Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
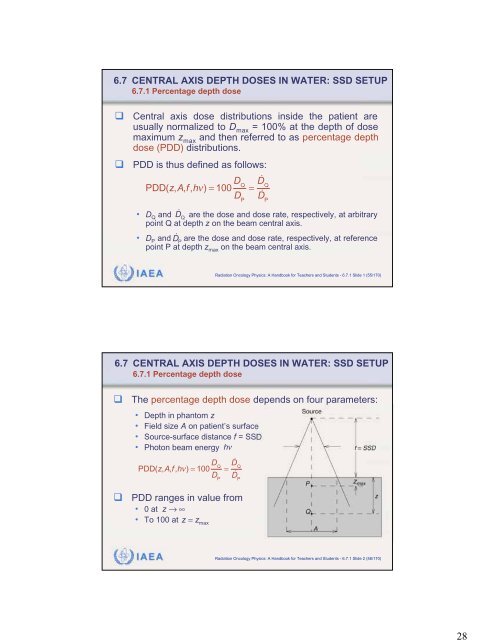
286.7 CENTRAL AXIS DEPTH DOSES IN WATER: SSD SETUP6.7.1 Percentage depth doseCentral axis dose distributions inside the patient areusually normalized to D max = 100% at the depth of dosemaximum z max and then referred to as percentage depthdose (PDD) distributions.PDD is thus defined as follows:PDD(z,A,f,h) = 100 D QD P=D Q D PQ• D Q and D are the dose and dose rate, respectively, at arbitrarypoint Q at depth z on the beam central axis.P• D P and D are the dose and dose rate, respectively, at referencepoint P at depth z max on the beam central axis.IAEA Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 6.7.1 Slide 1 (55/170)6.7 CENTRAL AXIS DEPTH DOSES IN WATER: SSD SETUP6.7.1 Percentage depth doseThe percentage depth dose depends on four parameters:• Depth in phantom z• Field size A on patient’s surface• Source-surface distance f = SSD• <strong>Photon</strong> beam energy hPDD(z,A,f,h) = 100 D QD P=D Q D PPDD ranges in value from• 0 at z • To 100 at z z= maxIAEA Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 6.7.1 Slide 2 (56/170)