Mobile communications for industrial applications - CERN
Mobile communications for industrial applications - CERN
Mobile communications for industrial applications - CERN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
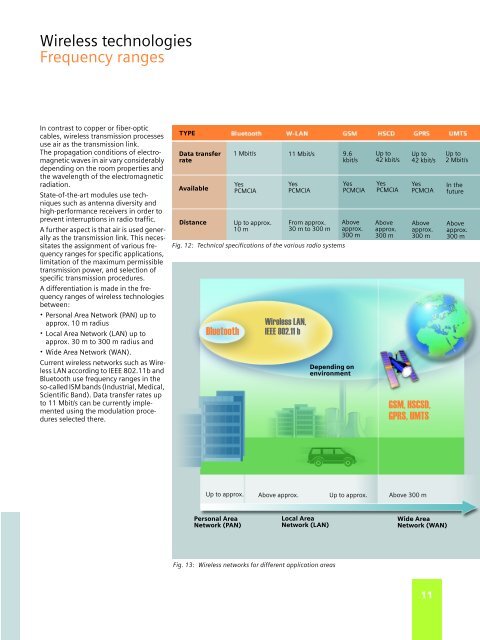
Wireless technologiesFrequency rangesIn contrast to copper or fiber-opticcables, wireless transmission processesuse air as the transmission link.The propagation conditions of electromagneticwaves in air vary considerablydepending on the room properties andthe wavelength of the electromagneticradiation.State-of-the-art modules use techniquessuch as antenna diversity andhigh-per<strong>for</strong>mance receivers in order toprevent interruptions in radio traffic.A further aspect is that air is used generallyas the transmission link. This necessitatesthe assignment of various frequencyranges <strong>for</strong> specific <strong>applications</strong>,limitation of the maximum permissibletransmission power, and selection ofspecific transmission procedures.A differentiation is made in the frequencyranges of wireless technologiesbetween:· Personal Area Network (PAN) up toapprox. 10 m radius· Local Area Network (LAN) up toapprox. 30 m to 300 m radius and· Wide Area Network (WAN).Current wireless networks such as WirelessLAN according to IEEE 802.11b andBluetooth use frequency ranges in theso-called ISM bands (Industrial, Medical,Scientific Band). Data transfer rates upto 11 Mbit/s can be currently implementedusing the modulation proceduresselected there.TYPEData transferrateAvailableDistanceBluetooth1 Mbit/sYesPCMCIAUp to approx.10 m11 Mbit/sYesPCMCIAFig. 12: Technical specifications of the various radio systemsWireless LAN,IEEE 802.11 bFrom approx.30 m to 300 m9.6kbit/sYesPCMCIAAboveapprox.300 mDepending onenvironmentUp to42 kbit/sYesPCMCIAAboveapprox.300 mUp to42 kbit/sYesPCMCIAAboveapprox.300 mGSM, HSCSD,GPRS, UMTSUp to2 Mbit/sIn thefutureAboveapprox.300 mUp to approx. Above approx. Up to approx.Above 300 mPersonal AreaNetwork (PAN)Local AreaNetwork (LAN)Wide AreaNetwork (WAN)Fig. 13: Wireless networks <strong>for</strong> different application areas11