lubricants and their properties, Additives, Lubricationsystems.Eng<strong>in</strong>e Cool<strong>in</strong>g System: Necessity of cool<strong>in</strong>g, Heat transfer and energy balance, Parametersaffect<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>e heat transfer, Cool<strong>in</strong>g system.Supercharg<strong>in</strong>g : Objective, Methods, Turbocharger, performance.Two- stroke Eng<strong>in</strong>es: Classification, Scaveng<strong>in</strong>g processes, advantages and disadvantages,Performance.Measurement, Test<strong>in</strong>g & Performance: Performance parameters, Type of tests – speed fuel andair consumption, friction, Indicated and brake power, Performance characteristics, Heat balancesheet.Air Pollution and Control: Sources and classification, Effects of air pollution, Pollutants from I.C. eng<strong>in</strong>es, Mechanism of formation of pollutants, Particulate emissions, Exhaust gas treatment.References:1. I.C. eng<strong>in</strong>e Analysis and practice –E.F. obert2. A Course <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternal combustion eng<strong>in</strong>es –M.L. Mathur & R.P. Sharma, Dhanpat, Rai & sons,New Delhi.3. Internal combustion eng<strong>in</strong>es- Maleev4. Heat Engg.-Vasandani & Kumar5. Internal Combustion Eng<strong>in</strong>e-Gill and Smith6. Internal combustion Eng<strong>in</strong>es and Air Pollution- R. Yadav, CPH, Allahabad7. I.C. Eng<strong>in</strong>es by V. Ganesam, TMH8. Internal combustion Eng<strong>in</strong>e- Heywood, Mc-Graw HillTOOL DESIGN1)Course Code (ME-501) Credit: 4(3-0-1.Broad classification of Tools‐cutt<strong>in</strong>g tools. Dies. Hold<strong>in</strong>g and measur<strong>in</strong>g tools2.Design of cutt<strong>in</strong>g tools : S<strong>in</strong>gle po<strong>in</strong>t and multipo<strong>in</strong>t cutt<strong>in</strong>g tools .S<strong>in</strong>gle po<strong>in</strong>t cutt<strong>in</strong>g tools : Classification. Nomenclature . geometry . design of s<strong>in</strong>gle po<strong>in</strong>t tools forShapers . planers . etc. Chip breakers and their design.Multipo<strong>in</strong>t Cutt<strong>in</strong>g Tools :Classification and specification. Nomenclature. Design of drills , mill<strong>in</strong>g cuttersBroaches, taps etc.Design of form tools : Flat and circular form tools, their design and application.3.Design of Dies : Classification of Dies , Design of Dies for bulk metal deformation , ‐ wire draw<strong>in</strong>g ,Extrusion, Forg<strong>in</strong>g and Roll<strong>in</strong>g . Design of Dies for sheet metal , Blank<strong>in</strong>g and Pierc<strong>in</strong>g . Bend<strong>in</strong>g andDeep draw<strong>in</strong>g . Design of Dies for Cast<strong>in</strong>g and Mould<strong>in</strong>g . Power Metallurgy die design .4 Design of Jigs and Fixtures : Classification of Jigs and Fixtures , Fundamental Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of design of jigs andfixtures, Location and clamp<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> jigs and fixtures , Simple design of drill<strong>in</strong>g jigs, mill<strong>in</strong>g fixtures , etc.<strong>in</strong>dex<strong>in</strong>g jigs and fixtures .
1)MACHINE –DESIGN- IICourse Code (ME-505) Credit 4(3-0-Spur gears:Conjugate action, <strong>in</strong>volute gears, gear cutt<strong>in</strong>g methods, tooth loads, strength of spur gearsI bend<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong> wear, dynamic load<strong>in</strong>g, gear materials, design of gears <strong>in</strong> volute sp<strong>in</strong>es gearcorrections.Helical Gears:Tooth relation ship, tooth proportions design of the helical gears, crossed helical gears.Worm gears:Types of worm gear<strong>in</strong>g, analysis of forces, power rat<strong>in</strong>g efficiency, worm gear standersand proportions.Bevel gears:Straight bevel gears, design for bend<strong>in</strong>g, wear and dynamic load<strong>in</strong>g, spiral bevel gears,hypoid gears.Antifriction bear<strong>in</strong>g:Types of ball bear<strong>in</strong>g, roller bear<strong>in</strong>g, needle roller bear<strong>in</strong>g, friction life ofbear<strong>in</strong>g, reliability considerations, selection of ball bear<strong>in</strong>g, roller bear<strong>in</strong>g, tapered roller bear<strong>in</strong>gs,thrust bear<strong>in</strong>g, lubrication and seal<strong>in</strong>g. Mount<strong>in</strong>g of bear<strong>in</strong>gs,Lubrication and slid<strong>in</strong>g bear<strong>in</strong>g:Type of lubrication, viscosity, hydrodynamic theory of lubrication,types of bear<strong>in</strong>g, design of bear<strong>in</strong>g us<strong>in</strong>g design charts, boundary lubrication, hydrostatic bear<strong>in</strong>g,hydrodynamic thrust bear<strong>in</strong>g.Eng<strong>in</strong>e Parts:Design of the connect<strong>in</strong>g rod, cross-head, crank shaft and piston, valve gearmechanism.References:1. Mechanical <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Desigh-Joseph E. Shigley McGraw –Hill Publications.2. Design of mach<strong>in</strong>e members- alex Valance V.I doughtie, Mg-graw Hill Co.3. Mach<strong>in</strong>e design D.N. Reshetov, Mir Publishers: Mosow.4. Mach<strong>in</strong>e design D.N. Reshetov, Mir Publisher: Mosow.5. Fundamentals of Mach<strong>in</strong>e desigh [Vol: 1-5] Porlov, ir. Pun: Mocow6. Mach<strong>in</strong>e elements: Dobrovsky, Mir, Pub. Moscow data books7. Fundamentals of Mach<strong>in</strong>e design-Rechard M. Phelan, Tata-McGraw Hill Pu. [1978]8. Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design-Maleev and Hartman, CBS.9. Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design –Sharma & Agrawal, Kataria10.Design of Mach<strong>in</strong>e Elements – Bhandari TMH11.Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design- Black & Adams, Mc Graw-HillMACHINE DESIGN – II LABAt least 2 experiments/turns (lecture-classes) from each of the 4 follow<strong>in</strong>g sections, say, 3 turns forA, 3 turns for B, 2 turns for C and 2 turns of D, total 10.A. Conventional Design & Draw<strong>in</strong>g-Conventional design & draw<strong>in</strong>g on small draw<strong>in</strong>g sheet us<strong>in</strong>g hand book for items such as eng<strong>in</strong>eparts, shafts, gears, bear<strong>in</strong>gs etc. by students.B. Computer and Language-Lectures should be given by teachers on <strong>in</strong>troduction to computer and languages such as C/Input Output statements, control statements, if, for while, switch statement etc. Function and its uses.Structure. To make student able to write computer program.C. Writ<strong>in</strong>g computer programme for conventional design-After section B, students can write compute program for the design done <strong>in</strong> section A/ theorysubjects.D. Auto CAD-
With <strong>in</strong>itial review teach<strong>in</strong>g of Auto CAD, students can do draw<strong>in</strong>g & draft<strong>in</strong>g of design done <strong>in</strong>section A.PROJECT MANAGMENTCourse Code (ME509) Credit 3(2-1-0)Project management concept, establish<strong>in</strong>g the project and goals; organiz<strong>in</strong>g human resource andcontract<strong>in</strong>g; organiz<strong>in</strong>g systems and proc<strong>edu</strong>res for implementation; project direction, coord<strong>in</strong>ationand control, project management performance; project management case studies, projectmanagement <strong>in</strong>formation system; computer based project management; future of projectmanagement.Development of Project Network:Time estimation, determ<strong>in</strong>ation of critical path (CPM) Event slacks and floats, choice of sch<strong>edu</strong>le <strong>in</strong>view of resource constra<strong>in</strong>ts. Programme evaluation review technique (PERT) examples. Illustrations& case studies.Misc. Topics:Introduction to MRP? ERP, TQM and E-commerce etc.REFERENCE:1. Project management-Kerzner, CBS.2. Essentials of project management-Dennis Lock, Groover,3. Projects-plann<strong>in</strong>g, analysis, selection, impletation & review -P, Chandra,TMH4. Project management Basic-R.L.Kimmons, Dekker.5. System analysis & Project management - Cleland & k<strong>in</strong>d McGraw hill.6. Practical Project management - RG Ghattas & Sandra L. Mckec, Pearson Education Asia.AUTOMATIC CONTROLSCourse Code (EEE-509) Credit 3(2-1-0)Introduction :Concept of automatic controls-loop and closed-loop systems, servomechanisms, blockdiagrams, transfer functions. Application of Laplace Transform <strong>in</strong> control system.Representation of control components and systems:Translation and rotational mechanical components, electrical components, series and parallelcomb<strong>in</strong>ations, cascade systems, analogous system.System Response: First and second order systems response to impulse, ramp and s<strong>in</strong>usoidal <strong>in</strong>puts,properties of unit step response of second order system, systems with velocity lag.Mode of Controls: Proportional control-proportional pus reset control proportional plus rate control,reset rate, two position control.Controller Mechanisms: Pneumatic, hydraulic and electric controllers, general pr<strong>in</strong>ciples forgenerat<strong>in</strong>g various control actions. Concept of control value.Control system analysis: Transient response of simple control systems stability of control systemRouth’s criterion.Frequency response analysis: Polar, Bode plots-experimental determ<strong>in</strong>ation of frequency response,Bode and Niquist stability criteria, ga<strong>in</strong> and phase marg<strong>in</strong>s.Root locus plots: Simple transfer functions transient response from root locus.
References:1. Automatic control Theory- Rave, McGraw- Hill Book Co.2. <strong>Industrial</strong> Automatic controls – lajoy, Longmans Green & Co.3. Automatic Control Systems – B.C. Kuo, Prentice – Hall [1976]4. Modern Control <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> – L<strong>in</strong>ear Control Systems- W-Leonhard, Allied Publishers Pvt. Ltd.[1976]5. Control systems <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>- I.J. Nagarth and M. Gopat New Age Pvt. Ltd.6. Automatic Process Control- D.P. Eckaman, Viley Eastern Ltd.QUALITY ENGINEERINGCourse Code ME-510 Credit : 4 (3-0-1)1. Concept of quality , basic statistical concept , Control of accuracy and precision , Process capability ,standardization and <strong>in</strong>terchangeability , Statistical quality control : Objectives , Applications ,Organization , Cost Aspects, theory of statistical tolerance.2. Control Charts : General theory of control charts , Group control chart , Shewhart control chartfor process control; control charts for variables such as X , R , Control charts for charts for attributessuch as c and p charts , Acceptance control chart ; Cumulative sum control charts ;Subgroup selection ; Process capability , Cause – effect and pareto diagrams3. Acceptance Sampl<strong>in</strong>g :Multiple and Sequential sampl<strong>in</strong>g plans , Multi-Cont<strong>in</strong>uous sampl<strong>in</strong>g Plans,Acceptance Sampl<strong>in</strong>g by variables , Advantages Limitations , Sampl<strong>in</strong>g plans us<strong>in</strong>g differentCriteria , Comparison of various types of sampl<strong>in</strong>g plans , Rectify<strong>in</strong>g Inspection .4. Reliability , Availability and ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>ability : Introduction to reliability , Bathtub curve , seriesand parallel system ; MTBF , Evaluation of Availability and Ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>ability .5. Quality Design : Design of experiment concept , System , Parameter and Tolerance Design ;concept of robust design , Taguchi Concept - Orthogonal arrays and S/N ratioReference Books:1.Quality Control and Introduction Statistics – Duncan A. J.2. Introduction to Quality Control – C.O.P. applications3. Statistical Quality Control by Grant andv Leavarworth .4. Ma<strong>in</strong>tenance for reliability by Rao .ENERGY MANAGMENTCourse Code ME-516 Credit : 4 (3-1-0)1. Introduction : The energy-economy l<strong>in</strong>k. Patterns of energy use <strong>in</strong> develop<strong>in</strong>g countries, the electricityeconomyl<strong>in</strong>k for develop<strong>in</strong>g economies, options to overcome the energy crisis. Characteristics ofconventional and non-conventional energy resources.
2. Conventional energy resources and their utilization; thermal, nuclear and hydro-electric power plants, useof diesel eng<strong>in</strong>es and gas turb<strong>in</strong>es for power generation. Comb<strong>in</strong>ed cycles for efficient power generation.3. Non-conventional energy resources and their utilization: solar , geothermal, w<strong>in</strong>d, wave, biomass andocean-thermal energy conversion and their limitations. Energy storage techniques.4. Energy conservation: energy audit<strong>in</strong>g, process energy and gross energy requirement, energy recovery:<strong>in</strong>sulation, heat recovery heat exchangers, heat-pumps, comb<strong>in</strong>ed heat and power plants (cogeneration),efficient light<strong>in</strong>g and energy conservation <strong>in</strong> build<strong>in</strong>gs.5. Environmental aspects of energy resource utilization: combustion generated air pollution, global warm<strong>in</strong>g,acid ra<strong>in</strong>, fly ash disposal, radioactive pollution and nuclear waste disposal.REFERENCES:(A) ‘Energy for a susta<strong>in</strong>able world’ by Goldemberg et al. Wiley Eastern Limited. 1988.(B) ‘Power Plant <strong>Tech</strong>nology’ by M.M.El-Wakil. McGraw-Hill. 1984.(C) ‘Manag<strong>in</strong>g energy <strong>in</strong> commerce and <strong>in</strong>dustry’ by Gordon A Payne. Butterworths, 1984.FLUID MACHINERYCourse Code (CE-576) Credit 4(2-1-1)1. Jet Theory: Introduction to hydro dynamic thrust of a jet on a fixed and mov<strong>in</strong> g suface (flat, curve),effect of <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ation of jet with the surface.2. Hydraulic Turb<strong>in</strong>es:Pelton Wheel, Francis and Kaplan turb<strong>in</strong>es classification of turb<strong>in</strong>es, work<strong>in</strong>gpr<strong>in</strong>ciples, work done, efficiency, draft tube theory, cavitations <strong>in</strong> turb<strong>in</strong>es, performance, test<strong>in</strong>g ofturb<strong>in</strong>es, model test<strong>in</strong>g, selection of a turb<strong>in</strong>es, stability of a turb<strong>in</strong>e (Static & dynamic),performance curves, constant efficeiency curves, Muschel curves, govern<strong>in</strong>g of turb<strong>in</strong>es, specificspeeds.3. Pumps:Centrifugal pumps, classifications, work done by impeller, efficiencies of centrifugal pumps,prim<strong>in</strong>g, specific speed, cavitations and separation, surg<strong>in</strong>g, check<strong>in</strong>g, model test<strong>in</strong>g, performancecharacteristics, reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g pumps, classification, work done (s<strong>in</strong>gle and double act<strong>in</strong>g), slip,variation of pressure, work saved by fitt<strong>in</strong>g air vessels, multicyl<strong>in</strong>der pumps, comparison ofcentrifugal and reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g pumps, design aspects.4. Hydraulic mach<strong>in</strong>es:Hydraulic systems, hydraulic press, cranks, jacks, accumulator, <strong>in</strong>tensifier, ram,fluid coupl<strong>in</strong>g, fluid torque converter, water hammer, jet pumps and air lift pumps.5. Gas Turb<strong>in</strong>es and Jet propulsion:Introduction, work<strong>in</strong>g cycle, different types of gas turb<strong>in</strong>es, jetpropulsion, thrust power and propulsion efficiency.References:1. Hydraulic Mach<strong>in</strong>es Dr. J. Lal2. Heat Engg. V.P. Vasandani & D.S. Kumar3. Hydraulic mach<strong>in</strong>es V.P. Vasandani4. Fluid mach<strong>in</strong>ery- K.R. Arora5. Fluid mach<strong>in</strong>ery – P.N. Modi & S.M. Seth.FLUID MACHINERY LAB
Say m<strong>in</strong>imum eight experiment follow<strong>in</strong>g or such experiment1. Impact of jet experiment2. Turb<strong>in</strong>e exp. On pelton wheel3. Turb<strong>in</strong>e exp. On Francis turb<strong>in</strong>e4. Turb<strong>in</strong>e exp. On Kaplan turb<strong>in</strong>e5. Exp. On Reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g pump6. Exp. On centrifugal pump.7. Exp on Hydraulic Jack/Press8. Exp. On Hydraulic Brake9. Exp. On Hydraulic Ram10. Study through first visit of any pump<strong>in</strong>g station/plant11. Study through second visit of any pump<strong>in</strong>g station/ plant12. Any other suitable experiment/test rig such as comparison & performance of different types ofpumps and turb<strong>in</strong>es.DESIGN AGAINST FATIGUE AND FAILURECREDITCourse Code ME-518 Credit 4 (3-1-0)A. FRACTURE OF CRACKED MEMBERS1. INTRODUCTION :(1) Cracks as stress raisers(2) Behavior at crack tips <strong>in</strong> real materials(3) Effects of cracks on strength(4) Effect of cracks on brittle versus ductile behaviors2. MATHEMATICS CONCEPT OF(1) Stra<strong>in</strong> Energy release rate ratio , G .(2) Stress <strong>in</strong>tensity factor K .3. APPLICATION OF K TO DESIGN & ANALYSIS(1) Mathematical form used to express K(2) Cases of special <strong>in</strong>terest for practical application(3) Discussion4. Fracture toughness values and trends(1) Trends of KIC with materials(2) Effects of temperature and load<strong>in</strong>g rates(3) Micro structural <strong>in</strong>fluences on KIC5. Plastic zone size and plasticity limitation on LEFM(1) Plastic zone size for plane stress(2) ) Plastic zone size for pla<strong>in</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>(3) Plasticity limitation on LEFM6. Standard Test Methods forFracture Toughness Test<strong>in</strong>gEffect of thickness on Fracture behaviourCOMPUTER AIDED DESIGN0-2)Course Code (ME-601) Credit 5(3-1. Introduction: Introduction to CAD / CAED / CAE and its eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g applications, importance& necessity.2. Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> C, C++Brief <strong>in</strong>troduction and review computer and languages. C, C++ Input output statements, controlstatement, if for while, switch statement, function. Po<strong>in</strong>ter nations.
Array, matrix, str<strong>in</strong>g, structure, class concept of object oriented Programm<strong>in</strong>g, Features of C++over C.3. Computer Graphics-Graphic systems, CTR, Display devices, Co-ord<strong>in</strong>ate representation, Graphic functions. Outputprimitives-Breseham's l<strong>in</strong>e draw<strong>in</strong>g and Mid-po<strong>in</strong>t circle algorithms. 2-D and 3-Dtransformations concatenation. Exercise and programs.Curve representation. Interpolation vs approximation. Spl<strong>in</strong>e curve. Bezier curves and itsproperties. Brief mention of other curves.Graphic - Polygon surface, quadric and super quadric surface and Bobby objects Solidmodel<strong>in</strong>g-Sweep representation wire mesh, constructive solid geometry and Boolen operations.Boundary representation, Colours.4. Computer Aided Design of Mach<strong>in</strong>e Elements and Other systems.CAD of mach<strong>in</strong>e elements such as shaft, spr<strong>in</strong>gs, bear<strong>in</strong>g and problem from other system such asheat exchanger, <strong>in</strong>ventory control etc. Writ<strong>in</strong>g computer program <strong>in</strong> C.A. Auto CADand its uses.5. Introduction to Numerical Methods and Optimization <strong>Tech</strong>nique-Introduction to Numerical techniques and optimization. Curve fitt<strong>in</strong>gs. least square method.Newton- Raphson method for root f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g an for optimization. Brief <strong>in</strong>troduction tonumerical differentiation and <strong>in</strong>tegration. L<strong>in</strong>ear programm<strong>in</strong>g for constra<strong>in</strong>ed optimization(only graphical method) .6.Introduction to F<strong>in</strong>ite Element Method (FEM)Introduction and applications of FEM. One / Two dimensional beam element (spr<strong>in</strong>g system)analysis.Books / References.1. Computer Graphic by Hearn & Baker, Prentice Hall.2.CAD / CAM by Groover3.Let us C by yaswant kanetkar and also on C ++4.Computer aided analysis & design of mach<strong>in</strong>e elements by Rao & Dukhipati5. Numerical methods us<strong>in</strong>g C by Xavier.6.Optimization - SS Rao7.FEM - SS Raosay m<strong>in</strong>imum 6 experiments from follow<strong>in</strong>gCAD LAB1. L<strong>in</strong>e draw<strong>in</strong>g or Circle draw<strong>in</strong>g algorithm experiment : writ<strong>in</strong>g the program and runn<strong>in</strong>g it onComputer.2.Transformations algorithm experiment for translation / rotations / scal<strong>in</strong>g : writ<strong>in</strong>g program andrunn<strong>in</strong>g it on computer.3.Design problem experiment: writ<strong>in</strong>g the program for design of of mach<strong>in</strong>e element or other systemand runn<strong>in</strong>g it on computer.4. Optimisation problem experiment: writ<strong>in</strong>g a program for optimiz<strong>in</strong>g a function and runn<strong>in</strong>g it oncomputer.5.Auto CAD experiment: understand<strong>in</strong>g and use of Auto CAD commands.6.Writ<strong>in</strong>g a small program for FEM for 2 spr<strong>in</strong>g system and runn<strong>in</strong>g it. OR us<strong>in</strong>g a FEM package.7.Use of graphic software standards packages e.g. GKss / PHICS / GL etc.8.Use of pro Eng<strong>in</strong>eer / Idea etc.Computer Aided Manufactur<strong>in</strong>gCourse Code (ME-602) Credit 5(3-0-2)
1. Introduction:Need and future of NC systems and CAM <strong>in</strong> India. Advantages & Disadvantages.Classification. Open and closed loop. Historical development and future trends. Closed loop.Historical development and future trends.2. Features of NC Programm<strong>in</strong>g:Difference between ord<strong>in</strong>ary and NC mach<strong>in</strong>e tools. Methods forImprov<strong>in</strong>g Accuracy and Productivity.3. NC Part Programm<strong>in</strong>g:(a)Manual (word address format) programm<strong>in</strong>g. Examples drill<strong>in</strong>g andmill<strong>in</strong>g.(b) APT programm<strong>in</strong>g, Geometry, Motion and Additional statements, Macro statement.4. System Device:Introduction to DC motors, stepp<strong>in</strong>g motors, Feed back device such as encoder,count<strong>in</strong>g devices, Digital to Analog converter and Vice versa.5. Interpolators:Pr<strong>in</strong>ciple, Digital Differential Analyses. L<strong>in</strong>ear Interpolator and its software<strong>in</strong>terpolator.6. Control of NC systems:Open and closed loops. Automatic control of closed loops with encoder &tachometers. Speed variation of DC motor. Adaptive control.7. Computer <strong>in</strong>tegrated manufactur<strong>in</strong>g system: Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g cell, Transfer l<strong>in</strong>es, FMS,CIM, CAD / CAM concept.8. Robotics:NC mach<strong>in</strong>e vs Robots. Types and generations of Robots. Robot applications. Economics,Robot programm<strong>in</strong>g methods. VAL and AML with examples. Introduction to Artificial<strong>in</strong>telligence for <strong>in</strong>telligent manufactur<strong>in</strong>g.Books / References:1. Computer control of Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g systems by Koren2. Robots by Koren3. NC Mach<strong>in</strong>es by Koren4. CAD / CAM by Groover.CAM LABM<strong>in</strong>imum four experiments1.Writ<strong>in</strong>g a part - program<strong>in</strong>g (<strong>in</strong> word address format or <strong>in</strong> APT) for a job for drill<strong>in</strong>g operation(contour<strong>in</strong>g and runn<strong>in</strong>g on NC mach<strong>in</strong>e.2.Writ<strong>in</strong>g a part programm<strong>in</strong>g (<strong>in</strong> word address format or <strong>in</strong> APT) for a job mill<strong>in</strong>g operation(conduct<strong>in</strong>g) and runn<strong>in</strong>g on NC mach<strong>in</strong>e.3. Experiment on Robots and its programs.4. Experiment of difference between ord<strong>in</strong>ary mach<strong>in</strong>e and NC mach<strong>in</strong>e, study or retrofitt<strong>in</strong>g.5.Experiment on difference between ord<strong>in</strong>ary mach<strong>in</strong>e and NC mach<strong>in</strong>e, study or retrofitt<strong>in</strong>g.6. Experiment on study of system devices such as motor and feed devices.7.Experiment on Mechatronics & controls.AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING1)Course Code (ME-603) Credit 4(2-1-Power Unit Gear Box:Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of design of ma<strong>in</strong> components. Valve mechanism. Power and Torque characteristic.Roll<strong>in</strong>g, air and gradient resistance. Tractive effort, Gear Box, Gear ratio determ<strong>in</strong>ation. Design ofgear Box.Transmission system:Requirements, clutches. Torque converts. Over Drive and free wheel, Universal jo<strong>in</strong>t. DifferentialGear Mechanism of Rear Axle. Automatic transmission, steer<strong>in</strong>g and Front Axle. Castor Angle,wheel camber & Toe <strong>in</strong> Toe out etc. Steer<strong>in</strong>g geometry. Ackerman mechanism, Understeer andOversteer.Brak<strong>in</strong>g System:
Generals requirements, Road, tyre adhesion, weight transfer, Brak<strong>in</strong>g ratio. Mechanical brakes,Hydraulic brakes. Vaccum and airbrakes. Thermal aspects.Chasis and suspension system:Loads on the frame. Strength and stiffness. Various suspension system.Electrical System:Types of start<strong>in</strong>g motors, generators & regulators, light<strong>in</strong>g system, Ignition system, Horn, Battery etc.Fuel System:Diesel & Petrol Vehicle system such as Fuel Injection Pump, <strong>in</strong>jector & Fuel Pump, Carburator etc.MPFI.Cool<strong>in</strong>g & Lubrication System:Different type of cool<strong>in</strong>g system and lubrication system. Ma<strong>in</strong>tenance System: Preventivema<strong>in</strong>tenance, break down ma<strong>in</strong>tenance, and over haul<strong>in</strong>g system.References:1. Automotive <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> - Heitner2. Automotive <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> - Kripal S<strong>in</strong>gh3. Automotive <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> - Narang4. Automotive Mechanics - Crouse5. Automotive <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> - Newton and Steed.AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING - LABSay any study & experiment from the follow<strong>in</strong>g1. Study & experiment on brak<strong>in</strong>g system.2. Study & experiment on fuel supply system.3. Study & experiment on ignition system.4. Study & experiment on steer<strong>in</strong>g system5. Study & experiment on transmission system6. Study & experiment on suspension system.7. Study safety aspect of automobile design.8. Study & experiment on Light<strong>in</strong>g or lubrication system.9. Study & experiment on lubrication and cool<strong>in</strong>g system10. Comparative study features of common small cars (such as Fiat, Ambassador, Maruti, Matiz,Santro, Indica and its variations) available <strong>in</strong> India.11. Comparative study & technical features of common scooter & motorcycles available <strong>in</strong> India. Casestudy / term paper.12. Comprative & technical features of common heavy vehicles available <strong>in</strong> India. case study / termpaper.13. Eng<strong>in</strong>e tun<strong>in</strong>g and carburator servic<strong>in</strong>g experiment.14. Experiment & study of MPFL system.15. Experiment on fuel consumption measurement.16. Review experiment on IC Eng<strong>in</strong>es & modern trends.17. Visit of a Automobile factory.18. Study & experiment of ma<strong>in</strong> gear box and differential gear box.MECHANICAL SYSTEMS DESIGNCourse Code (ME-606) Credit 4(3-1-0)1. <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Process and Systems Approach: Applications of systems concepts <strong>in</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>,Identification of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Identification of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g functions, systems approach, <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>Activities Matrix, Def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the proposed effort, Role of <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> problem solv<strong>in</strong>g. Concurrent<strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>. A case study : eg. Viscous lubrication system <strong>in</strong> wire draw<strong>in</strong>g.
2. Problem formulation: Nature of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g problems, needs statement, Hierarchial Nature ofsystems hierarchial nature of problem environment, Problem scope and constra<strong>in</strong>ts. A case Study;e.g.Heat<strong>in</strong>g duct <strong>in</strong>sulation-System High - Speed belt drive system.3. System Theories: System analysis View-po<strong>in</strong>ts, Black Box approach, state theory approach,component <strong>in</strong>tegration approach. Decision. Process approach; A case study: e.g. Automobile<strong>in</strong>strumentation panel system.4. System Model<strong>in</strong>g:Need for model<strong>in</strong>g, model<strong>in</strong>g types and purpose, L<strong>in</strong>ear graph model<strong>in</strong>g concepts,Mathematical Model<strong>in</strong>g, Concepts, A case study: e.g. A compound bar system.5. L<strong>in</strong>ear Graph Analysis: Graph model<strong>in</strong>g and analysis process, Path problem, Network flow problem,A case study: e.g. Alum<strong>in</strong>ium extrusion system.6. Optimization concepts: Optimization process, Motivation and freedom of choice goals andobjectives- Criteria, Methods of optimization analytical comb<strong>in</strong>atorial , subjective. A case study : e.g.Alum<strong>in</strong>ium extrusion system.7. System Evaluation: Feasibility assessment, plann<strong>in</strong>g horizon, time value of money, F<strong>in</strong>ancialanalysis. A case study e.g. manufacture of a maize-starch system.8. Calculus Methods for optimization: Model with one decision variable, Model with two decisionvariables, Model with equality constra<strong>in</strong>t, Model with <strong>in</strong>equality constra<strong>in</strong>t. A case study : e.g.Optimization of an <strong>in</strong>sulation - system.9. Decision Analysis: Elements of a decision problem, Decision model Probability a dignity function,Expected monetary value. Unity value, Baye's theorem : A case study : e.g. Installation of amach<strong>in</strong>ery.10. Systems Simulation: Simulation concepts, simulation models, Icons Analog Analytical, Wait<strong>in</strong>g L<strong>in</strong>esimulation, Simulation process problem def<strong>in</strong>ition, <strong>in</strong>put model construction, solution process,limitations of simulation approach : A case study : e.g. An <strong>in</strong>ventory control <strong>in</strong> a <strong>Production</strong>-Plant.Suggested Text Books / References:1. Design and Plann<strong>in</strong>g of <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> systems- by D.D. Raredith, K.V. Wong, R.W. Woodhead, andR.R. Worthman, Prentice Hall Inc. Englewood Clifts, New Jersey.2. Design <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Design Method- by J.R. Dixon, Tata Mc.Graw-Hill Publish<strong>in</strong>g Company, NewDelhi.3. An Introduction to <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Design Method- by V. Gupta and P.N. Murthy, Tata Mc-Graw-Hill.4- <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Design- Robert Matousck, Blackie and Son Ltd. Glasgow.5. Optimization <strong>Tech</strong>niques- S.S. Rao.6. System Analysis and Project Management- Devid I Cleland, William R. K<strong>in</strong>g. McGraw-Hill.TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENTCourse Code ME-665 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-0)-Concept of quality, Quality control and quality management.-Science of quality. Human resources and quality-Quality Organization and management: Quality manual. Quality cost .Quality related tasks- Quality Information system : plann<strong>in</strong>g. Hardware-software-Statistical process control and quality development techniques-Controll<strong>in</strong>g quality through measurement and through count<strong>in</strong>g- Quality system and ISO 9000 series- Quality assurance. Reports on quality. Quality audit Quality tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g-Newer quality management approaches-Quality ToolsROBOTICESCourse Code ME-670 CREDIT; 3(3-0-0)
INTRODUCTION : Past , Present and future ; Robot Term<strong>in</strong>ology ; Applications , Components and Subsystems, Classification of Robot , End Effectors , Different types of grippers and design concepts.ROBOT K8INAMETICS : Object location , Homogeneous , Transformations , Direct and <strong>in</strong>versek<strong>in</strong>ematics , Manipulator motion .ROBOT DRIVES, ACTUATORS and CONTROL: Drive systems hydraulics , pneumatic and electrical .DC Motor , Stepper Motor , Robot motion and path control , Controller.SENSORS AND PERCEPTION : Type of sensors , vision system . Computer <strong>in</strong>terfacesFINITE ELEMENT METHOD IN ENGINEERINGCourse Code ME-671 CREDIT; 3(3-0-0)Approaches of FEM- Discrete, Variational and Weighted Residual; Direct Problems- Spr<strong>in</strong>g, HydraulicNetwork; Resistance Network and Truss Systems; 1-D Field and Beam Bend<strong>in</strong>g Problems; 2-D andAxisymetric Field and Stress Problems; Plate Bend<strong>in</strong>g; 3-D Stress Analysis; Solutions of UnsteadyProblems related to Stress? Analysis, Heat Conduction,?? Fluid flow and Vibration. Solutions of PlaneStress, Plane Stra<strong>in</strong> and Axisymetric Plasticity Problems.ADVANCED WELDING? TECHOLOGYCourse Code ME-6723(3-0-0)CREDIT;1. A review of various metal jo<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g? techniques such as weld<strong>in</strong>g, braz<strong>in</strong>g, solder<strong>in</strong>g and adhesivebond<strong>in</strong>g, weld<strong>in</strong>g compared with other processes of fabrication. Classification of weld<strong>in</strong>g processes.Application of weld<strong>in</strong>g processes.2. Fusion Weld<strong>in</strong>g: Mechanism of arc <strong>in</strong>itiation and ma<strong>in</strong>tenance, Temperature distribution.<strong>Tech</strong>niques, scope and limitations of manual metal arc. TIG, MIG, submerged arc. Electroslagweld<strong>in</strong>g. Plasma Arc and Electro gas weld<strong>in</strong>g. Various gas weld<strong>in</strong>g processes e.g. oxyacetylene oxyhydrogenweld<strong>in</strong>g processes.3. Resistance weld<strong>in</strong>g, Modern weld<strong>in</strong>g processes viz. Electron Beam, Ultrasonic; Explosive, laser beamprocesses and their applications. Solid state weld<strong>in</strong>g processes viz.? Friction, Diffusion, cold pressureprocess and their applications.4. Oxygen cutt<strong>in</strong>g Plasma Arc cutt<strong>in</strong>g. laser cutt<strong>in</strong>g processes etc.5. Braz<strong>in</strong>g, solder<strong>in</strong>g and adhesive bond<strong>in</strong>g. Scope and application.6. Weld<strong>in</strong>g? defect? and remedies. Weld crack<strong>in</strong>g and prevention. Test<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong>spection of welds.MECHATRONICSCourse Code ME-673 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-0)Fundamentals of Mechatronics, def<strong>in</strong>itions and Concepts;Conventional vs Mechantronics Systems; Need of?Mechantronics <strong>in</strong> Mechanical <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>; Sensors and Transducers with? Special?? reference to Mechatronics.
Signals System and actuat<strong>in</strong>g devices; real time <strong>in</strong>terfac<strong>in</strong>g. Applications of? Mechatronics <strong>in</strong> Manufactur<strong>in</strong>gand Automation Case Studies.METAL FORMING1- Fundaments of Elasticity, Plasticity and Viscoplastcity, Stress and stra<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>variant?Elesticity- State?? of stress and stra<strong>in</strong>, stress-stra<strong>in</strong> relations,? stra<strong>in</strong>-displacement relations.Plasticity and Viscoplasticity: Yeld?? criterian, effective stress and stra<strong>in</strong>, state of plastic stra<strong>in</strong>,Plastic stra<strong>in</strong> rate, Flow rule, Effective stra<strong>in</strong> rate, plastic anisotropy and viscoplasticity(determ<strong>in</strong>ation of load and power) concept of solid and flow formulations.?2- Analysiz of Deformation Processes us<strong>in</strong>g SSM, UBM & SLMPla<strong>in</strong> stra<strong>in</strong> Problems: Draw<strong>in</strong>g and Extrusion of sheet, Roll<strong>in</strong>g and forg<strong>in</strong>g of strips.Axisymmetric?? Problems: Draw<strong>in</strong>g and Extrusion of bar and tube, forg<strong>in</strong>g of solid and Hallowdisc.Sheet metal problems: Axisymmetric deep draw<strong>in</strong>g and stretch<strong>in</strong>g.ENERGY CONSERVATIONCourse Code ME-674 CREDIT : 3(3-0-0)1.Introduction: The energy crisis and options: the energy conservation option, energy <strong>in</strong>tensity ofdeveloped and develop<strong>in</strong>g economies, energy audit<strong>in</strong>g ? basic requirements, scope and purpose,process energy and gross energy requirements.2.Efficient energy conversion: efficient combustion, waste as a fuel, comb<strong>in</strong>ed cycles for efficientpower generation, comb<strong>in</strong>ed heat and power plants, comb<strong>in</strong>ed cool<strong>in</strong>g and power plants.3. Energy recovery: <strong>in</strong>sulation: <strong>in</strong>sulat<strong>in</strong>g materials, economic thickness of <strong>in</strong>sulation; heat recoveryheat exchangers: recuperative heat exchangers, run-around coil systems, regenerative heat exchangers;heat pumps; and heat-pipes.4. Process <strong>in</strong>tegration: basic concepts of p<strong>in</strong>ch technology, stream networks, significance of the p<strong>in</strong>ch,design of energy recovery system.5. Energy conservation <strong>in</strong> build<strong>in</strong>gs: degree-days, steady state loads and comfort. Condition<strong>in</strong>g the airfor process requirements and human comfort, thermal performance monitor<strong>in</strong>g, efficient light<strong>in</strong>gsystems, solar passive features.6. Economics of energy sav<strong>in</strong>g schemes and case studies.REFERENCES(A) Energy efficiency? by Eastop and Croft, Longman Scientific and <strong>Tech</strong>nical, 1990(B) Manag<strong>in</strong>g energy <strong>in</strong> commerce and <strong>in</strong>dustry? by Gordon A Payne, Butterworths, 1984.CAD OF THERMAL SYSTEMSCourse Code ME-675 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-0)
Study of the design aspects. Fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics and materials requirementsof at least two of the? follow<strong>in</strong>g types of heat exchange equipment: :Liquid-to-liquid. Liquid -to-gasand gas-to-gas heat exchangers. Cool<strong>in</strong>g???? tower, Familiarity with the use of the design related<strong>in</strong>ternational/national and other codes.Preparation of necessary computer programs for design<strong>in</strong>g the thermal system. Learn<strong>in</strong>g of thetechniques for present<strong>in</strong>g design features of the thermal equipment.Reference Book:1. Process Heat Transfer by D.Q.Kern2. Heat Exchanger Design by A.P.Fraas and M.N.Ozisik3. Heat Exchangers: Selection., Rat<strong>in</strong>g and Thermal Design-Hongtan Lui & Sadic Kakac.CRC Press.. ISO, ISI and TEMA Codes.Metal Form<strong>in</strong>gCourse Code ME-676 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-0)METAL FORMINGUNIT-IPlasticity –True stress stra<strong>in</strong> diagrams <strong>in</strong> simple tension – Deviation from <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>stress – Stra<strong>in</strong> curves. Three dimensional stress system, stra<strong>in</strong> tensor andyield Criteria of metals.UNIT-IIFundamentals of metal form<strong>in</strong>g – Classification of form<strong>in</strong>g processes – Cold work<strong>in</strong>g– Recovery – Recrystallisation and gra<strong>in</strong> growth, hot work<strong>in</strong>g. Stra<strong>in</strong> rate effects– work of plastic deformationUNIT-IIIFlow stress curves – Super plasticity <strong>in</strong> materials – Hot work<strong>in</strong>g and cold work<strong>in</strong>goperation – Relative merits and applications.UNIT-IVSheet metal work<strong>in</strong>g: Standard die sets, simple, compound, comb<strong>in</strong>ation, progressiveand transfer dies. Process parameters and estimation of loads <strong>in</strong> shear<strong>in</strong>g,bend<strong>in</strong>g, deep draw<strong>in</strong>g, shear sp<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g operations. Mechanical and hydraulicpresses, relative merits and application – constructional features and operation.UNIT-VFORGING: Open die and closed die forg<strong>in</strong>g, mach<strong>in</strong>e forg<strong>in</strong>g, upset forg<strong>in</strong>g etc.,forg<strong>in</strong>g loads, forg<strong>in</strong>g die design. Estimation of forg<strong>in</strong>g loads for rectangular andcyl<strong>in</strong>drical slugs. Forgeability Tests. Defects <strong>in</strong> forg<strong>in</strong>g, Forg<strong>in</strong>g equipment – constructionalfeatures and operation.UNIT-VIROLLING: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of roll<strong>in</strong>g, Process parameters, Estimation of roll<strong>in</strong>g loads byconsideration of stresses. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of roll pass design for various product shapes.Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of r<strong>in</strong>g roll<strong>in</strong>g. Process<strong>in</strong>g maps and their applications <strong>in</strong> metal work<strong>in</strong>goperation. Roll<strong>in</strong>g mills – Their constructional features and operation.
UNIT- VIIEXTRUSION: Classification of extrusion processes, extrusion equipment. Hot extrusion.Deformation and defects <strong>in</strong> extrusion. Analysis of the extrusion proceses, cold extrusion. Extrusionof tub<strong>in</strong>g and production of seamless pipe and tub<strong>in</strong>g.UNIT- VIIIDRAWING OF RODS, WIRES AND TUBES: Road and wire draw<strong>in</strong>g, tube draw<strong>in</strong>g process,residual stresses <strong>in</strong> rod, wire and tubes.TEXT BOOK:G. E Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy.REFERENCE BOOKS :1.” An Introduction to the Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Metal Work<strong>in</strong>g “ by Geoffery W. Rowe.2. “ Sheet work<strong>in</strong>g of Metal “ by Eary and Reads.3. “ Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Sciences “ by Amitabh Ghosh and Mallik.4. “ Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>Tech</strong>nology” by P. N. Rao.REVERSE ENGINEERINGCourse Code ME-677 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-0)1- Introduction of Reverse and? concurrent eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. Elements of concurrent eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. Advantageand applications.2- Theory of? measurements. L<strong>in</strong>ear, angular, curved surfaces, methods of advanced Measur<strong>in</strong>g devices,Coord<strong>in</strong>ate Measur<strong>in</strong>g mach<strong>in</strong>e. Elements to CMM. Data accumulation, retrieval..3- Geometric Modell<strong>in</strong>g. 2D and 3D Graphics, concepts of various transformation of Geometric Models,Wireframe surface and solid modell<strong>in</strong>g techniques, representation of parametric and non-parametriccurvesand surfaces, Mathematical representation of solid and solid model<strong>in</strong>g- based applications.CAD/CAM data exchanges. Visual realism and Graphics Tools, Applications, Auto-CAD, Auto surt,Auto Mil. And UNIGRAPHICS. CAD/CAM <strong>in</strong>terfaces, process plann<strong>in</strong>g, computer aidedproduction plann<strong>in</strong>g systems. Capacity plann<strong>in</strong>t. Part Programm<strong>in</strong>g. APT, CAPPS programm<strong>in</strong>g,Geometry def<strong>in</strong>ition, Tool Path generation.4- Rapid Prototyp<strong>in</strong>g: Concurrent <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>, Need of Rapid Prototyp<strong>in</strong>g. <strong>Tech</strong>niques, Res<strong>in</strong>s, (Lasereng<strong>in</strong>es) Laser, Laser production and control. Post cur<strong>in</strong>g, Data rerrieval from? CAD,? MIC codesgeneration, Apparatus for quality measurement.(CMM)SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT0-0)Course Code ME-678 CREDIT : 3 (3-1. Introduction to Logistics and Supply Cha<strong>in</strong> Management.Concepts, Drivers and obstacles.2. Plann<strong>in</strong>g Demand and supply <strong>in</strong> a supply cha<strong>in</strong>-Demand forecast<strong>in</strong>g, Aggregate Plann<strong>in</strong>g.3. Management of Inventory <strong>in</strong> global? supply Cha<strong>in</strong>.4. Role of Information <strong>Tech</strong>nology <strong>in</strong> supply cha<strong>in</strong>.? e-Bus<strong>in</strong>ess and the supply cha<strong>in</strong>5. Factors <strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g logistics and? decision.6. Bench mak<strong>in</strong>g and performance measurement.
MECHANICAL VIBRATIONCourse Code ME-679 CREDIT : 3 (3-0-0)UNIT - IIntroductionPeriodic motion, harmonic motion, superposition of simple harmonic motions, beats,Fourier analysis 3S<strong>in</strong>gle Degree Freedom SystemFree vibration, Natural frequency, Equivalent systems, Energy method for determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gnatural frequency, response to an <strong>in</strong>itial disturbance, Torsional vibrations, Dampedvibrations, Vibrations of systems with viscous damp<strong>in</strong>g, Logarithmic decrement 5UNIT - IIS<strong>in</strong>gle Degree Freedom: Forced VibrationForced vibration, Harmonic excitation with viscous damp<strong>in</strong>g, steady state vibrations,Forced vibrations with rotat<strong>in</strong>g and reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g unbalance, Support excitation, Vibrationisolation, Transmissibility, Vibration measur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>struments, Displacement, velocity andacceleration measur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>struments 8UNIT- IIITwo Degree Freedom systemsIntroduction, Pr<strong>in</strong>cipal modes, Double pendulum, Torsional system with damp<strong>in</strong>g,coupled system, undamped dynamic vibration absorbers, Centrifugal pendulumabsorbers, Dry friction damper 8UNIT- IVMulti Degree Freedom system: Exact AnalysisUndamped free and forced vibrations of multi-degree freedom systems, <strong>in</strong>fluencenumber, Reciprocal theorem, Torsional vibration of multi-degree rotor system, Vibrationof gear system, Pr<strong>in</strong>cipal coord<strong>in</strong>ates, Cont<strong>in</strong>uous systems- Longitud<strong>in</strong>al vibrations ofbars, Torsional vibrations of circular shafts 8UNIT- VMulti Degree Freedom system: Numerical AnalysisRayleigh’s, Dunkerely’s, Holzer’s ad Stodola methods, Rayleigh-Ritz method 5CRITICAL SPEED OF SHAFTSShaft with one disc with and without damp<strong>in</strong>g, Multi-disc shafts, Secondary criticalspeed. 3Books and References:1. Mechanical Vibrations – P. Sr<strong>in</strong>ivasan, TMH2. Mechanical Vibrations – G. K. Groover, Ja<strong>in</strong> Brothers, Roorkee3. Mechanical Vibrations – W. T. Thomson4. Mechanical Vibrations – JS Rao & K Gupta, New Age5. Mechanical Vibrations – Tse, Morse & H<strong>in</strong>kle6. Mechanical Vibrations – V. Rama Murthy, Narosa Publications