Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
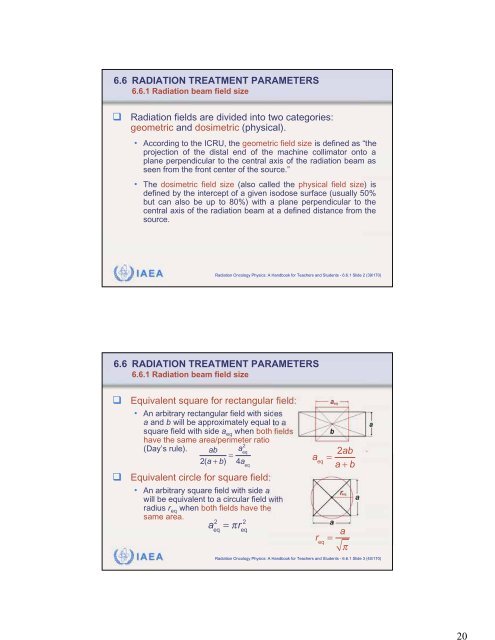
206.6 RADIATION TREATMENT PARAMETERS6.6.1 Radiation beam field sizeRadiation fields are divided into two categories:geometric and dosimetric (physical).• According to the ICRU, the geometric field size is defined as “theprojection of the distal end of the machine collimator onto aplane perpendicular to the central axis of the radiation beam asseen from the front center of the source.”• The dosimetric field size (also called the physical field size) isdefined by the intercept of a given isodose surface (usually 50%but can also be up to 80%) with a plane perpendicular to thecentral axis of the radiation beam at a defined distance from thesource.IAEA Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 6.6.1 Slide 2 (39/170)6.6 RADIATION TREATMENT PARAMETERS6.6.1 Radiation beam field sizeEquivalent square for rectangular field:• An arbitrary rectangular field with sidesa and b will be approximately equal to asquare field with side a eq when both fieldshave the same area/perimeter ratio(Day’s rule). ab2(a + b) = a 2eq4a eqEquivalent circle for square field:• An arbitrary square field with side awill be equivalent to a circular field withradius r eq when both fields have thesame area.a 2 2eq= r eqa eq= 2aba + br eq= a IAEA Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 6.6.1 Slide 3 (40/170)