Continuing Medical Education - News & Information - The Regional ...
Continuing Medical Education - News & Information - The Regional ...
Continuing Medical Education - News & Information - The Regional ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
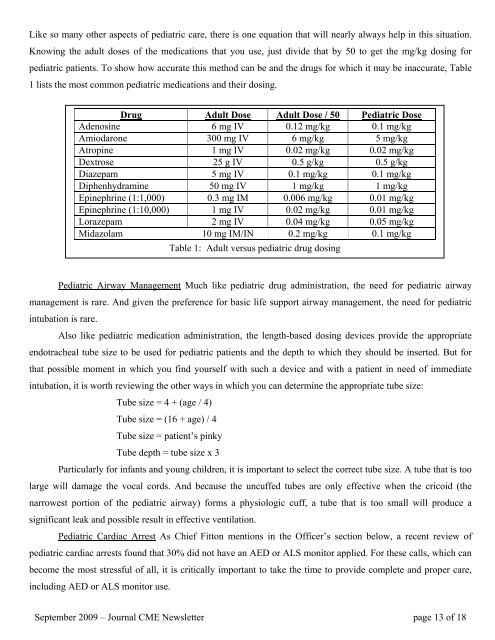
Like so many other aspects of pediatric care, there is one equation that will nearly always help in this situation.Knowing the adult doses of the medications that you use, just divide that by 50 to get the mg/kg dosing forpediatric patients. To show how accurate this method can be and the drugs for which it may be inaccurate, Table1 lists the most common pediatric medications and their dosing.Drug Adult Dose Adult Dose / 50 Pediatric DoseAdenosine 6 mg IV 0.12 mg/kg 0.1 mg/kgAmiodarone 300 mg IV 6 mg/kg 5 mg/kgAtropine 1 mg IV 0.02 mg/kg 0.02 mg/kgDextrose 25 g IV 0.5 g/kg 0.5 g/kgDiazepam 5 mg IV 0.1 mg/kg 0.1 mg/kgDiphenhydramine 50 mg IV 1 mg/kg 1 mg/kgEpinephrine (1:1,000) 0.3 mg IM 0.006 mg/kg 0.01 mg/kgEpinephrine (1:10,000) 1 mg IV 0.02 mg/kg 0.01 mg/kgLorazepam 2 mg IV 0.04 mg/kg 0.05 mg/kgMidazolam 10 mg IM/IN 0.2 mg/kg 0.1 mg/kgTable 1: Adult versus pediatric drug dosingPediatric Airway Management Much like pediatric drug administration, the need for pediatric airwaymanagement is rare. And given the preference for basic life support airway management, the need for pediatricintubation is rare.Also like pediatric medication administration, the length-based dosing devices provide the appropriateendotracheal tube size to be used for pediatric patients and the depth to which they should be inserted. But forthat possible moment in which you find yourself with such a device and with a patient in need of immediateintubation, it is worth reviewing the other ways in which you can determine the appropriate tube size:Tube size = 4 + (age / 4)Tube size = (16 + age) / 4Tube size = patient’s pinkyTube depth = tube size x 3Particularly for infants and young children, it is important to select the correct tube size. A tube that is toolarge will damage the vocal cords. And because the uncuffed tubes are only effective when the cricoid (thenarrowest portion of the pediatric airway) forms a physiologic cuff, a tube that is too small will produce asignificant leak and possible result in effective ventilation.Pediatric Cardiac Arrest As Chief Fitton mentions in the Officer’s section below, a recent review ofpediatric cardiac arrests found that 30% did not have an AED or ALS monitor applied. For these calls, which canbecome the most stressful of all, it is critically important to take the time to provide complete and proper care,including AED or ALS monitor use.September 2009 – Journal CME <strong>News</strong>letter page 13 of 18