White Paper PDF - Ortho Providers
White Paper PDF - Ortho Providers
White Paper PDF - Ortho Providers
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
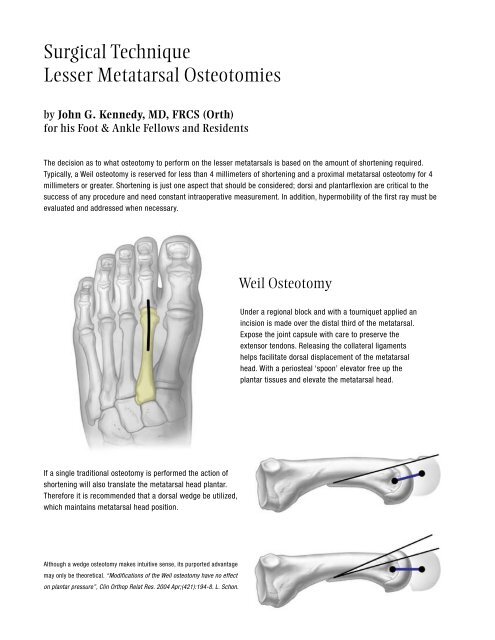
Surgical TechniqueLesser Metatarsal Osteotomiesby John G. Kennedy, MD, FRCS (Orth)for his Foot & Ankle Fellows and ResidentsThe decision as to what osteotomy to perform on the lesser metatarsals is based on the amount of shortening required.Typically, a Weil osteotomy is reserved for less than 4 millimeters of shortening and a proximal metatarsal osteotomy for 4millimeters or greater. Shortening is just one aspect that should be considered; dorsi and plantarflexion are critical to thesuccess of any procedure and need constant intraoperative measurement. In addition, hypermobility of the first ray must beevaluated and addressed when necessary.Weil OsteotomyUnder a regional block and with a tourniquet applied anincision is made over the distal third of the metatarsal.Expose the joint capsule with care to preserve theextensor tendons. Releasing the collateral ligamentshelps facilitate dorsal displacement of the metatarsalhead. With a periosteal ‘spoon’ elevator free up theplantar tissues and elevate the metatarsal head.If a single traditional osteotomy is performed the action ofshortening will also translate the metatarsal head plantar.Therefore it is recommended that a dorsal wedge be utilized,which maintains metatarsal head position.Although a wedge osteotomy makes intuitive sense, its purported advantagemay only be theoretical. “Modifications of the Weil osteotomy have no effecton plantar pressure”, Clin <strong>Ortho</strong>p Relat Res. 2004 Apr;(421):194-8. L. Schon.
1-3mm osteotomyDorsally at the articular margin of the head begin the osteotomy, staying fairly horizontal, parallel to theground or plane of the foot. Depending on the amount of plantar prominence a second dorsal wedge cutcan be made. Incremental cuts that fine-tune the correction are preferred to a single wedge cut.Slide the bone to the desired shortened and dorsiflexed position. Holdreduction with a 0.7mm K-wire that is placed in the orientation and to thedepth of the eventual screw. Check clinically and fluoroscopically that thecorrect position has been achieved. Measure the screw length with the wiregauge. Insert the 1.7mm self-drilling cannulated screw over the K-wire andtighten. If required insert a second wire and screw. Remove any overhangingbone at the articular margin of the dorsal cortex.The remaining metatarsals are evaluated andcorrected as needed for length and plantarflexion.The wound is closed in layers. In the presence of a proximal interphalangeal (PIP) or distal interphalangeal (DIP)deformity, these may need to be addressed with a tendon lengthening and/or transfers, as well as IP fusions.Because the osteotomy shifts the center of rotation of the metatarsal phalangeal joint, there is a significant risk of adorsiflexion deformity. The joint is therefore taped for 4 weeks post-operatively, and then followed with appropriatephysical therapy.
Proximal Segmental OsteotomyFor patients requiring larger corrections in length and plantarflexionUnder a regional block and with a tourniquet applied an incision is madeover the proximal half of the metatarsal shaft. Care should be afforded to theneurovascular bundle.In the area of the metaphysis the position ofthe osteotomy is estimated and marked.A plate is applied and fit to the bone and temporarilysecured using a clamp or K-wires. The position ofthe osteotomy relative to the plate is evaluated. Theholes proximal to the osteotomy are predrilled andmeasured. The plate is removed. With retractorsfirmly supporting the metatarsal and protectingplantar soft tissues begin the osteotomy.
The proximal cut is made perpendicular to the shaft. A second cut is made at a distance and angle that will facilitate thedesired amount of correction. This cannot be determined by radiograph alone and must be evaluated by clinical judgment atthe time of surgery, therefore it is recommended to start with a small amount of bony resection and build-up as required. If adorsiflexion wedge cut is performed, the plate should be contoured accordingly.Reapply the plate and proximally fix with screws. Appose boneends and temporarily clamp or K-wire the distal fragment to theplate. Drill, measure and insert distal screws.Because the metadiaphysis of the metatarsal has relativelypoor blood supply, the healing potential of this osteotomy canbe improved by using local graft. A 3mm burr can create ‘spotwelding’sites in the cortex on either side of the plate and thesecan be filled with calcaneal autograft.The wound is closed in layers. A postoperative splint is required for two weeks followed by a CAM boot foranother 4-6 weeks.Disclosure: The author did not receive any outside funding or grants in support of this work. Neither he nor a member of his immediate family received payments or other benefits or a commitment or agreementto provide such benefits from a commercial entity.