Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Chapter 6 External Photon Beams: Physical Aspects - IRSN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
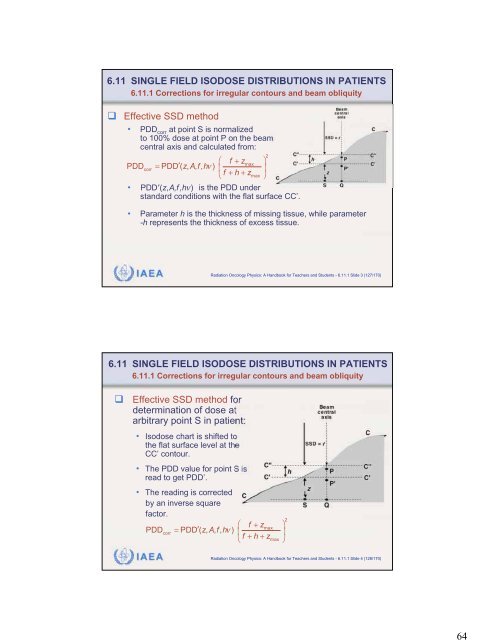
646.11 SINGLE FIELD ISODOSE DISTRIBUTIONS IN PATIENTS6.11.1 Corrections for irregular contours and beam obliquity Effective SSD method• PDD corr at point S is normalizedto 100% dose at point P on the beamcentral axis and calculated from:f zmaxPDDcorr= PDD ( zAfh , , , ) +f + h+zmax• PDD(z,A,f,h) is the PDD understandard conditions with the flat surface CC’.• Parameter h is the thickness of missing tissue, while parameter-h represents the thickness of excess tissue.2IAEA Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 6.11.1 Slide 3 (127/170)6.11 SINGLE FIELD ISODOSE DISTRIBUTIONS IN PATIENTS6.11.1 Corrections for irregular contours and beam obliquityEffective SSD method fordetermination of dose atarbitrary point S in patient:• Isodose chart is shifted tothe flat surface level at theCC’ contour.• The PDD value for point S isread to get PDD’.• The reading is correctedby an inverse squarefactor.2f zmax + PDDcorr= PDD ( zAfh , , , ) f + h+zmaxIAEA Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 6.11.1 Slide 4 (128/170)